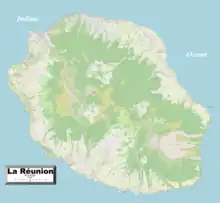
Geography of Réunion
Réunion is an island in Southern Africa, in the Indian Ocean, east of Madagascar. It is an overseas region of France. The total area of the island is 2,512 km², of which 10 km² is water. The island has a coastline of 207 km. The maritime claims of Réunion include an exclusive economic zone of 200 nautical miles, and a territorial sea of 12 nautical miles (22 km). Reunion is geologically situated in the Somali plate.
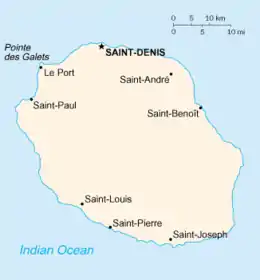 Map of Réunion | |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Indian Ocean |
| Coordinates | 21°06′S 55°36′E |
| Area | 2,512 km2 (970 sq mi) |
| Coastline | 207 km (128.6 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 3,069 m (10069 ft) |
| Highest point | Piton des Neiges |
| Administration | |
France | |
| Overseas department | Réunion |
| Largest settlement | Saint-Denis (pop. 133,700) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 793,000 (2007) |
| Pop. density | 315.68/km2 (817.61/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Creoles, French, African, Tamil, other Indians, Malagasy, Chinese and Vietnamese |
Climate
The climate in Réunion is tropical, but temperature moderates with elevation. The weather is cool and dry from May to November, and hot and rainy from November to April. The terrain is mostly rugged and mountainous, with fertile lowlands along the coast. The lowest point is the Indian Ocean and the highest is Piton des Neiges at 3,069 m.
Natural resources
Réunion's natural resources are fish, arable land and hydropower. In 1993, 60 km² of the land was irrigated. The use of the land in 1993 is described in the table below:
| Use | Percentage of Area |
|---|---|
| arable land | 17 |
| permanent crops | 2 |
| permanent pastures | 5 |
| forests and woodland | 35 |
| other | 41 |
Natural hazards
Local natural hazards include: periodic, devastating cyclones (December to April), and Piton de la Fournaise (2,631 m) on the southeastern coast is an active volcano.