Otenabant
Otenabant (CP-945,598) is a drug which acts as a potent and highly selective CB1 antagonist.[1] It was developed by Pfizer for the treatment of obesity,[2] but development for this application has been discontinued following the problems seen during clinical use of the similar drug rimonabant.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
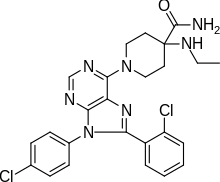
| Formula | C25H25Cl2N7O |
| Molar mass | 510.42 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
See also
References
- Kim MA, Yun H, Kwak H, Kim J, Lee J (2008). "Design, chemical synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel triazolyl analogues of taranabant (MK-0364), a cannabinoid-1 receptor inverse agonist". Tetrahedron. 64 (48): 10802–10809. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2008.09.057.
- Woods SC (November 2007). "The endocannabinoid system: novel pathway for cardiometabolic Risk-factor reduction". Journal of the American Academy of Physician Assistants. Suppl Endocannabinoid (11): 7–10. doi:10.1097/01720610-200711000-00005. PMID 18047036. S2CID 25472128.
- "Pfizer Pharmaceutical News and Media - Pfizer: One of the world's premier biopharmaceutical companies". www.pfizer.com.
| Phytocannabinoids (comparison) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endocannabinoids |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists / neocannabinoids |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric CBRTooltip Cannabinoid receptor ligands | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Endocannabinoid enhancers (inactivation inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Anticannabinoids (antagonists/inverse agonists/antibodies) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transporter (modulators) |
| ||||||||||||
| Enzyme (modulators) |
| ||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.