Geography of Guinea-Bissau
The geography of Guinea-Bissau is that of low coastal plains bordering the Atlantic Ocean. The country borders Senegal in the north and Guinea in the southeast.
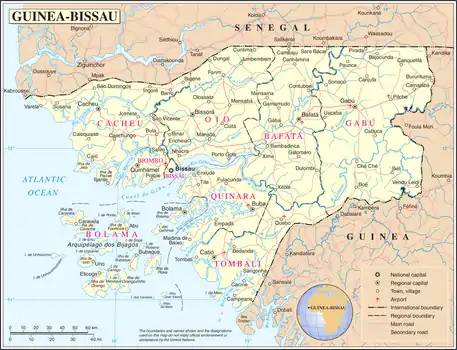
Terrain and ecology
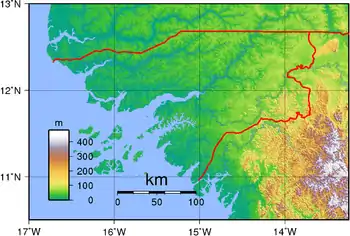
The terrain of Guinea-Bissau is mostly low coastal plain with swamps of Guinean mangroves rising to Guinean forest-savanna mosaic in the east.[1] A recent global remote sensing analysis suggested that there were 1,203km² of tidal flats in Guinea-Bissau, making it the 28th ranked country in terms of tidal flat area. [2]
The lowest point on Guinea-Bissau is at sea level at the Atlantic Ocean.[1] The highest point in Guinea-Bissau is Monte Torin with an elevation of 262 m (860 ft).[1]
Natural resources found in Guinea-Bissau include fish, timber, phosphates, bauxite, clay, granite, limestone and unexploited deposits of petroleum.[1] 10.67% of the land is arable and 235.6 square kilometres are irrigated.[1]
Natural hazards include a hot, dry, dusty harmattan haze that may reduce visibility during the dry season and brush fires.[1] Severe environmental issues include deforestation; soil erosion; overgrazing and overfishing.[1]
Near the Senegal border there have been historic sightings of the painted hunting dog, Lycaon pictus, but that endangered canid may now be extirpated in that locale.[3]
Climate
Guinea-Bissau's climate is tropical. This means it is generally hot and humid. It has a monsoonal-type rainy season (June to November) with southwesterly winds and a dry season (December to May) with northeasterly harmattan winds.[1]
Guinea-Bissau is warm all year around and there is little temperature fluctuation; it averages 26.3 °C (79.3 °F). The average rainfall for the capital city Bissau is 2,024 millimetres (79.7 in) although this is almost entirely accounted for during the rainy season which falls between June and September/October. From December through April, the country receives very little rainfall.
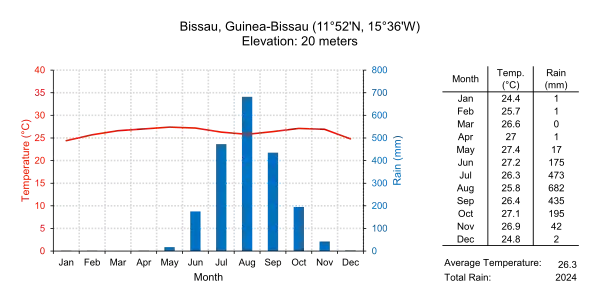
| Climate data for Bissau, Guinea-Bissau (1974-1994) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 36.7 (98.1) |
38.3 (100.9) |
38.9 (102.0) |
41.1 (106.0) |
39.4 (102.9) |
35.6 (96.1) |
33.3 (91.9) |
32.8 (91.0) |
33.9 (93.0) |
34.4 (93.9) |
35.0 (95.0) |
35.6 (96.1) |
41.1 (106.0) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 31.1 (88.0) |
32.8 (91.0) |
33.9 (93.0) |
33.3 (91.9) |
32.8 (91.0) |
31.1 (88.0) |
29.4 (84.9) |
30.0 (86.0) |
30.0 (86.0) |
31.1 (88.0) |
31.7 (89.1) |
30.6 (87.1) |
31.5 (88.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 24.4 (75.9) |
25.6 (78.1) |
26.6 (79.9) |
27.0 (80.6) |
27.5 (81.5) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.1 (79.0) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.4 (79.5) |
27.0 (80.6) |
26.9 (80.4) |
24.8 (76.6) |
26.3 (79.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 17.8 (64.0) |
18.3 (64.9) |
19.4 (66.9) |
20.6 (69.1) |
22.2 (72.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.2 (72.0) |
18.9 (66.0) |
21.1 (70.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 12.2 (54.0) |
13.3 (55.9) |
15.6 (60.1) |
16.7 (62.1) |
17.2 (63.0) |
19.4 (66.9) |
19.4 (66.9) |
19.4 (66.9) |
19.4 (66.9) |
20.0 (68.0) |
15.0 (59.0) |
12.8 (55.0) |
12.2 (54.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 0.5 (0.02) |
0.8 (0.03) |
0.5 (0.02) |
0.8 (0.03) |
17.3 (0.68) |
174.8 (6.88) |
472.5 (18.60) |
682.5 (26.87) |
434.9 (17.12) |
194.8 (7.67) |
41.4 (1.63) |
2.0 (0.08) |
2,022.8 (79.63) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 248 | 226 | 279 | 270 | 248 | 210 | 186 | 155 | 180 | 217 | 240 | 248 | 2,707 |
| Source 1: Sistema de Clasificación Bioclimática Mundial[4] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: World Climate Guides (sunshine only)[5] | |||||||||||||
Bissagos Islands
Information from the CIA World Factbook

_(2).jpg.webp)

- Location
- Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Guinea and Senegal
- Geographic coordinates
- 12°00′N 15°00′W
- Map references
- Area
-
- Total: 36,125 km2
- Land: 28,120 km2
- Water: 8,005 km2
- Area—comparative
- Slightly less than three times the size of Connecticut
- Land boundaries
- Coastline
- 350 km
- Maritime claims
- Territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
- Exclusive economic zone: 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
- Terrain
- Mostly low coastal plain rising to savanna in east
- Elevation extremes
-
- Lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
- Highest point: Unnamed location in the northeast corner of the country 300 m
- Natural resources
- Fish, timber, phosphates, bauxite, unexploited deposits of petroleum
- Land use
-
- Arable land: 10.67%
- Permanent crops: 8.89%
- Other: 80.44% (2012 est.)
- Irrigated land
- 223.6 km2 (2003)
- Total renewable water resources
- 31 km3
- Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural)
-
- Total: 0.18 km3/yr (18%/6%/76%)
- Per capita: 135.7 m3/yr (2005)
- Natural hazards
- Hot, dry, dusty harmattan haze may reduce visibility during dry season; brush fires
- Environment—current issues
- Deforestation; soil erosion; overgrazing; overfishing
- Environment—international agreements
-
- Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
- Signed, but not ratified: None of the selected agreements[1]
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of Guinea-Bissau, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northernmost point – the northern section of the border with Senegal*
- Easternmost point – unnamed location on the border with Guinea immediately south-west of the Guinean village of Sofan, Gabú Region
- Southernmost point – unnamed headland on Ilha Cataque, Tombali Region
- Westernmost point - Cape Roxo at the point where the border with Senegal enters the Atlantic Ocean, Cacheu Region
- *Note: Guinea-Bissau does not have a northernmost point, the border here being formed by a straight horizontal line
See also
Line notes
- U.S. Central Intelligence Agency. World Factbook
- Murray, N.J.; Phinn, S.R.; DeWitt, M.; Ferrari, R.; Johnston, R.; Lyons, M.B.; Clinton, N.; Thau, D.; Fuller, R.A. (2019). "The global distribution and trajectory of tidal flats". Nature. 565 (7738): 222–225. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0805-8. PMID 30568300. S2CID 56481043.
- C. Michael Hogan. 2009. Painted Hunting Dog: Lycaon pictus, GlobalTwitcher.com, ed. N. Stromberg Archived December 9, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- "GUINEA-BISSAU - BISSAU". Centro de Investigaciones Fitosociológicas. Archived from the original on 2007-08-07. Retrieved 2011-10-04.
- "Bissau Climate Guide". Centro de Investigaciones Fitosociológicas. Archived from the original on 2007-08-07. Retrieved 2011-10-04.
References
- C. Michael Hogan. 2009. Painted Hunting Dog: Lycaon pictus, GlobalTwitcher.com, ed. N. Stromberg
- U.S. Central Intelligence Agency.
