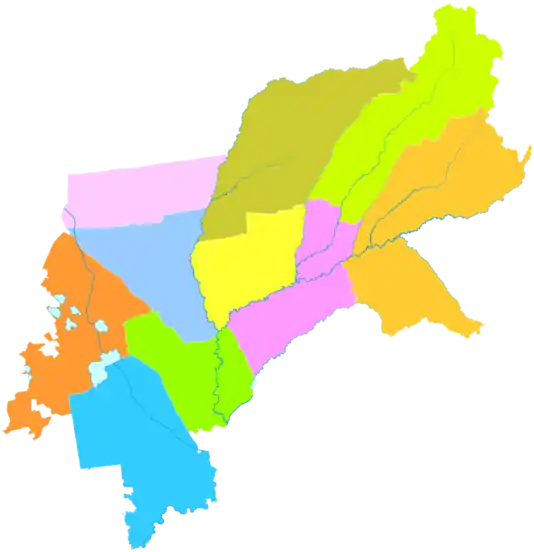
Suihua
Suihua (Chinese: 绥化) is a prefecture-level city in west-central Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, adjacent to Yichun to the east, Harbin, the provincial capital, to the south, Daqing to the west and Heihe to the north. It has 3,756,167 inhabitants at the 2020 census, of whom 698,025 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of Beilin District.
Suihua
绥化市 Suihwa | |
|---|---|
 Suihua People's Square | |
.png.webp) Location of Suihua City (yellow) in Heilongjiang (light grey) | |
 Suihua Location of the city centre in Heilongjiang | |
| Coordinates (Suihua municipal government): 46°39′14″N 126°58′08″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Heilongjiang |
| County-level divisions | 10 |
| Municipal seat | Beilin District |
| Government | |
| • Type | Prefecture-level city |
| • CPC Suihua Secretary | Zhang Jingchuan (张晶川) |
| • Mayor | Wang Jinhui (王金会) |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 34,964.17 km2 (13,499.74 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 2,756.4 km2 (1,064.3 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 2,756.4 km2 (1,064.3 sq mi) |
| Population (2020 census)[1] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 3,756,167 |
| • Density | 110/km2 (280/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 698,025 |
| • Urban density | 250/km2 (660/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 698,025 |
| • Metro density | 250/km2 (660/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 152000 |
| Area code | 0455 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-HL-12 |
| Licence plates | 黑M |
| Climate | Dwa |
| Website | www |
| Suihua | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 "Suihua", as written in Chinese calligraphy | |||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 绥化 | ||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 綏化 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Manchu name | |||||||
| Manchu script | ᠰᡠᡳᡥᠠ | ||||||
| Romanization | Suiha | ||||||
| Russian name | |||||||
| Russian | Суйхуа | ||||||
Geography
Suihua is located in the northern part of the Songnen Plain (Songhuajiang-Nenjiang Plain), and situated in the central part of Heilongjiang Province. Bordering prefectures are:
- Daqing (W)
- Harbin (S)
- Heihe (N)
- Qiqihar (NW)
- Yichun (E)
The city is located at latitude 45° 03′–48° 02′ N and longitude 124° 13′–128° 30' E. The total area of the city is 35,211 square kilometres (13,595 sq mi).
Transportation
The railway station of Suihua is located at the crossing of Taiping Road (太平路) and Beilin Road (北林路) in the eastern region of the city proper. The Harbin-Jiamusi Railway and the Harbin-Heihe Railway connect the city with Harbin, Jiamusi and several other cities in Heilongjiang Province. There are also buses to Daqing, Qiqihar and other cities in Heilongjiang.
Climate
Suihua has a humid continental climate (Köppen Dwa), with long, bitterly cold, but dry winters, and humid, very warm summers. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from −20.2 °C (−4.4 °F) in January to 22.5 °C (72.5 °F) in July, while the annual mean is 3.3 °C (37.9 °F). A majority of the annual precipitation occurs in July and August alone.
| Climate data for Suihua (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1971–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | −0.3 (31.5) |
8.0 (46.4) |
19.9 (67.8) |
29.5 (85.1) |
34.5 (94.1) |
39.4 (102.9) |
36.2 (97.2) |
35.5 (95.9) |
30.9 (87.6) |
25.5 (77.9) |
15.8 (60.4) |
4.5 (40.1) |
39.4 (102.9) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −13.9 (7.0) |
−7.9 (17.8) |
1.7 (35.1) |
12.8 (55.0) |
21.0 (69.8) |
26.0 (78.8) |
27.5 (81.5) |
25.9 (78.6) |
20.8 (69.4) |
11.3 (52.3) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
−11.8 (10.8) |
9.3 (48.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −19.3 (−2.7) |
−14.0 (6.8) |
−3.9 (25.0) |
6.8 (44.2) |
14.8 (58.6) |
20.6 (69.1) |
22.9 (73.2) |
21.0 (69.8) |
14.7 (58.5) |
5.6 (42.1) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
−16.8 (1.8) |
3.8 (38.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −24.1 (−11.4) |
−19.7 (−3.5) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
0.8 (33.4) |
8.7 (47.7) |
15.4 (59.7) |
18.6 (65.5) |
16.6 (61.9) |
9.2 (48.6) |
0.5 (32.9) |
−10.9 (12.4) |
−21.2 (−6.2) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −40.1 (−40.2) |
−36.5 (−33.7) |
−29.6 (−21.3) |
−13.8 (7.2) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
3.4 (38.1) |
9.6 (49.3) |
6.7 (44.1) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
−16.7 (1.9) |
−30.3 (−22.5) |
−36.9 (−34.4) |
−40.1 (−40.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 4.3 (0.17) |
4.6 (0.18) |
12.4 (0.49) |
22.9 (0.90) |
50.3 (1.98) |
94.0 (3.70) |
155.6 (6.13) |
119.7 (4.71) |
58.2 (2.29) |
25.1 (0.99) |
11.7 (0.46) |
7.4 (0.29) |
566.2 (22.29) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 5.9 | 4.1 | 5.6 | 7.0 | 11.3 | 14.5 | 14.4 | 13.5 | 9.0 | 7.0 | 6.1 | 6.7 | 105.1 |
| Average snowy days | 8.4 | 5.8 | 7.6 | 3.1 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.0 | 7.7 | 10 | 44.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 73 | 68 | 58 | 51 | 53 | 65 | 77 | 79 | 70 | 63 | 66 | 73 | 66 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 172.9 | 202.7 | 244.6 | 238.9 | 261.4 | 256.3 | 239.0 | 234.4 | 232.5 | 197.7 | 166.6 | 151.1 | 2,598.1 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 62 | 69 | 66 | 58 | 56 | 54 | 50 | 54 | 63 | 59 | 60 | 57 | 59 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration[2][3] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China[4] | |||||||||||||
History

Suihua's history can be stretched back to over 10,000 years ago. Paleolithic Age stone tools were unearthed at Hailun and Zhaodong. Neolithic sites belong to the Ang'angxi Culture type were also discovered at Anda. Sushen, the ancestors of the Manchu, inhabited in this region During the Xia Dynasty and Shang Dynasty. During the Yuan Dynasty, agriculture developed rapidly in Suihua.
Qing dynasty
From 1653, Suihua area was under the rule of Ningguta General. In 1683, the position of Heilongjiang General was established, Suihua was under the rule of Heilongjiang General. On November 20, 1885, the Directly Ruled Ting of Suihua (綏化直隸廳) was established at Beilin Tuanzi, a barren at that time. In 1905 it was redesigned as Suihua Fu (綏化府).[5]
Republic of China (1912–49)
In 1912, an army regiment was established in Suihua. The outbreak of plague caused 1683 deaths that year. In February 1913, 3000 brigands attacked the county seat, and was flattened by the garrison corps. In August 1917, in Suihua established the first telephone company. In July 1919, the 2nd High School of Heilongjiang Province was created. In February 1929, the county government was formally established.
In April 1932, the Japanese entered the city, resistance army led by Ma Zhanshan withdrew. The Manchukuo county government was created on July 12, 1933. In December 1934, Suihua county was put under the administration of Binjiang Province. In 1939, the county was incorporated into Bei'an Province, and the county hospital was built. On July 28, 1941, Counter-Japanese United Army organized the National Salvation Society at Shuanghe, Wuying villages. The Manchu government ordered the peasants to supply military grain, and often faced heavy resistance. In 1943 the Suihua-Jiamusi railway was opened to traffic. The Soviets took the city on August 27, 1945, and Chen Lei was made the first County CPC secretary in November.
The land reform movement began in 1947. Many Suihua people joined the Chinese civil war, especially the Siping Campaign. On May 13, 1949, Suihua County Government was renamed Suihua People's Government.[6]
People's Republic of China (1949–present)
Suihua is approved to become a prefecture-level city in 1999, and officially designated a prefecture-level city on June 14, 2000.
Administrative divisions
| Map | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Hanzi | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2010 est.) |
Area (km2) | Density (/km2) |
| Beilin District | 北林区 | Běilín Qū | 877,114 | 2,756.4 | 318 |
| Anda City | 安达市 | Āndá Shì | 472,826 | 3,586.3 | 132 |
| Zhaodong City | 肇东市 | Zhàodōng Shì | 903,067 | 4,331.96 | 208 |
| Hailun City | 海伦市 | Hǎilún Shì | 769,437 | 4,667.26 | 165 |
| Wangkui County | 望奎县 | Wàngkuí Xiàn | 458,725 | 2,313.78 | 198 |
| Lanxi County | 兰西县 | Lánxī Xiàn | 424,562 | 2,499.35 | 170 |
| Qinggang County | 青冈县 | Qīnggāng Xiàn | 474,422 | 2,684.71 | 177 |
| Qing'an County | 庆安县 | Qìng'ān Xiàn | 386,162 | 5,468.7 | 71 |
| Mingshui County | 明水县 | Míngshuǐ Xiàn | 320,695 | 2,305.46 | 139 |
| Suileng County | 绥棱县 | Suíléng Xiàn | 331,343 | 4,350.25 | 76 |
Economy
As an agricultural production hub in Heilongjiang province,[7] Suihua's GDP has reached RMB 73.34 billion in 2010, an increase of 14.8 percent over the previous year.[8] To the city's GDP, the main contributors are the agricultural sector and service sector. Petrochemicals, textiles and machinery are some other pillar industries in Suihua. In 2015, Suihua had a GDP of RMB 127.22 billion.[9]
References
- "China: Hēilóngjiāng (Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties) - Population Statistics, Charts and Map".
- 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 5 July 2023.
- 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 5 July 2023.
- 绥化 - 气象数据 -中国天气网 (in Chinese). Weather China. Retrieved 23 August 2022.
- 绥化地区地方志编纂委员会 (December 1995). 绥化地区志 上. Harbin: 黑龙江人民出版社 [Heilongjiang People's Press]. p. 119.
- Li Chengxiu (黎成修) (December 1986). 绥化县志 [Suihua County Almanac]. Harbin: 黑龙江人民出版社 [Heilongjiang People's Press]. pp. 7–12.
- Profiles of China Provinces, Cities and Industrial Parks
- 2010年绥化市国民经济和社会发展统计公报 (in Simplified Chinese). Heilongjiang Bureau of Statistics. Archived from the original on 2011-12-31.
- 2015年黑龙江各市GDP和人均GDP排名. 排行榜. 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2020-04-28.
External links
- Suihua Official Website (in Chinese)