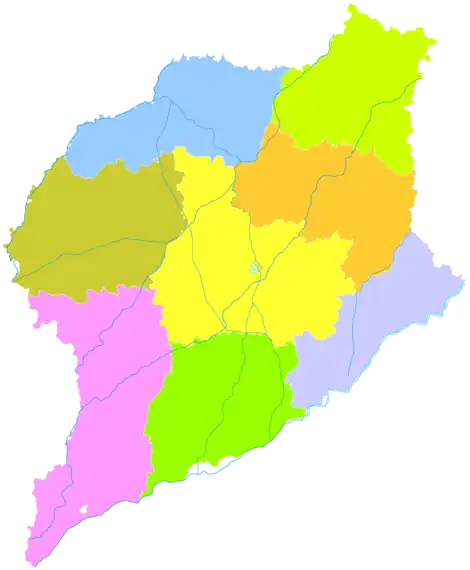
Liaocheng
Liaocheng (Chinese: 聊城; pinyin: Liáochéng), is a prefecture-level city in western Shandong province, China. It borders the provincial capital of Jinan to the southeast, Dezhou to the northeast, Tai'an to the south, and the provinces of Hebei and Henan to the west. The Grand Canal flows through the city center. Its population was 5,789,863 at the 2010 census whom 1,229,768 lived in the built-up area made up of Donchangfu district, even though large parts remain rural.[3]
Liaocheng
聊城市 | |
|---|---|
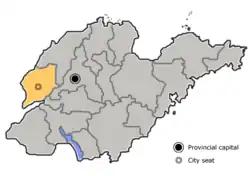 Location of Liaocheng in Shandong | |
| Coordinates (Liaocheng municipal government): 36°27′21″N 115°59′07″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Shandong |
| County-level divisions | 8 |
| Township-level divisions | 134 |
| Municipal seat | Dongchangfu District |
| Government | |
| • CPC Secretary | Song Yuanfang (宋远方) |
| • Mayor | Lin Fenghai (林峰海) |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 8,721 km2 (3,367 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,254 km2 (484 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,254 km2 (484 sq mi) |
| Population (2020 census for total, 2010 census for otherwise)[2] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 5,952,128 |
| • Density | 680/km2 (1,800/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,229,768 |
| • Urban density | 980/km2 (2,500/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,229,768 |
| • Metro density | 980/km2 (2,500/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Area code | 0635 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-SD-15 |
| License Plate Prefix | 鲁P |
| Website | www |
During the Song dynasty, the area of present-day Liaocheng included the prefectures of Bo and Ji. In 2007, the city is named China's top ten livable cities by Chinese Cities Brand Value Report, which was released at 2007 Beijing Summit of China Cities Forum.[4]
Administration
The prefecture-level city of Liaocheng administers eight county-level divisions, including two districts, one county-level city, and five counties.
- Dongchangfu District (东昌府区)
- Chiping District (茌平区)
- Linqing City (临清市)
- Yanggu County (阳谷县)
- Dong'e County (东阿县)
- Gaotang County (高唐县)
- Guan County (冠县)
- Shen County (莘县)
These are further divided into 134 township-level divisions.
| Map |
|---|
Climate
| Climate data for Liaocheng (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 15.8 (60.4) |
21.8 (71.2) |
28.4 (83.1) |
33.6 (92.5) |
37.2 (99.0) |
40.7 (105.3) |
40.7 (105.3) |
36.3 (97.3) |
36.1 (97.0) |
34.5 (94.1) |
26.5 (79.7) |
19.0 (66.2) |
40.7 (105.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 4.2 (39.6) |
8.3 (46.9) |
14.7 (58.5) |
21.2 (70.2) |
26.6 (79.9) |
31.5 (88.7) |
31.9 (89.4) |
30.5 (86.9) |
27.1 (80.8) |
21.3 (70.3) |
12.7 (54.9) |
5.8 (42.4) |
19.7 (67.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −1.6 (29.1) |
2.1 (35.8) |
8.3 (46.9) |
14.9 (58.8) |
20.4 (68.7) |
25.3 (77.5) |
26.9 (80.4) |
25.6 (78.1) |
20.9 (69.6) |
14.5 (58.1) |
6.8 (44.2) |
0.3 (32.5) |
13.7 (56.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −5.9 (21.4) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
3.2 (37.8) |
9.4 (48.9) |
14.8 (58.6) |
19.9 (67.8) |
23.1 (73.6) |
21.9 (71.4) |
16.4 (61.5) |
9.6 (49.3) |
2.2 (36.0) |
−3.9 (25.0) |
9.0 (48.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −20.6 (−5.1) |
−16.9 (1.6) |
−10.1 (13.8) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
3.6 (38.5) |
10.2 (50.4) |
16.9 (62.4) |
11.7 (53.1) |
4.9 (40.8) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
−17.9 (−0.2) |
−16.9 (1.6) |
−20.6 (−5.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 4.0 (0.16) |
8.7 (0.34) |
11.0 (0.43) |
31.7 (1.25) |
45.8 (1.80) |
72.3 (2.85) |
156.5 (6.16) |
150.8 (5.94) |
50.3 (1.98) |
30.4 (1.20) |
19.7 (0.78) |
5.2 (0.20) |
586.4 (23.09) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 2.1 | 3.3 | 3.1 | 5.0 | 6.6 | 7.6 | 10.8 | 9.7 | 6.6 | 5.4 | 4.1 | 2.5 | 66.8 |
| Average snowy days | 2.4 | 2.7 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8 | 1.9 | 8.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 64 | 60 | 56 | 62 | 67 | 66 | 80 | 84 | 79 | 73 | 70 | 68 | 69 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 135.5 | 140.4 | 187.8 | 208.5 | 235.4 | 209.5 | 172.3 | 174.4 | 168.9 | 165.0 | 141.0 | 135.9 | 2,074.6 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 44 | 45 | 50 | 53 | 54 | 48 | 39 | 42 | 46 | 48 | 46 | 45 | 47 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[5][6] | |||||||||||||
Education
- Liaocheng University (聊城大学)
- Liaocheng NO.1 high school (聊城一中)
History
People's Republic of China
In August 1949, Liaocheng was detached from Shandong and attached to Pingyuan. In November 1952, Pingyuan was dissolved and Liaocheng returned to Shandong.
Notable people
- Fu Sinian (傅斯年; 1896–1950)
- Ji Xianlin (季羡林; 1911–2009)
- Kong Fansen (孔繁森; 1944–1994)
- Wei Fenghe (魏凤和; b.1954)
- Chen Xu (陳旭; b. 1962)
Attractions

Transportation
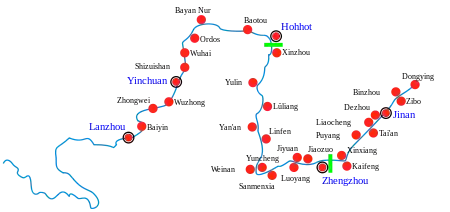
The town is served by Liaocheng railway station. A station on the high-speed network, Liaocheng West railway station, is under construction.
Sister cities
Liaocheng is a sister city of the following cities:
- Uiryeong County, South Gyeongsang, South Korea (since June 7, 2001)
- Blacktown, New South Wales, Australia (October 14, 2003)
- Gwangmyeong, Gyeonggi, South Korea (May 3, 2005)
- Naberezhnye Chelny, Tatarstan, Russia (since 2009)
Furthermore, there is a partnership with the district Offenbach in Germany.
References
- 最新人口信息 www.hongheiku.com (in Chinese). hongheiku. Retrieved 2021-01-12.
- "China: Shāndōng (Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties) - Population Statistics, Charts and Map".
- "China: Shāndōng (Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties) - Population Statistics, Charts and Map".
- "China's Top 10 Most Livable Cities". hnloudi.gov.cn. Hunan Loudi Official Government. 2012-03-28. Archived from the original on 2013-04-10. Retrieved 2014-08-04.
- 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
External links
- Government website of Liaocheng (available in Chinese, English, Japanese and Korean)