Suburban trains in Budapest
Suburban trains in Budapest are known in Hungarian as Budapesti elővárosi vonatok, serving fourteen lines in the Budapest metropolitan area, three of which are part of the BHÉV system. The system is operated by Hungarian State Railways.[1]
| Budapesti elővárosi vonatok | |
|---|---|
 | |
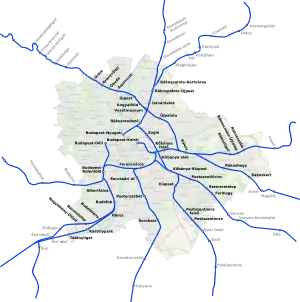 | |
| Overview | |
| Owner | Hungarian State Railways |
| Locale | Budapest metropolitan area, Hungary |
| Transit type | Commuter rail |
| Number of lines | 14 |
| Number of stations | 333 |
| Operation | |
| Operator(s) | Hungarian State Railways |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) |
Services
The HÉV lines are indicated by a H letter followed by a number. H5 terminates at Szentendre, H6 at Ráckeve, H8 at Gödöllő and 9 at Csömör. H7 does not cross the administrative boundary of Budapest. The numbering was introduced in 2011, continuing with the numbering of the existing M4 subway line.
From 15 December 2013, suburban trains departing from the Budapest-Déli Railway Terminal were piloted, and from 14 December 2014 all suburban trains received numbered services.
Trains that stop at every station are designated as S (similar to numerous S-train services), trains making fewer stops are designated as G, and express trains are designated as Z. [2]
Lines
As of 2023, the following services are operated:[3]
| Service | Route | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Batthyány tér – Békásmegyer – Szentendre | 10-20 minutes | |
| Közvágóhíd – Dunaharaszti – Tököl – Ráckeve | 15-60 minutes on weekdays and 30-60 minutes on weekends | |
| Boráros tér – Kvassay híd – Csepel | 6-15 minutes | |
| Örs vezér tere – Cinkota – Gödöllő | 30-60 minutes | |
| Örs vezér tere – Cinkota – Csömör | 30-60 minutes | |
| Budapest Déli – Kelenföld - Biske – Tatabánya – Komárom – Győr | 60 minutes[4] | |
| Budapest Keleti – Kelenföld - Biske – Tatabánya – Komárom – Győr | Two outbound trips per day[4] | |
| Budapest Déli – Kelenföld - Biske – Tatabánya – Oroszlány | 60 minutes[4] | |
| Budapest Nyugati – Kőbánya-Kispest - Cegled – Kecskemét – Kiskunfélegyháza – Szeged | One outbound trip per day[5] | |
| Budapest Nyugati – Kőbánya-Kispest - Ócsa – Dabas – Táborfalva – Lajosmizse (–Kecskemét) | 60 minutes on weekdays and 120 minutes on weekends[6] | |
| Budapest Déli – Kelenföld - Tárnok – Martonvásár – Kápolnásnyék – Székesfehérvár (– Fonyód) | Two round-trips per day[7] | |
| Budapest Déli – Kelenföld - Velence – Székesfehérvár | One round-trip on weekends[7] | |
| Budapest Déli – Kelenföld - Tárnok – Martonvásár – Kápolnásnyék – Székesfehérvár | 30 minutes on weekdays and 60 minutes on weekends[7] | |
| Budapest Déli – Kelenföld - Tárnok – Martonvásár – Kápolnásnyék – Székesfehérvár – Siófok – Fonyód – Keszthely | One outbound trip per day[7] | |
| Kőbánya-Kispest – Kelenföld – Tárnok – Martonvásár (– Kápolnásnyék) | 60 minutes[7] | |
| Budapest Déli – Kelenföld – Százhalombatta (– Pusztaszabolcs – Dombóvár) | 60 minutes[8] | |
| Dombóvár – Sárbogárd – Pusztaszabolcs – Kelenföld – Budapest Déli | Two inbound trips on weekdays[8] | |
| Budapest Déli – Kelenföld – Százhalombatta – Pusztaszabolcs – Dombóvár | One outbound trip except Saturdays[8] | |
| Budapest Déli – Kelenföld – Százhalombatta – Pusztaszabolcs – Dunaújváros | 60 minutes[8] | |
| Budapest Déli – Kelenföld – Százhalombatta – Pusztaszabolcs – Dunaújváros | Rush-hour service on weekdays[8] | |
| Kőbánya-Kispest – Kelenföld – Tárnok – Martonvásár – Kápolnásnyék – Székesfehérvár | 60 minutes[7] | |
| Tárnok – Kelenföld – Budapest Déli | One inbound trip per day[7] | |
| Budapest Nyugati – Kőbánya-Kispest – Úllő – Monor (– Cegléd – Szolnok) | 30 minutes[9] | |
| Szolnok – Cegléd – Monor – Kőbánya-Kispest – Budapest Nyugati | Two inbound trips on weekdays[9] | |
| Budapest Nyugati – Kőbánya-Kispest – Monor – Cegléd – Szolnok | 60 minutes[9] | |
| Budapest Keleti – Rákos – Sülysáp (– Nagykáta – Szolnok) | 30 minutes[10] | |
| Budapest Keleti – Rákos – Sülysáp (– Nagykáta – Szolnok) | Seven round-trips per day[10] | |
| Budapest Keleti – Rákos – Sülysáp – Nagykáta – Szolnok | 60 minutes[10] | |
| Budapest Nyugati – Vác (– Szob) | 30 minutes[11] | |
| Budapest Nyugati – Vác – Szob | Rush-hour service on weekdays[11] | |
| Budapest Nyugati – Vác – Szob | 60 minutes[11] | |
| Budapest Nyugati – Vácrátót – Vác | 60 minutes[12] | |
| Budapest Nyugati – Vácrátót – Vác | Weekday rush-hour service[12] | |
| Budapest Nyugati – Pilisvörösvár – Esztergom | Individual services[13] | |
| Budapest Nyugati – Pilisvörösvár – Esztergom | 30 minutes[13] | |
| Pilisvörösvár – Rákos | 30 minutes[13] | |
| Budapest Keleti – Rákos – Gödöllő (– Aszód – Hatvan – Füzesabony) | 30 minutes[14] | |
| Isaszeg – Budapest Keleti | Three inbound trips on weekdays[14] |
Future developments
Plans exist to build a cross-city tunnel linking Déli station with Nyugati station to provide through services between the two.[15]
References
- Dull Szabolcs (8 February 2016). "Elővárosi vasúttá alakítják át a HÉV-et". index.hu. Retrieved 8 February 2016.
- "Újabb lépés a budapesti S-Bahn felé: viszonylatszámok december 14-től". vonatosszeallitas.hu. Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- "Budapest és környékének vasúti hálózata" (PDF) (in Hungarian). 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- "1 Budapest — Hegyeshalom — Rajka" (PDF) (in Hungarian). MÁV Group. 1 July 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- "140 [Budapest —] Cegléd — Szeged" (PDF) (in Hungarian). MÁV Group. 1 July 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- "142 Budapest — Lajosmizse — Kecskemét" (PDF) (in Hungarian). MÁV Group. 17 March 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- "30a Budapest — Székesfehérvár" (PDF) (in Hungarian). MÁV Group. 16 June 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- "40a Budapest — Pusztaszabolcs" (PDF) (in Hungarian). MÁV Group. 1 June 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- "100a Budapest — Cegléd — Szolnok" (PDF) (in Hungarian). MÁV Group. 1 July 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- "120a Budapest — Újszász — Szolnok" (PDF) (in Hungarian). MÁV Group. 1 July 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- "70 Budapest — Szob [— Štúrovo]" (PDF) (in Hungarian). MÁV Group. 17 March 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- "71 Budapest — Vácrátót — Vác" (PDF) (in Hungarian). MÁV Group. 1 June 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- "2 Budapest — Esztergom" (PDF) (in Hungarian). MÁV Group. 1 June 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- "80a Budapest — Hatvan" (PDF) (in Hungarian). MÁV Group. 1 July 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- "New Transportation Projects Proposed in Budapest: Metro 5, New Vehicles and a Railway Tunnel". Hungary Today. 13 November 2018. Retrieved 30 July 2019.
