Naphthoylindoles
Naphthoylindoles are a class of synthetic cannabinoids.[1]
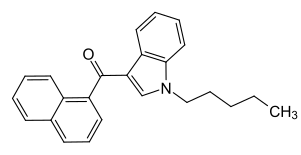
Chemical structure of JWH-018, a simple naphthoylindole
Pharmacology
Behaving similarly in vivo to endocannabinoids such as anandamide or 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), Naphthoylindoles can bind to endocannabinoid receptors in animals, presenting as CB1 and/or CB2 partial/full agonists.
History
They have gained notoriety over the years for illicit usage and distribution in Europe and North America, typically marketed as "herbal incense blends."[2]
References
- Manera C, Tuccinardi T, Martinelli A (2008). "Indoles and related compounds as cannabinoid ligands". Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry. 8 (4): 370–87. doi:10.2174/138955708783955935. PMID 18473928.
- "Synthetic cannabinoids drug profile". emcdda.europa.eu. EMCDDA. Retrieved 21 May 2023.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.