Timeline of Siena
Prior to 15th century
| History of Italy |
|---|
 |
|
|
- 1st C. CE – Saena Julia founded by Romans.
- 1205 – Palazzo Tolomei built (approximate date).[1]
- 1233 - "The people again rose against the nobles in the hope of ousting them entirely from office."[2]
- 1240 – University of Siena established.[2]
- 1248 - Plague.[2]
- 1255
- Gran Tavola bank founded.
- Basilica of San Francesco built.
- 1260 – Battle of Montaperti.
- 1263 – Siena Cathedral built.
- 1265 – Basilica of San Domenico built.
- 1287 – Noveschi in power.
- 1308 – Palazzo Pubblico built.[3]
- 1328 – Famine.[4]
- 1348
- Black Death plague.
- Torre del Mangia built.[2]
- 1349 - Piazza del Campo paved in fishbone-patterned red brick.[2]
- 1355 - Arrival of Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor in Siena
- 1360 – Public clock installed.[5]
15th century
- 1419 - Fonte Gaia built.
- 1423 - Council of Siena begins.
- 1438 - Loggia della Mercanzia built (approximate date).[6]
- 1459 – Palazzo Marsili rebuilt.[6]
- 1462 – Loggia del Papa erected.[6]
- 1463 – Palazzo Piccolomini-delle Papesse built.[6]
- 1472
- Monte dei Paschi di Siena founded.
- Palazzo Spannocchi built (approximate date).
- 1478 - The Pazzi conspiracy led to war a war lasting to 1480.[2]
- 1482 & 1483 - Riots.[2]
- 1484 – Printing press in operation.
- 1490 – Basilica dell'Osservanza built (approximate date).
- 1495
- Palazzo delle Papesse completed (approximate date).
- Piccolomini Library built (approximate date).[6]
16th–18th centuries
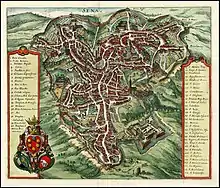
Map of Siena, 1640
- 1504 – Santo Spirito renovated.
- 1506 – Palazzo Chigi-Saracini renovated.
- 1508 – Palazzo del Magnifico built.[6]
- 1520 – Palazzo Bichi built (approximate date).[6]
- 1527 – Accademia degli Intronati founded (approximate date).
- 1533 – Santa Maria dei Servi consecrated.
- 1554 – Battle of Marciano.
- 1555 – Republic of Siena surrenders to Spain; Siena ceded to Duchy of Florence.[2]
- 1604 – Porta Camollia rebuilt.[6]
- 1613 – San Martino renovated.
- 1656 – Palio di Siena horse race begins.[2]
- 1691 – Accademia dei Fisiocritici founded.[7]
- 1729 – Consolidation of districts; elimination of contrade Gallo, Leone, Orso, Quercia, Spadaforte, and Vipera.
19th century
- 1816
- Fine Arts Institution founded.[2]
- The natural history museum of the Royal Academy of the Physiocritics founded.[2]
- 1848 – Palazzo Buonsignori restored.[6]
- 1854 – Palazzo del Capitano restored.[6]
- 1856 – Orto Botanico dell'Università di Siena laid out.
- 1858 – Municipal Archivio instituted.[8][2]
- 1865 – Empoli-Siena railway begins operating.
- 1866 – Cemetery della Misericordia established.
- 1871 – Mens Sana in Corpore Sano 1871 formed.
- 1897 – Population: 30,468.[9]
20th century

Allied bombing of Nazi railyard, Siena, c. 1944
- 1901 – Population: 25,539.[2]
- 1904 – Società Studio e Divertimento formed.
- 1911 – Population: 41,673.[10]
- 1923 – Stadio Artemio Franchi – Montepaschi Arena opens.
- 1932
- Accademia Musicale Chigiana founded.
- Pinacoteca Nazionale inaugurated.
- 1935 – Siena railway station opens.
- 1944 – Bombing by Allies.
- 1959 – Biblioteca Comunale degli Intronati (library) active.[11]
- 1976 – Palasport Mens Sana arena opens.
- 1995 – Santa Maria della Scala museum opens.
21st century

Siena, 2009
- 2003
- Fondazione Musei Senesi established.[12]
- Siena–Ampugnano Airport renovated.[13]
See also
- Siena history
- History of Siena
- List of governors of Siena
- List of mayors of Siena
- Republic of Siena, 11th–16th centuries
- Archivio di Stato di Siena (state archives)
Other cities in the macroregion of Central Italy:(it)
- Timeline of Ancona, Marche region
- Timeline of Arezzo, Tuscany region
- Timeline of Florence, Tuscany
- Timeline of Livorno, Tuscany
- Timeline of Lucca, Tuscany
- Timeline of Perugia, Umbria region
- Timeline of Pisa, Tuscany
- Timeline of Pistoia, Tuscany
- Timeline of Prato, Tuscany
- Timeline of Rome, Lazio region
References
- Hastings 1902.
- Britannica 1910.
- Gardner 1909.
- Schevill 1909.
- Gerhard Dohrn-van Rossum [in German] (1996). "The First Public Clocks". History of the Hour: Clocks and Modern Temporal Orders. University of Chicago Press. p. 129. ISBN 978-0-226-15510-4.
- Baedeker 1909.
- "La Storia dell'Accademia". Accademia dei Fisiocritici Onlus. Archived from the original on August 1, 2012. Retrieved August 13, 2012.
- Heywood 1905.
- "Italy". Statesman's Year-Book. London: Macmillan and Co. 1899. hdl:2027/nyp.33433081590550 – via HathiTrust.
- "Italy". Statesman's Year-Book. London: Macmillan and Co. 1913. hdl:2027/njp.32101072368374.
- "(Comune: Siena)". Anagrafe delle biblioteche italiane (Registry of Italian Libraries) (in Italian). Istituto Centrale per il Catalogo Unico. Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- "Forty-three museums scattered throughout the Province of Siena are part of the Fondazione Musei Senesi". Siena: Fondazione Musei Senesi. Archived from the original on April 15, 2013. Retrieved August 13, 2012.
- "Our history". Aeroporto di Siena. Retrieved August 13, 2012.
Further reading
Wikimedia Commons has media related to History of Siena.
- Josiah Conder (1834), "Siena", Italy, The Modern Traveller, vol. 33, London: J.Duncan
- Gilbert Hastings (1902), Siena: its architecture and art, London: De La More Press, OCLC 3571094, OL 7173091M
- William Heywood; Lucy Olcott (1905), Guide to Siena: History and Art (3rd ed.), Siena: E. Torrini, OCLC 6980800, OL 22881481M
- "Siena", Central Italy and Rome: Handbook for Travellers (15th ed.), Leipzig: Karl Baedeker, 1909, OCLC 423237
- Edmund Garratt Gardner (1909), The story of Siena and San Gimignano, Mediaeval Towns (3rd ed.), London: J.M. Dent & Co., OL 23342474M
- Ferdinand Schevill (1909), Siena: the story of a mediaeval commune, New York: Scribner, OL 7186295M
- Paoli, Cesare; Ashby, Thomas (1910). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 25 (11th ed.). pp. 48–53.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.