International Bank Account Number
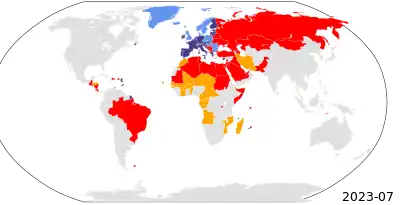
The International Bank Account Number (IBAN) is an internationally agreed upon system of identifying bank accounts across national borders to facilitate the communication and processing of cross border transactions with a reduced risk of transcription errors. An IBAN uniquely identifies the account of a customer at a financial institution.[1] It was originally adopted by the European Committee for Banking Standards (ECBS) and since 1997 as the international standard ISO 13616 under the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The current version is ISO 13616:2020, which indicates the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) as the formal registrar. Initially developed to facilitate payments within the European Union, it has been implemented by most European countries and numerous countries in other parts of the world, mainly in the Middle East and the Caribbean. As of July 2023, 86 countries were using the IBAN numbering system.[2]

The IBAN consists of up to 34 alphanumeric characters comprising a country code; two check digits; and a number that includes the domestic bank account number, branch identifier, and potential routing information. The check digits enable a check of the bank account number to confirm its integrity before submitting a transaction.
Background
Before IBAN, differing national standards for bank account identification (i.e. bank, branch, routing codes, and account number) were confusing for some users. This often led to necessary routing information being missing from payments. Routing information as specified by ISO 9362 (also known as Business Identifier Codes (BIC), SWIFT ID or SWIFT code, and SWIFT-BIC) does not require a specific format for the transaction so the identification of accounts and transaction types is left to agreements of the transaction partners. It also does not contain check digits, so errors of transcription were not detectable and it was not possible for a sending bank to validate the routing information prior to submitting the payment. Routing errors caused delayed payments and incurred extra costs to the sending and receiving banks and often to intermediate routing banks.[3]
In 1997, to overcome these difficulties, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) published ISO 13616:1997.[4] This proposal had a degree of flexibility that the European Committee for Banking Standards (ECBS) believed would make it unworkable, and they produced a "slimmed down" version of the standard which, amongst other things, permitted only upper-case letters and required that the IBAN for each country have a fixed length.[5] ISO 13616:1997 was subsequently withdrawn and replaced by ISO 13616:2003.[4] The standard was revised again in 2007 when it was split into two parts. ISO 13616-1:2007 "specifies the elements of an international bank account number (IBAN) used to facilitate the processing of data internationally in data interchange, in financial environments as well as within and between other industries" but "does not specify internal procedures, file organization techniques, storage media, languages, etc. to be used in its implementation".[6] ISO 13616-2:2007 describes "the Registration Authority (RA) responsible for the registry of IBAN formats that are compliant with ISO 13616-1 [and] the procedures for registering ISO 13616-compliant IBAN formats".[7] The official IBAN registrar under ISO 13616-2:2007 is SWIFT.[8]
IBAN imposes a flexible but regular format sufficient for account identification and contains validation information to avoid errors of transcription. It carries all the routing information needed to get a payment from one bank to another wherever it may be; it contains key bank account details such as country code, branch codes (known as sort codes in the UK and Ireland) and account numbers, and it contains check digits which can be validated at source according to a single standard procedure.[9] Where used, IBANs have reduced trans-national money transfer errors to under 0.1% of total payments
Structure
The IBAN consists of up to 34 alphanumeric characters, as follows:
- country code using ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 – two letters,
- check digits – two digits, and
- Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN) – up to 30 alphanumeric characters that are country-specific.[2]
The check digits represent the checksum of the bank account number which is used by banking systems to confirm that the number contains no simple errors.
In order to facilitate reading by humans, IBANs are traditionally expressed in groups of four characters separated by spaces, the last group being of variable length as shown in the example below; when transmitted electronically however spaces are omitted.[2]
| Human readable | IE12 BOFI 9000 0112 3456 78 |
| Machine readable | IE12BOFI90000112345678 |
Permitted IBAN characters are the digits 0 to 9 and the 26 Latin alphabetic characters A to Z.[10] This applies even in countries where these characters are not used in the national language (e.g. Greece).
Basic Bank Account Number
The Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN) format is decided by the national central bank or designated payment authority of each country. There is no consistency between the formats adopted. The national authority may register its BBAN format with SWIFT but is not obliged to do so. It may adopt IBAN without registration. SWIFT also acts as the registration authority for the SWIFT system, which is used by most countries that have not adopted IBAN. A major difference between the two systems is that under SWIFT there is no requirement that BBANs used within a country be of a pre-defined length.
The BBAN must be of a fixed length for the country and comprise case-insensitive alphanumeric characters. It includes the domestic bank account number, branch identifier, and potential routing information. Each country can have a different national routing/account numbering system, up to a maximum of 30 alphanumeric characters.
Check digits
The check digits enable the sending bank (or its customer) to perform a sanity check of the routing destination and account number from a single string of data at the time of data entry.[5] This check is guaranteed to detect any instances where a single character has been omitted, duplicated, mistyped or where two characters have been transposed. Thus routing and account number errors are virtually eliminated.[10]
Processing
One of the design aims of the IBAN was to enable as much validation as possible to be done at the point of data entry.[11] In particular, the computer program that accepts an IBAN will be able to validate:
- Country code
- Number of characters in the IBAN correspond to the number specified for the country code
- BBAN format specified for the country code
- Account number, bank code and country code combination is compatible with the check digits
The check digits are calculated using MOD-97-10 as per ISO/IEC 7064:2003[10] (abbreviated to mod-97 in this article), which specifies a set of check character systems capable of protecting strings against errors which occur when people copy or key data. In particular, the standard states that the following can be detected:
- All single substitution errors (the substitution of a single character for another, for example
4234for1234) - All or nearly all single (local) transposition errors (the transposition of two single characters, either adjacent or with one character between them, for example
12354or12543for12345) - All or nearly all shift errors (shifts of the whole string to the left or right)
- High proportion of double substitution errors (two separate single substitution errors in the same string, for example
7234587for1234567) - High proportion of all other errors
The underlying rules for IBANs is that the account-servicing financial institution should issue an IBAN, as there are a number of areas where different IBANs could be generated from the same account and branch numbers that would satisfy the generic IBAN validation rules. In particular cases where 00 is a valid check digit, 97 will not be a valid check digit, likewise, if 01 is a valid check digit, 98 will not be a valid check digit, similarly with 02 and 99.
The UN CEFACT TBG5 has published a free IBAN validation service in 32 languages for all 57 countries that have adopted the IBAN standard.[12] They have also published the Javascript source code of the verification algorithm.[13]
An English language IBAN checker for ECBS member country bank accounts is available on its website.[14]
Algorithms
Validating the IBAN
An IBAN is validated by converting it into an integer and performing a basic mod-97 operation (as described in ISO 7064) on it. If the IBAN is valid, the remainder equals 1.[Note 1] The algorithm of IBAN validation is as follows:[9]
- Check that the total IBAN length is correct as per the country. If not, the IBAN is invalid
- Move the four initial characters to the end of the string
- Replace each letter in the string with two digits, thereby expanding the string, where A = 10, B = 11, ..., Z = 35
- Interpret the string as a decimal integer and compute the remainder of that number on division by 97
If the remainder is 1, the check digit test is passed and the IBAN might be valid.
Example (fictitious United Kingdom bank, sort code 12-34-56, account number 98765432):
• IBAN: GB82 WEST 1234 5698 7654 32 • Rearrange: W E S T12345698765432 G B82 • Convert to integer: 3214282912345698765432161182 • Compute remainder: 3214282912345698765432161182 mod 97 = 1
Generating IBAN check digits
According to the ECBS "generation of the IBAN shall be the exclusive responsibility of the bank/branch servicing the account".[9] The ECBS document replicates part of the ISO/IEC 7064:2003 standard as a method for generating check digits in the range 02 to 98. Check digits in the ranges 00 to 96, 01 to 97, and 03 to 99 will also provide validation of an IBAN, but the standard is silent as to whether or not these ranges may be used.
The preferred algorithm is:[9]
- Check that the total IBAN length is correct as per the country. If not, the IBAN is invalid.
- Replace the two check digits by 00 (e.g., GB00 for the UK).
- Move the four initial characters to the end of the string.
- Replace the letters in the string with digits, expanding the string as necessary, such that A or a = 10, B or b = 11, and Z or z = 35. Each alphabetic character is therefore replaced by 2 digits
- Convert the string to an integer (i.e. ignore leading zeroes).
- Calculate mod-97 of the new number, which results in the remainder.
- Subtract the remainder from 98 and use the result for the two check digits. If the result is a single-digit number, pad it with a leading 0 to make a two-digit number.
Modulo operation on IBAN
Any computer programming language or software package that is used to compute D mod 97 directly must have the ability to handle integers of more than 30 digits. In practice, this can only be done by software that either supports arbitrary-precision arithmetic or that can handle 219-bit (unsigned) integers,[Note 2] features that are often not standard. If the application software in use does not provide the ability to handle integers of this size, the modulo operation can be performed in a piece-wise manner (as is the case with the UN CEFACT TBG5 JavaScript program).
Piece-wise calculation D mod 97 can be done in many ways. One such way is as follows:[15]
- Starting from the leftmost digit of D, construct a number using the first 9 digits and call it N.[Note 3]
- Calculate N mod 97.
- Construct a new 9-digit N by concatenating the above result (step 2) with the next 7 or 8 digits of D. If there are fewer than 7 digits remaining in D but at least one, then construct a new N, which will have less than 9 digits, from the above result (step 2) followed by the remaining digits of D
- Repeat steps 2–3 until all the digits of D have been processed
The result of the final calculation in step 2 will be D mod 97 = N mod 97.
Example
In this example, the above algorithm for D mod 97 will be applied to D = 3214282912345698765432161182. (The digits are colour-coded to aid the description below.) If the result is one, the IBAN corresponding to D passes the check digit test.
- Construct N from the first 9 digits of D
- N = 321428291
- Calculate N mod 97 = 70
- Construct a new 9-digit N from the above result (step 2) followed by the next 7 digits of D.
- N = 702345698
- Calculate N mod 97 = 29
- Construct a new 9-digit N from the above result (step 4) followed by the next 7 digits of D.
- N = 297654321
- Calculate N mod 97 = 24
- Construct a new N from the above result (step 6) followed by the remaining 5 digits of D.
- N = 2461182
- Calculate N mod 97 = 1
From step 8, the final result is D mod 97 = 1 and the IBAN has passed this check digit test.
National check digits
In addition to the IBAN check digits, many countries have their own national check digits used within the BBAN, as part of their national account number formats. Each country determines its own algorithm used for assigning and validating the national check digits - some relying on international standards, some inventing their own national standard, and some allowing each bank to decide if or how to implement them. Some algorithms apply to the entire BBAN, and others to one or more of the fields within it. The check digits may be considered an integral part of the account number, or an external field separate from the account number, depending on the country's rules.
Most of the variations used are based on two categories of algorithms:
- ISO 7064 MOD-97-10: Treat the account number as a large integer, divide it by 97 and use the remainder or its complement as the check digit(s).
- Weighted sum: Treat the account number as a series of individual numbers, multiply each number by a weight value according to its position in the string, sum the products, divide the sum by a modulus (usually 10 or 11) and use the remainder or its complement as the check digit.
In both cases, there may first be a translation from alphanumeric characters to numbers using conversion tables. The complement, if used, means the remainder r is subtracted from a fixed value, usually the modulus or the modulus plus one (with the common exception that a remainder of 0 results in 0, denoted as 0 → 0,as opposed to e.g. 0 → 97 meaning that if the reminder is zero the checksum is 97). Note that some national specifications define the weights order from right to left, but since the BBAN length in the IBAN is fixed, they can be used from left to right as well.
| Country | Algorithm | Weights | Modulo | Complement | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albania[16] | Weighted | 9, 7, 3, 1, 9, 7, 3, 1 | 10 | 10 − r, 0 → 0 | Applies only to the bank code + branch code fields. |
| Belgium[17] | ISO 7064 MOD-97-10 (variant) | 97 | r, 0 → 97 | Applied to bank code + account number. | |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina[18] | ISO 7064 MOD-97-10 | 97 | 98 − r | ||
| Croatia[17] | ISO 7064 MOD-11-10 | 11, 10 | 11 − r | Calculated separately for the bank code (seven digits) and account number (ten digits). Both should be 9. | |
| Czech Republic[17] | Weighted | 6, 3, 7, 9, 10, 5, 8, 4, 2, 1 | 11 | 11 − r, 0 → 0 | Calculated separately for the account number (ten digits) and branch number (six digits, using the last six weights). Both should be 0. |
| East Timor | ISO 7064 MOD-97-10 | 97 | 98 − r | Applied to the whole bban (bank code concatenated with account number) appended with "00". | |
| Estonia[17][19][20] | Weighted | 7, 1, 3, 7, 1, 3, 7, 1, 3, 7, 1, 3, 7 | 10 | 10 − r, 0 → 0 | Applies only to the branch code + account number fields (ignoring the bank code). Before multiplying by weights the resulting part of IBAN (i.e. branch code + account number) is reversed. |
| Finland[17] | Luhn | 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2 | 10 | 10 − r, 0 → 0 | Uses the Luhn Algorithm, where the sum is taken of the individual digits of the multiplication products rather than the products themselves. |
| France[17] | ISO 7064 MOD-97-10 (variant) | 97 | 97 − r | The mapping form characters to coefficients is non-standard: the digits 0–9 are converted to their respective values, letters 'A–I' converted to 1–9, letters J–R converted to 1–9 and letters S–Z converted to 2–9, respectively. After the transliteration, the part of IBAN is read as number. This is performed for bank code, branch code, and account number. Each of them is then multiplied by the proper multiplier (89, 15, 3) respectively (these constants are remainders of dividing , and by 97 respectively - using them do not change the result, but simplify the calculation[21]). The three numbers are then summed and the algorithm is performed on the result of this summation. | |
| Hungary[17] | Weighted | 9, 7, 3, 1, 9, 7, 3, 1, 9, 7, 3, 1, 9, 7, 3, 1 | 10 | 10 − r, 0 → 0 | There are two separate check digits—one for the bank code + branch code, and one for the account number, each calculated separately. |
| Iceland[17] | Weighted | 3, 2, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2 | 11 | 11 − r, 0 → 0 | Applies only to the first eight digits of the national identification number (kennitala), with the check digit stored at the 9th. |
| Italy[17] | Conversion + Sum | 26 | r | Characters are converted to digits using two different conversion tables, one for odd positions and one for even positions (the first character is considered odd).
Odd-positioned digits 0–9 are converted to their respective values in the sequence 1, 0, 5, 7, 9, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, and characters in the range A–Z are converted to 1, 0, 5, 7, 9, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 2, 4, 18, 20, 11, 3, 6, 8, 12, 14, 16, 10, 22, 25, 24, 23 respectively. Even-positioned characters are converted using the natural zero-based value, i.e. digits 0–9 converted to the respective numbers 0–9, and letters A–Z to the range 0–25. After conversion the numbers are summed (without weights), and the result taken modulo 26. This is then converted back into a single letter in the range A–Z (in natural order) which is used as the check digit (or rather, check character). | |
| Mauritania | ISO 7064 MOD-97-10 (variant) | 97 | 97 − r | ||
| Monaco[17] | ISO 7064 MOD-97-10 (variant) | 97 | 97 − r | Uses the same algorithm as France. | |
| Montenegro[17] | ISO 7064 MOD-97-10 | 97 | 98 − r | ||
| North Macedonia[17] | ISO 7064 MOD-97-10 | 97 | 98 − r | ||
| Norway[17] | Weighted | 5, 4, 3, 2, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2 | 11 | 11 − r, 0 → 0, 1 → invalid | If the first two digits of the account number (not the bank code) are both zeros, then the calculation applies only to the remaining four digits of the account number, otherwise it applies to the entire BBAN (bank code + account number). |
| Poland[17][22] | Weighted | 3, 9, 7, 1, 3, 9, 7 | 10 | 10 − r, 0 → 0 | Applies only to the bank code + branch code (without the account number). |
| Portugal[17] | ISO 7064 MOD-97-10 | 97 | 98 − r | ||
| San Marino[17] | Conversion + Sum | 26 | r | Uses the same algorithm as Italy. | |
| Serbia[17] | ISO 7064 MOD-97-10 | 97 | 98 − r | ||
| Slovakia[17] | Weighted | 6, 3, 7, 9, 10, 5, 8, 4, 2, 1 | 11 | 11 − r, 0 → 0 | Calculated separately for the account number (ten digits) and branch number (six digits, using the last six weights). Same as Czech Republic. |
| Slovenia[17] | ISO 7064 MOD-97-10 | 97 | 98 − r | ||
| Spain[17] | Weighted | 1, 2, 4, 8, 5, 10, 9, 7, 3, 6 | 11 | 11 − r, 0 → 0, 1 → 1 | There are two separate check digits—one for the bank code + branch code, and one for the account number, each calculated separately. The account number is ten characters long and uses all of the weights, whereas the bank code + branch code are eight characters long and thus use only the last eight weights in the calculation (or equivalently, pad with two zeros on the left and use the ten weights). |
| Tunisia[17] | ISO 7064 MOD-97-10 (variant) | 97 | 97 − r |
Adoption
International bank transactions use either an IBAN or the ISO 9362 Business Identifier Code system (BIC or SWIFT code) in conjunction with the BBAN (Basic Bank Account Number).[23]
EEA and territories
The banks of most countries in Europe publish account numbers using both the IBAN format and the nationally recognised identifiers, this being mandatory within the European Economic Area.[24]
Day-to-day administration of banking in British Overseas Territories varies from territory to territory; some, such as South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, have too small a population to warrant a banking system while others, such as Bermuda, have a thriving financial sector.[25] The use of the IBAN is up to the local government—Gibraltar, formerly part of the European Union is required to use the IBAN,[24] as are the Crown Dependencies, which use the British clearing system,[26] and the British Virgin Islands have chosen to do so. As of April 2013, no other British Overseas Territories have chosen to use the IBAN.[2] Banks in the Caribbean Netherlands also do not use the IBAN.

Single Euro Payments Area
The IBAN designation scheme was chosen as the foundation for electronic straight-through processing in the European Economic Area. The European Parliament mandated that a bank charge needs to be the same amount for domestic credit transfers as for cross-border credit transfers regulated in decision 2560/2001 (updated in 924/2009).[24] This regulation took effect in 2003. Only payments in euro up to €12,500 to a bank account designated by its IBAN were covered by the regulation, not payments in other currencies.
The Euro Payments regulation was the foundation for the decision to create a Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA). The European Central Bank has created the TARGET2 interbank network that unifies the technical infrastructure of the 26 central banks of the European Union (although Sweden has opted out). SEPA is a self-regulatory initiative by the banking sector of Europe as represented in the European Payments Council (EPC). The European Union made the scheme mandatory through the Payment Services Directive published in 2007. Since January 2008, all countries were required to support SEPA credit transfer, and SEPA direct debit was required to be supported since November 2009. The regulation on SEPA payments increased the charge cap (same price for domestic payments as for cross-border payments) to €50,000.
With a further decision of the European Parliament, the IBAN scheme for bank accounts fully replaced the domestic numbering schemes from 31 December 2012.[27] On 16 December 2010, the European Commission published regulations that made IBAN support mandatory for domestic credit transfer by 2013 and for domestic direct debit by 2014 (with a 12 and 24 months transition period respectively).[28] Some countries had already replaced their traditional bank account scheme by IBAN. This included Switzerland where IBAN was introduced for national credit transfer on 1 January 2006 and the support for the old bank account numbers was not required from 1 January 2010.[29]
Based on a 20 December 2011 memorandum,[30] the EU parliament resolved the mandatory dates for the adoption of the IBAN on 14 February 2012.[31] On 1 February 2014, all national systems for credit transfer and direct debit were abolished and replaced by an IBAN-based system.[31] This was then extended to all cross-border SEPA transactions on 1 February 2016 (Article 5 Section 7).[31] After these dates the IBAN is sufficient to identify an account for home and foreign financial transactions in SEPA countries and banks are no longer permitted to require that the customer supply the BIC for the beneficiary's bank.
In the run-up to the 1 February 2014 deadline, it became apparent that many old bank account numbers had not been allocated IBANs—an issue that was addressed on a country-by-country basis. In Germany, for example, Deutsche Bundesbank and the German Banking Industry Committee required that all holders of German bank codes ("Bankleitzahl") published the specifics of their IBAN generation format taking into account not only the generation of check digits but also the handling of legacy bank codes, thereby enabling third parties to generate IBANs independently of the bank.[32] The first such catalogue was published in June 2013 as a variant of the old bank code catalog ("Bankleitzahlendatei").[33]
Non-EEA
Banks in numerous non-European countries including most states of the Middle East, North Africa and the Caribbean have implemented the IBAN format for account identification.[2] In some countries the IBAN is used on an ad hoc basis, an example was Ukraine where account numbers used for international transfers by some domestic banks had additional aliases that followed the IBAN format as a precursor to formal SWIFT registration.[34] This practice in Ukraine ended on 1 November 2019 when all Ukrainian banks had fully switched to the IBAN standard.[35]
The degree to which a bank verifies the validity of a recipient's bank account number depends on the configuration of the transmitting bank's software—many major software packages supply bank account validation as a standard function.[36] Some banks outside Europe may not recognize IBAN, though this is expected to diminish with time. Non-European banks usually accept IBANs for accounts in Europe, although they might not treat IBANs differently from other foreign bank account numbers. In particular, they might not check the IBAN's validity prior to sending the transfer.[37]
Banks in the United States do not use IBAN as account numbers for U.S. accounts and use ABA routing transit numbers.[38] Any adoption of the IBAN standard by U.S. banks would likely be initiated by ANSI ASC X9, the U.S. financial services standards development organization: a working group (X9B20) was established as an X9 subcommittee to generate an IBAN construction for U.S. bank accounts.[39]
Canadian financial institutions have not adopted IBAN and use routing numbers issued by Payments Canada for domestic transfers, and SWIFT for international transfers. There is no formal governmental or private sector regulatory requirement in Canada for the major banks to use IBAN.
Australia and New Zealand do not use IBAN. They use Bank State Branch codes for domestic transfers and SWIFT for international transfers.[40]
IBAN formats by country
This table summarises the IBAN formats by country:[2]
- The kk after the two-character ISO country code represents the check digits calculated from the rest of the IBAN characters. If it is a constant for the country concerned, this will be stated in the Comments column. This happens where the BBAN has its own check digits that use the same algorithm as the IBAN check digits
- The BBAN format column shows the format of the BBAN part of an IBAN in terms of upper case alpha characters (A–Z) denoted by "a", numeric characters (0–9) denoted by "n" and mixed case alphanumeric characters (a–z, A–Z, 0–9) denoted by "c". For example, the Bulgarian BBAN (4a,6n,8c) consists of 4 alpha characters, followed by 6 numeric characters, then by 8 mixed-case alpha-numeric characters
- Descriptions in the Comments field have been standardised with country-specific names in brackets. The format of the various fields can be deduced from the BBAN field
| Country | Chars | BBAN Format | IBAN Fields | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albania | 28 | 8n,16c | ALkk bbbs sssx cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code s = Branch code x = National check digit c = Account number |
| Andorra | 24 | 8n,12c | ADkk bbbb ssss cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code s = Branch code c = Account number |
| Austria | 20 | 16n | ATkk bbbb bccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Azerbaijan | 28 | 4a,20c | AZkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Bahrain | 22 | 4a,14c | BHkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc cc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Belarus | 28 | 4c, 4n, 16c | BYkk bbbb aaaa cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank or branch code a = Balance account number c = Account number |
| Belgium | 16 | 12n | BEkk bbbc cccc ccxx |
b = National bank code c = Account number x = National check digits |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | 20 | 16n | BAkk bbbs sscc cccc ccxx |
k = IBAN check digits (always "39") b = National bank code s = Branch code c = Account number x = National check digits |
| Brazil | 29 | 23n,1a,1c | BRkk bbbb bbbb ssss sccc cccc ccct n |
b = National bank code s = Branch code c = Account number t = Account type (cheque account, savings account etc.) n = Owner account number ("1", "2" etc.)[41] |
| Bulgaria | 22 | 4a,6n,8c | BGkk bbbb ssss ttcc cccc cc |
b = BIC bank code s = Branch (BAE) number t = Account type c = Account number |
| Costa Rica | 22 | 18n | CRkk 0bbb cccc cccc cccc cc |
0 = always zero b = bank code c = Account number |
| Croatia | 21 | 17n | HRkk bbbb bbbc cccc cccc c |
b = Bank code c = Account number |
| Cyprus | 28 | 8n,16c | CYkk bbbs ssss cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code s = Branch code c = Account number |
| Czech Republic | 24 | 20n | CZkk bbbb pppp ppcc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code p = Account number prefix c = Account number |
| Denmark | 18 | 14n | DKkk bbbb cccc cccc cx |
b = National bank code c = Account number x = National check digit |
| Dominican Republic | 28 | 4c,20n | DOkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = Bank identifier c = Account number |
| East Timor | 23 | 19n | TLkk bbbc cccc cccc cccc cxx |
k = IBAN check digits (always = "38") b = Bank identifier c = Account number x = National check digits |
| Egypt | 29 | 25n | EGkk bbbb ssss cccc cccc cccc cccc c |
b = National bank code s = Branch code c = Account number |
| El Salvador | 28 | 4a, 20n | SVkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Estonia | 20 | 16n | EEkk bbss cccc cccc cccx |
b = National bank code s = Branch code c = Account number x = National check digit |
| Faroe Islands[Note 4] | 18 | 14n | FOkk bbbb cccc cccc cx |
b = National bank code c = Account number x = National check digit |
| Finland | 18 | 14n | FIkk bbbb bbcc cccc cx |
b = Bank and branch code c = Account number x = National check digit |
| France[Note 5] | 27 | 10n,11c,2n | FRkk bbbb bsss sscc cccc cccc cxx |
b = National bank code s = Branch code (code guichet) c = Account number x = National check digits (clé RIB) |
| Georgia | 22 | 2a,16n | GEkk bbcc cccc cccc cccc cc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Germany | 22 | 18n | DEkk bbbb bbbb cccc cccc cc |
b = Bank and branch identifier (Bankleitzahl or BLZ) c = Account number |
| Gibraltar | 23 | 4a,15c | GIkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc ccc |
b = BIC bank code c = Account number |
| Greece | 27 | 7n,16c | GRkk bbbs sssc cccc cccc cccc ccc |
b = National bank code s = Branch code c = Account number |
| Greenland[Note 4] | 18 | 14n | GLkk bbbb cccc cccc cx |
b = National bank code c = Account number x = National check digit |
| Guatemala | 28 | 4c,20c | GTkk bbbb mmtt cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code c = Account number m = Currency code t = Account type |
| Hungary | 28 | 24n | HUkk bbbs sssx cccc cccc cccc cccx |
b = National bank code s = Branch code c = Account number x = National check digit |
| Iceland | 26 | 22n | ISkk bbss ttcc cccc iiii iiii ii |
b = National bank code s = Branch code t = Account type c = Account number i = Account holder's kennitala (national identification number) |
| Iraq | 23 | 4a,15n | IQkk bbbb sssc cccc cccc ccc |
b = National bank code s = Branch code c = Account number |
| Ireland | 22 | 4a,6n,8n | IEkk qqqq bbbb bbcc cccc cc |
q = BIC bank code b = Bank/branch code (sort code) c = Account number |
| Israel | 23 | 19n | ILkk bbbs sscc cccc cccc ccc |
b = National bank code s = Branch code c = Account number 13 digits (padded with zeros) |
| Italy | 27 | 1a,10n,12c | ITkk xbbb bbss sssc cccc cccc ccc |
x = Check character (CIN) b = National bank code (Associazione Bancaria Italiana or Codice ABI) s = Branch code (Coordinate bancarie or CAB – Codice d'Avviamento Bancario) c = Account number |
| Jordan | 30 | 4a,4n,18c | JOkk bbbb ssss cccc cccc cccc cccc cc |
b = National bank code s = Branch code c = Account number |
| Kazakhstan | 20 | 3n,13c | KZkk bbbc cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Kosovo | 20 | 4n,10n,2n | XKkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Kuwait | 30 | 4a,22c | KWkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc cccc cccc cc |
b = National bank code c = Account number. |
| Latvia | 21 | 4a,13c | LVkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc c |
b = BIC bank code c = Account number |
| Lebanon | 28 | 4n,20c | LBkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Libya | 25 | 21n | LYkk bbbs sscc cccc cccc cccc c |
b = National bank code s = Branch code c = Account number |
| Liechtenstein | 21 | 5n,12c | LIkk bbbb bccc cccc cccc c |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Lithuania | 20 | 16n | LTkk bbbb bccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Luxembourg | 20 | 3n,13c | LUkk bbbc cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Malta | 31 | 4a,5n,18c | MTkk bbbb ssss sccc cccc cccc cccc ccc |
b = BIC bank code s = Branch code c = Account number |
| Mauritania | 27 | 23n | MRkk bbbb bsss sscc cccc cccc cxx |
k = IBAN check digits (always "13") b = National bank code s = Branch code (code guichet) c = Account number x = National check digits (clé RIB) |
| Mauritius | 30 | 4a,19n,3a | MUkk bbbb bbss cccc cccc cccc 000m mm |
b = National bank code s = Branch identifier c = Account number 0 = Zeroes m = Currency code |
| Monaco | 27 | 10n,11c,2n | MCkk bbbb bsss sscc cccc cccc cxx |
b = National bank code s = Branch code (code guichet) c = Account number x = National check digits (clé RIB'). |
| Moldova | 24 | 2c,18c | MDkk bbcc cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Montenegro | 22 | 18n | MEkk bbbc cccc cccc cccc xx |
k = IBAN check digits (always = "25") b = Bank code c = Account number x = National check digits |
| Netherlands[Note 6] | 18 | 4a,10n | NLkk bbbb cccc cccc cc |
b = BIC Bank code c = Account number |
| North Macedonia | 19 | 3n,10c,2n | MKkk bbbc cccc cccc cxx |
k = IBAN check digits (always = "07") b = National bank code c = Account number x = National check digits |
| Norway | 15 | 11n | NOkk bbbb cccc ccx |
b = National bank code c = Account number x = Modulo-11 national check digit |
| Pakistan | 24 | 4a,16c | PKkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Palestinian territories | 29 | 4a,21c | PSkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc cccc cccc c |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Poland | 28 | 24n | PLkk bbbs sssx cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code s = Branch code x = National check digit c = Account number, |
| Portugal | 25 | 21n | PTkk bbbb ssss cccc cccc cccx x |
k = IBAN check digits (always = "50") b = National bank code (numeric only) s = Branch code (numeric only) c = Account number (numeric only) x = National check digits (numeric only) |
| Qatar | 29 | 4a,21c | QAkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc cccc cccc c |
b = National bank code c = Account number[42] |
| Romania | 24 | 4a,16c | ROkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = BIC Bank code (first four alpha characters) c = Branch code and account number (bank-specific format) |
| Russia (effective April 2023)[2] |
33 | 14n,15c | RUkk bbbb bbbb bsss sscc cccc cccc cccc c |
b = Bank code s = Branch code c = Account number |
| Saint Lucia | 32 | 4a,24c | LCkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = Bank code c = Account number |
| San Marino | 27 | 1a,10n,12c | SMkk xbbb bbss sssc cccc cccc ccc |
x = Check character (CIN) b = National bank code (Associazione bancaria italiana or Codice ABI) s = Branch code (Coordinate bancarie or CAB – Codice d'Avviamento Bancario) c = Account number |
| São Tomé and Príncipe | 25 | 21n | STkk bbbb ssss cccc cccc cccc c |
b = National bank code s = Branch number c = Account number |
| Saudi Arabia | 24 | 2n,18c | SAkk bbcc cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code c = Account number preceded by zeros, if required |
| Serbia | 22 | 18n | RSkk bbbc cccc cccc cccc xx |
k = IBAN check digits (always = "35") b = National bank code |
| Seychelles | 31 | 4a,20n,3a | SCkk bbbb bb ss cccc cccc cccc cccc mmm |
b = Bank code s = Branch code c = Account number m = Currency code |
| Slovakia | 24 | 20n | SKkk bbbb pppp ppcc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code p = Account number prefix c = Account number |
| Slovenia | 19 | 15n | SIkk bbss sccc cccc cxx |
k = IBAN check digits (always = "56") b = National bank code s = Branch code c = Account number x = National check digits |
| Spain | 24 | 20n | ESkk bbbb ssss xxcc cccc cccc |
kk = Iban check digits code b = National bank s = Branch code x = Check digits c = Account number |
| Sudan | 18 | 14n | SDkk bbcc cccc cccc cc |
k = IBAN check digits b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Sweden | 24 | 20n | SEkk bbbc cccc cccc cccc cccx |
b = National bank code c = Account number x = Check digits |
| Switzerland | 21 | 5n,12c | CHkk bbbb bccc cccc cccc c |
b = National bank code c = Code identifying a bank account |
| Tunisia | 24 | 20n | TNkk bbss sccc cccc cccc ccxx |
k = IBAN check digits (always "59") b = National bank code s = Branch code c = Account number x = National check digits |
| Turkey | 26 | 5n,1n,16c | TRkk bbbb b0cc cccc cccc cccc cc |
b = National bank code 0 = Zero (reserved) c = Account number |
| Ukraine | 29 | 6n, 19c | UAkk bbbb bbcc cccc cccc cccc cccc c |
b = Bank code c = Account number preceded by zeros, if required |
| United Arab Emirates | 23 | 3n,16n | AEkk bbbc cccc cccc cccc ccc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| United Kingdom[Note 7] | 22 | 4a,14n | GBkk bbbb ssss sscc cccc cc |
b = BIC bank code s = Bank and branch code (sort code) c = Account number |
| Vatican City | 22 | 3n,15n | VAkk bbbc cccc cccc cccc cc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
| Virgin Islands, British | 24 | 4a,16n | VGkk bbbb cccc cccc cccc cccc |
b = National bank code c = Account number |
In addition to the above, the IBAN is under development in countries below but has not yet been catalogued for general international use.[43][44]
In this list
"kk"represent the IBAN checksum"a"represents an alphabetic character"c"represents an alphanumeric character"n"represents a numeric character.
| Country | Chars | BBAN Format | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Algeria | 26 | 22n | DZkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nn |
| Angola | 25 | 21n | AOkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn n |
| Benin | 28 | 2c, 22n | BJkk ccnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn |
| Burkina Faso | 28 | 2c, 22n | BFkk ccnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn |
| Burundi | 27 | 5n, 5n, 11n, 2n | BIkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnn |
| Cabo Verde | 25 | 21n | CVkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn n |
| Cameroon | 27 | 23n | CMkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnn |
| Central African Republic | 27 | 23n | CFkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnn |
| Chad | 27 | 23n | TDkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnn |
| Comoros | 27 | 23n | KMkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnn |
| Congo, Republic of the | 27 | 23n | CGkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnn |
| Côte d'Ivoire | 28 | 1a, 23n | CIkk annn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn |
| Djibouti | 27 | 23n | DJkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnn |
| Equatorial Guinea | 27 | 23n | GQkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnn |
| Gabon | 27 | 23n | GAkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnn |
| Guinea-Bissau | 25 | 2c, 19n | GWkk ccnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn n |
| Honduras | 28 | 4a, 20n | HNkk aaaa nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn |
| Iran | 26 | 22n | IRkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nn |
| Madagascar | 27 | 23n | MGkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnn |
| Mali | 28 | 2c, 22n | MLkk annn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn |
| Morocco | 28 | 24n | MAkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn |
| Mozambique | 25 | 21n | MZkk nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn n |
| Nicaragua | 32 | 4a, 24n | NIkk aaaa nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn |
| Niger | 28 | 2a, 22n | NEkk aann nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn |
| Senegal | 28 | 2a, 22n | SNkk aann nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn |
| Togo | 28 | 2a, 22n | TGkk aann nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn nnnn |
See also
Notes
- In equations, the remainder of A divided by B is denoted A mod B or A (mod B), e.g., 2 = 14 mod 12 . See Remainders.
- The IBAN value, ZZ59ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ, is converted to the largest possible integer, approximately 3.5 × 1065 per ISO 7064 MOD-97-10 (before taking the modulus). 2219 - 1 is approximately equal to 8.4 × 1065, thus 219-bit unsigned integers can accommodate all valid IBAN values.
- 231 is approximately equal to 2.1 × 109, making it possible for any 9-digit integer to be handled using 32 bit integer arithmetic
- Registered at SWIFT as part of Denmark, but with its own country code.
- French Guiana, French Polynesia, French Southern Territories, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, New Caledonia, Réunion, Saint Barthélemy, Saint Martin (French part), Saint Pierre and Miquelon, and Wallis and Futuna Islands have their own ISO country code but use "FR" as their IBAN country code.
- Not applicable to Aruba, Curaçao, Sint Maarten, and the Caribbean Netherlands.
- The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the Isle of Man and the Bailiwicks of Guernsey and Jersey use this format. British Overseas Territories have their own formats — only Gibraltar and the British Virgin Islands use IBANs.
References
- "What is IBAN, BBAN, SWIFT, BIC, ACH, SEPA, SCT and SDD?". www.iban.com. Retrieved 2023-02-01.
- "IBAN REGISTRY – This registry provides detailed information about all ISO 13616-compliant national IBAN formats. – Release 95 – July 2023". SWIFT. July 2023. Retrieved 17 August 2023.
- "Handbook for the Standardisation and Application of Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN) and International Bank Account Number (IBAN) in Cyprus" (PDF). Central Bank of Cyprus. September 2003. Introduction. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "Banking and related financial services -- International Bank Account Number (IBAN)". International Organization for Standardization. 24 July 2003. Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- "IBAN Standard Implementation Guidelines – SIG203 V4" (PDF). European Committee for Banking Standards. December 2000. 9.3 Ordering customer. Retrieved 8 August 2012.
IBANs make validation possible for telebanking, FEDI
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "ISO 13616-1:2007 Financial services — International bank account number (IBAN) — Part 1: Structure of the IBAN". International Organization for Standardization. Retrieved 31 January 2010.
- "ISO 13616-2:2007 Financial services – International bank account number (IBAN) -- Part 2: Role and responsibilities of the Registration Authority". International Organization for Standardization. Retrieved 31 January 2010.
- "ISO13616 IBAN Registry". Swift. Retrieved 18 January 2010.
- "IBAN: International Bank Account Number" (PDF). EBS204 V3.2. European Committee for Banking Standards. August 2003. Retrieved 3 August 2021.
- "ISO/IEC 7064:2003 – Information technology – Security techniques – Check character systems". International Organization for Standardization. Retrieved 31 January 2010.
- "Handbook for the Standardisation and Application of Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN) and International Bank Account Number (IBAN) in Cyprus" (PDF). Central Bank of Cyprus. September 2003. Section 4 – Advantages. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
Reduction of human errors
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "International Bank Account Number (IBAN) – IBAN online check". UN/CEFACT United Nations Centre for Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business. 23 April 2012. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- "International Bank Account Number (IBAN) – Basic information". UN/CEFACT United Nations Centre for Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business. 23 April 2012. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- "Iban Checker". European Banking Resources. ecbs.org. 22 September 2008. Retrieved 30 September 2012.
- "Standard 48 – Format of the IBAN issued in the UK (International Bank Account Number)" (PDF). UK Payments Administration. June 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 August 2012.
- "On the Structure and the Use of the International Bank Account Number (IBAN)" (PDF). p. 13.
- "Register of European Account Numbers (TR201 V3.9)" (PDF). February 2005.
- "The Instruction on the structure and use of International Number of the Bank Account (IBAN) - Published in the Official Gazette of Republika Srpska".
- "Estonia sample php code for parsing IBANs" (PDF). p. 5.
- "Check Digit Calculator of Domestic Account Number and reference number of invoice (Javascript source code)".
- "Clé RIB", Wikipédia (in French), 2021-12-23, retrieved 2023-05-22
- "Suma lub cyfra kontrolna".
- "International Wire Transfer: The Info You Need to Know". American Express. Retrieved 9 March 2020.
- "REGULATION (EC) No 924/2009 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 16 September 2009 on cross-border payments in the Community and repealing Regulation (EC) No 2560/2001". EUR-Lex. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- "Bermuda Monetary Authority: Home Page". 2013. Archived from the original on 10 October 2012. Retrieved 2 April 2013.
- "World Payments Guide". PacNet Services Ltd. 2011. Retrieved 2 April 2013.
- "Frist für Umstieg auf SEPA-Produkte: Dt Widerstand programmiert" [Deadline for migration to SEPA products: Dt programmed resistance] (in German). Dow Jones Deutschland. 14 December 2010. Archived from the original on 17 December 2010. Retrieved 18 December 2010.
- "Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council establishing technical requirements for credit transfers and direct debits in euros and amending Regulation (EC) No 924/2009". the European Parliament and of the Council of the European Union. 16 December 2010. Retrieved 17 January 2011.
- "IBAN-Nummer: Noch kein Obligatorium" [IBAN Number: Not mandatory] (in German). 29 November 2009. Retrieved 18 December 2010.
- "Commissioner Michel Barnier welcomes agreement by Council and Parliament establishing SEPA migration end-dates" (Press release). European Commission. 20 December 2010. MEMO/11/935.
- "European Parliament legislative resolution of 14 February 2012 on the proposal for a regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council establishing technical requirements for credit transfers and direct debits in euros and amending Regulation (EC) No 924/2009". European Parliament. 14 February 2012. P7_TA-PROV(2012)0037.
- "Rundschreiben Nr. 73/2012 Abkommen über IBAN-Regeln" [Circular no 70/2012 Agreement regarding IBAN rules] (PDF) (in German). Deutsche Bundesbank. 18 December 2012. Retrieved 11 June 2013.
- "IBAN-Regeln – Bankleitzahlendatei" [IBAN Rules – Bank [sort] codes] (in German). Deutsche Bundesbank. 3 June 2013. Archived from the original on 7 June 2013. Retrieved 11 June 2013.
- Засідання Комітету з питань банківської інфраструктури та платіжних систем [News: Committee Meeting banking infrastructure and payment systems] (in Ukrainian). 28 March 2013. Archived from the original on 29 July 2013. Retrieved 2 April 2013.
- Усі українські банки перейшли на використання IBAN - Нацбанк [All Ukrainian banks have switched to IBAN - National Bank] (in Ukrainian). 1 November 2019. Retrieved 1 November 2019.
- "Bank Account Validation". SAP work portal. SAP. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- "Avoiding the Pitfalls of IBAN Payments". Reed Business Information Limited. 2013. pp. 1–4. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- "Understanding SWIFT and IBAN: Essential Details When Making A Money Transfer". Currency Solutions. 2013. Retrieved 22 May 2013.
- "X9 Board, Subcommittees and Working Groups: X9B20 – (IBAN) International Bank Account Number". Accredited Standards Committee X9. Retrieved 26 April 2019.
- "IBAN SWIFT Codes". Switzerland Buying Guide. 2013. Archived from the original on 7 July 2014. Retrieved 4 July 2013.
- "IBAN Implementation Guidelines for Brazil - Circular 3.625" (PDF). Banco Central do Brasil. 14 February 2013. Retrieved 1 August 2013.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "IBAN Registry (Qatar - Page 63)" (PDF). SWIFT. November 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 November 2013. Retrieved 21 November 2013.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "IBAN countries". Nordea. 2020. Retrieved 13 August 2020.
- "Experimental IBAN Countries". IBAN.com. 28 July 2020. Retrieved 13 August 2020.
External links
- "Official ISO 13616 Registry" (PDF). Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT).
- "ISO 13616-1:2007". International Organization for Standardization (ISO).