Sanmenxia
Sanmenxia (simplified Chinese: 三门峡; traditional Chinese: 三門峽; pinyin: Sānménxiá; postal: Sanmenhsia) is a prefecture-level city in the west of Henan Province, China. The westernmost prefecture-level city in Henan, Sanmenxia borders Luoyang to the east, Nanyang to the southeast, Shaanxi Province to the west and Shanxi Province to the north. The city lies on the south side of the Yellow River at the point where the river cuts through the Loess Plateau on its way to the North China Plain.
Sanmenxia
三门峡市 Sanmenhsia | |
|---|---|
 | |
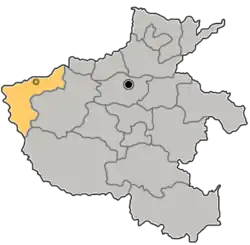 Location of Sanmenxia City jurisdiction in Henan | |
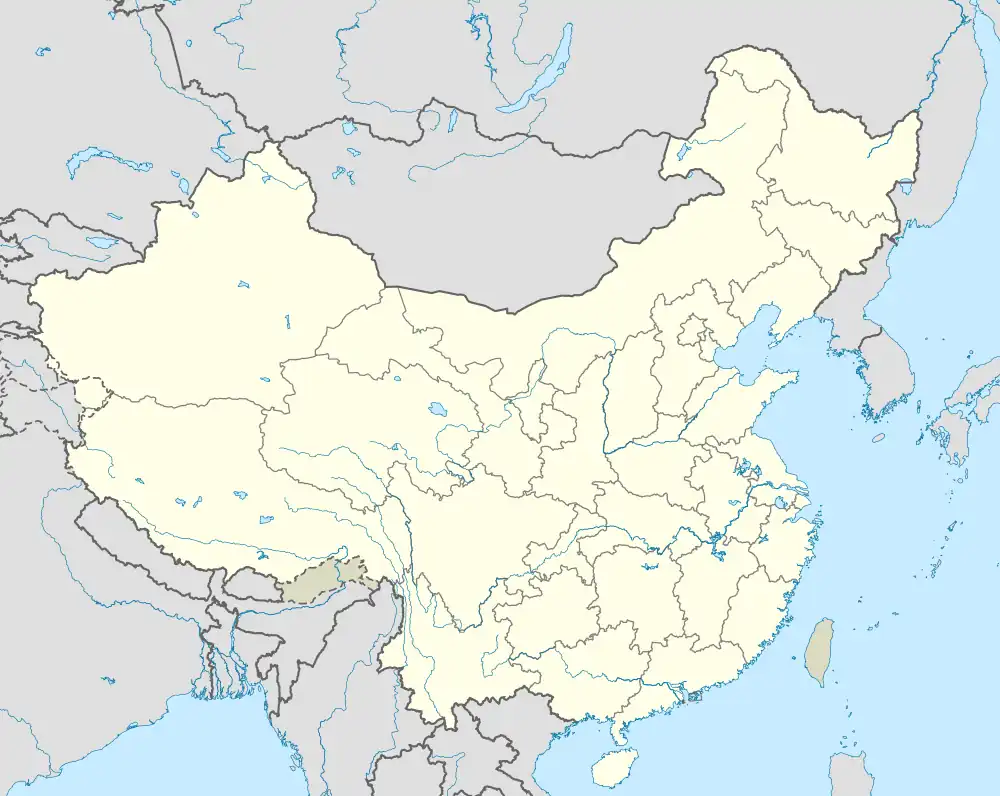 Sanmenxia Location in China | |
| Coordinates (Sanmenxia government): 34°46′24″N 111°12′01″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Henan |
| Municipal seat | Hubin District |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 10,475 km2 (4,044 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,814.3 km2 (700.5 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 2,995.3 km2 (1,156.5 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 376 m (1,234 ft) |
| Population (2020 census)[1] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 2,034,872 |
| • Density | 190/km2 (500/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 615,220 |
| • Urban density | 340/km2 (880/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 820,300 |
| • Metro density | 270/km2 (710/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal Code | 472000 |
| Area code | (0)398 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-HA-12 |
| GDP | 70.6 billion RMB (10.8 billion USD)[2] |
| Major Ethnicities | Han |
| County-level divisions | 6 |
| License plate prefixes | 豫M |
| Website | smx |
As of the 2020 census, it was home to 2,034,872 inhabitants of which 820,300 lived in the built-up area made of Hubin, Shanzhou urban districts and Pinglu County in neighboring Shanxi (205,080 inhabitants), now within the agglomeration.
Names and History
The city's name in Chinese (三门峡) means "The Gorge of Three Gateways" and is derived from two islands that split the Yellow River into three parts.
According to Chinese mythology, Yu the Great used a divine axe to cut the mountain ridge three times, creating the Sanmenxia gorges to prevent massive flooding. The three "men" or gates were then named "The Gateway of Man" (人门), "The Gateway of Gods" (神门) and "The Gateway of Devils" (鬼门).
With the construction of the Sanmenxia Dam in the late 1950s, the ancient passes were flooded.
During the Western Zhou Dynasty, Sanmenxia was part of the territory of the State of Western Guo, ruled by relatives of the ruling Ji family of Zhou. Guo moved its capital from modern day Baoji to Shangyang (上阳), next to Sanmenxia. Later, this territory was annexed the State of Jin.
Archaeological finds near Sanmenxia between 1956 and 1991 revealed mass chariot graves and bronzeware of Western Guo State rulers. Furthermore, the archaeological site “Shihao Section of Xiaohan Ancient Road”, an excavated pathway that is part of the world heritage site “Silk Roads: the Routes Network of Chang'an-Tianshan Corridor”, is also located in Sanmenxia. In 2011, the Sanmenxia Cultural Sports Centre Stadium opened. The association football venue has a capacity of 22,000.
Geography and climate
Sanmenxia is located in western Henan on the southern (right) bank of the Yellow River, and is surrounded on three sides by mountains, with elevations generally increasing from northeast to southwest. Most of the prefecture is at an altitude of 300 to 1,500 metres (980 to 4,920 ft), although the highest peak in the province, at 2,413.8 metres (7,919 ft), is located in Lingbao. The prefecture is at the intersection of Henan, Shanxi, and Shaanxi provinces, bordering Luoyang to the east, Nanyang to the south, Weinan (Shaanxi) to the west, and Yuncheng (Shanxi) to the north across the Yellow River.
Sanmenxia has a mostly dry, monsoon-influenced continental climate with four seasons. Winters are moderately cold and very dry, while summers are hot and humid. Monthly daily average temperatures range from −0.3 °C (31.5 °F) in January to 26.4 °C (79.5 °F) in July, and the annual mean is 13.9 °C (57.0 °F). More than half of the annual precipitation falls from July to September. There are between 184 and 218 frost-free days per annum. In the Köppen system, the city is in the transition zone between a humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cwa) and humid continental climate (Köppen Dwa), and receives barely enough precipitation to avoid being semi-arid (Köppen BSk).[3]
| Climate data for Sanmenxia (1991–2018 normals, extremes 1971–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 15.6 (60.1) |
23.3 (73.9) |
29.7 (85.5) |
36.7 (98.1) |
39.8 (103.6) |
41.4 (106.5) |
41.6 (106.9) |
39.6 (103.3) |
39.2 (102.6) |
33.3 (91.9) |
26.3 (79.3) |
18.4 (65.1) |
41.6 (106.9) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 5.2 (41.4) |
9.4 (48.9) |
15.6 (60.1) |
22.6 (72.7) |
27.4 (81.3) |
31.5 (88.7) |
32.4 (90.3) |
30.7 (87.3) |
25.8 (78.4) |
20.3 (68.5) |
12.9 (55.2) |
6.6 (43.9) |
20.0 (68.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.1 (32.2) |
3.8 (38.8) |
9.5 (49.1) |
16.1 (61.0) |
21.1 (70.0) |
25.4 (77.7) |
27.0 (80.6) |
25.5 (77.9) |
20.5 (68.9) |
14.6 (58.3) |
7.5 (45.5) |
1.6 (34.9) |
14.4 (57.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −3.7 (25.3) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
4.8 (40.6) |
10.8 (51.4) |
15.6 (60.1) |
20.1 (68.2) |
22.9 (73.2) |
21.6 (70.9) |
16.6 (61.9) |
10.4 (50.7) |
3.6 (38.5) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
10.0 (50.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −12.5 (9.5) |
−10.9 (12.4) |
−6.2 (20.8) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
4.7 (40.5) |
12.4 (54.3) |
15.8 (60.4) |
12.8 (55.0) |
6.5 (43.7) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
−8.0 (17.6) |
−12.8 (9.0) |
−12.8 (9.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 3.8 (0.15) |
8.6 (0.34) |
17.4 (0.69) |
36.6 (1.44) |
57.8 (2.28) |
63.5 (2.50) |
105.0 (4.13) |
79.2 (3.12) |
89.7 (3.53) |
49.4 (1.94) |
24.3 (0.96) |
3.7 (0.15) |
539 (21.23) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 3.2 | 3.6 | 5.3 | 6.5 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 9.8 | 9.3 | 9.9 | 7.7 | 5.7 | 2.7 | 79.9 |
| Average snowy days | 4.4 | 3.9 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.7 | 3.1 | 14.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 53 | 53 | 52 | 54 | 56 | 59 | 70 | 72 | 72 | 69 | 64 | 55 | 61 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 143.3 | 136.5 | 170.1 | 202.5 | 220.5 | 216.2 | 208.5 | 190.0 | 147.5 | 148.6 | 140.3 | 145.5 | 2,069.5 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 46 | 44 | 46 | 51 | 51 | 50 | 48 | 46 | 40 | 43 | 46 | 48 | 47 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration[4][5] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China[6] | |||||||||||||
Administration
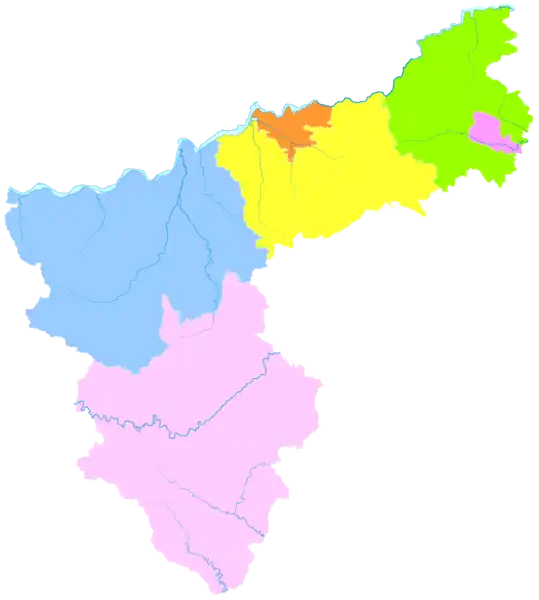
The prefecture-level city of Sanmenxia administers two districts, two county-level cities and two counties.
- Hubin District (湖滨区)
- Shanzhou District (陕州区)
- Lingbao City (灵宝市)
- Yima City (义马市)
- Lushi County (卢氏县)
- Mianchi County (渑池县)
| Map |
|---|
References
- "China: Hénán (Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties) - Population Statistics, Charts and Map".
- Exchange rate as of 28 May 2011.
- Peel, M. C. and Finlayson, B. L. and McMahon, T. A. (2007). "Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification". Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 11: 1633-1644. ISSN 1027-5606.
- 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- 三门峡 - 气象数据 -中国天气网 (in Chinese). Weather China. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
External links
- Government Website of Sanmenxia (in Chinese)
- City Map (in Chinese)