1971 in spaceflight
1971 saw the last three known deaths of cosmonauts of the Soviet space program and the only deaths in space. Their mission was to man humanity's first space station. The experimental bay door failed to separate so the first crew failed to dock and second crew were killed on re-entry. 1971 also saw the launch of the first and only British satellite on top of a British rocket after that success the program was cancelled.
.jpg.webp) | |
| Orbital launches | |
|---|---|
| First | 12 January |
| Last | 29 December |
| Total | 133 |
| Successes | 118 |
| Failures | 15 |
| Catalogued | 120 |
| National firsts | |
| Orbital launch | |
| Rockets | |
| Maiden flights | Soyuz-M Delta M6 Thor LV-2F Burner IIA Titan III(24)B Titan III(33)B Titan IIID |
| Retirements | Black Arrow Delta E1 Delta M Delta M6 Delta N6 Europa Long March 1 R-36OM Soyuz-L Thor LV-2F Burner II Thorad SLV-2G Agena-D Titan III(23)B |
| Crewed flights | |
| Orbital | 4 |
| Total travellers | 12 |
Launches
| Date and time (UTC) | Rocket | Flight number | Launch site | LSP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Payload (⚀ = CubeSat) |
Operator | Orbit | Function | Decay (UTC) | Outcome | ||
| Remarks | |||||||
January | |||||||
| 12 January 09:30[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 25 January[3] | Successful | ||||
| 13 January 20:10 |
|||||||
| NRC | Suborbital | Aeronomy | 13 January | Successful | |||
| 14 January 12:00:00[4] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Radar target | 21 February 1972[3] | Successful | ||||
| 20 January 11:24:00[1] |
|||||||
| Sun-synchronous | Weather | 14 July 2005[3] | Successful | ||||
| 21 January 02:32 |
|||||||
| NRC | Suborbital | Auroral/Ionospheric | 21 January | Successful | |||
| 21 January 08:40[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 2 February[3] | Successful | ||||
| 21 January 18:20 |
|||||||
| NRO | Low Earth | Optical imaging | 9 February | Successful | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | Film return | January | Successful | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | Film return | February | Successful | |||
| 22 January 04:44 |
|||||||
| NRC | Suborbital | Auroral/Ionospheric | 22 January | Successful | |||
| 26 January 00:36:03 |
|||||||
| Intelsat | Geosynchronous | Communications | In orbit | Successful | |||
| 26 January 12:44:33[4] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Calibration | 16 June[3] | Successful | ||||
| 26 January 17:23 |
|||||||
| NRC | Suborbital | Solar/Ionospheric | 26 January | Successful | |||
| 31 January 21:03 |
|||||||
| NASA | Selenocentric | Lunar orbiter | 9 February 21:05 | Successful | |||
| NASA | Selenocentric | Lunar lander | 5 February 09:17 | Successful | |||
| Crewed flight with three astronauts, third crewed Lunar landing | |||||||
February | |||||||
| 3 February 01:41:40 |
|||||||
| NATO | Geosynchronous | Communications | In orbit | Successful | |||
| Final flight of Delta M | |||||||
| 5 February 22:46 |
|||||||
| NRC | Suborbital | Auroral/Ionospheric | 5 February | Successful | |||
| 9 February 18:48:48[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | ASAT target | 25 February (destroyed) | Successful | ||||
| Destroyed by Kosmos 397, debris still in orbit | |||||||
| 16 February 04:00:00 |
|||||||
| ISAS | Low Earth | Technology | In orbit | Successful | |||
| 17 February 03:52:05 |
|||||||
| US Air Force | Low Earth | Weather | In orbit | Successful | |||
| NRL | Low Earth | Calibration | 17 October 1989 | Successful | |||
| NRL | Low Earth | Calibration | 20 September 1989 | Successful | |||
| NRL | Low Earth | Calibration | 7 January 1990 | Successful | |||
| 17 February 20:04:30 |
|||||||
| NRO | Intended: Low Earth | Optical imaging | +18 seconds | Launch failure | |||
| Engine failure due to chain of malfunctions caused by fuel additive loading error | |||||||
| 17 February 21:09[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | ELINT | 6 April 1980 | Successful | ||||
| 18 February 13:59[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 3 March[3] | Successful | ||||
| 20 February 03:33 |
|||||||
| NRC | Suborbital | Auroral/Ionospheric | 20 February | Successful | |||
| 25 February 01:13 |
|||||||
| NASA | Suborbital | Aeronomy | 25 February | Successful | |||
| 25 February 11:11[9] |
|||||||
| Initial: Low Earth Final: Medium Earth |
ASAT test | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Intercepted and destroyed Kosmos 394 | |||||||
| 26 February 05:06[1] |
|||||||
| Deployed: Low Earth Final: Medium Earth |
Test flight | 10 December 1995[3] | Successful | ||||
| 28 February 20:10 |
|||||||
| NRC | Suborbital | Aeronomy | 28 February | Successful | |||
March | |||||||
| 3 March 06:52 |
|||||||
| NRC | Suborbital | Auroral | 3 March | Successful | |||
| 3 March 09:30[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 17 March[3] | Successful | ||||
| 3 March 12:15[6] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Technology | 17 June 1979 | Successful | ||||
| 5 March 08:15:02[4] |
|||||||
| Intended: Low Earth | Calibration | +133 seconds | Launch failure | ||||
| Second stage malfunction, failed to orbit[10] | |||||||
| 5 March[1] | |||||||
| Intended: Low Earth | Optical imaging | 5 March[3] | Launch failure | ||||
| Intended: Low Earth | |||||||
| 13 March 16:15:00 |
|||||||
| NASA | Highly elliptical | Gamma-ray astronomy | 2 October 1974 | Successful | |||
| Only flight of Delta M6 | |||||||
| 18 March 21:45:00[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | ASAT target | 4 April (destroyed) | Successful | ||||
| Destroyed by Kosmos 402, debris still in orbit | |||||||
| 20 March 03:24 |
|||||||
| NRC | Suborbital | Test flight Auroral/Ionospheric | 20 March | Successful | |||
| 21 March 03:45 |
|||||||
| NRO | Molniya | ELINT | In orbit | Successful | |||
| Maiden flight of Titan III(33)B, first Jumpseat satellite | |||||||
| 24 March 20:10 |
|||||||
| AFCRL | Suborbital | Auroral/Aeronomy | 24 March | Successful | |||
| 24 March 21:05 |
|||||||
| NRO | Low Earth | Optical imaging | 12 April | ||||
| 27 March 10:59[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 9 April[3] | Successful | ||||
April | |||||||
| 1 April 02:57:07 |
|||||||
| CSA/NASA | Low Earth | Ionospheric | In orbit | Successful | |||
| Final flight of Delta E1 | |||||||
| 1 April 11:29[9] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Ocean surveillance | 6 May | Successful | ||||
| 2 April 08:20[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 14 April[3] | Successful | ||||
| 4 April 14:27[9] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | ASAT test | 4 April | Successful | ||||
| Intercepted and destroyed Kosmos 400 | |||||||
| 5 April | |||||||
| US Air Force | Suborbital | REV test | 5 April | Successful | |||
| 7 April 07:10[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | ELINT | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| 14 April 08:00[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 24 April[3] | Successful | ||||
| 15 April 09:19 |
|||||||
| CNES | Low Earth | Ionospheric | 28 January 1980 | Successful | |||
| 17 April 11:44:58[1] |
|||||||
| Sun-synchronous | Weather | 10 January 1991[3] | Successful | ||||
| 19 April 01:40:00[13] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Space station | 11 October[3] | Successful | ||||
| First space station, visited by two crews. First crew failed to dock, second killed after departure | |||||||
| 22 April 15:30 |
|||||||
| NRO | Low Earth | Optical imaging | 13 May | Successful | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | Film return | April/May | Successful | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | Film return | May | Successful | |||
| Final flight of Titan III(23)B | |||||||
| 22 April 23:54:06[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth (Salyut 1) | Crewed | 24 April 23:40:00[14] | Spacecraft failure | ||||
| Crewed flight with three cosmonauts. First mission to dock with a space station, aborted after spacecraft failed to achieve hard dock with Salyut 1 | |||||||
| 23 April 11:30[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| 24 April 07:32:29 |
|||||||
| CRS / NASA | Low Earth | Atmospheric | 29 November | Successful | |||
| 24 April 11:15:02[4] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Calibration | 29 December[3] | Successful | ||||
| 28 April 14:35[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Geodesy | In orbit | Successful | ||||
May | |||||||
| 5 May 07:43:01 |
|||||||
| US Air Force | Geosynchronous | Missile defence | In orbit | Successful | |||
| 6 May 06:20[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 18 May[3] | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | 25 May[3] | Successful | |||||
| 7 May 14:20[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| 9 May 01:11:02 |
|||||||
| NASA | Intended: Areocentric | Mars orbiter | 9 May | Launch failure | |||
| Upper stage thrust vectoring failed due to gyroscope malfunction, failed to orbit | |||||||
| 10 May 16:58:42[13] |
|||||||
| Intended: Areocentric Achieved: Low Earth |
Mars orbiter | 12 May[3] | Launch failure | ||||
| Blok D failed to ignite due to programming error; coast phase incorrectly entered in years instead of hours[15] | |||||||
| 18 May 08:00[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 29 May[3] | Successful | ||||
| 19 May 10:20:00[4] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Calibration | 8 November[3] | Successful | ||||
| 19 May 16:22:44[13] |
|||||||
| Areocentric | Mars orbiter | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Heliocentric | Mars lander | 27 November | Spacecraft failure | ||||
| Lander failed to achieve soft landing, instead impacting the planet[15] | |||||||
| 22 May 00:51[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Navigation | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| 27 May 11:59:55[4] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Calibration | 26 November[3] | Successful | ||||
| 28 May 10:30[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 10 June[3] | Successful | ||||
| 28 May 15:26:30[13] |
|||||||
| Areocentric | Mars orbiter | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Heliocentric | Mars lander | 2 December | Spacecraft failure | ||||
| Lander failed 20 seconds after landing[15] | |||||||
| 29 May 03:49[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | ELINT | 15 January 1980 | Successful | ||||
| 30 May 22:23:04 |
|||||||
| NASA | Areocentric | Mars orbiter | In orbit | Successful | |||
| First spacecraft to orbit Mars upon orbital insertion on 14 November. Deactivated on 27 October 1972 | |||||||
June | |||||||
| 4 June 18:10:00[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Magnetospheric | 11 May 2002[3] | Successful | ||||
| Ceased operations on 12 January 1972 | |||||||
| 6 June 04:55:09[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth (Salyut 1) | Crewed | 29 June 23:16:52[16] | Spacecraft failure | ||||
| Crewed flight with three cosmonauts. First mission to occupy a space station, and only mission to occupy Salyut 1. Crew killed by depressurisation of spacecraft during reentry | |||||||
| 7 June 05:26 |
|||||||
| AFCRL | Suborbital | Ionospheric | 7 June | Successful | |||
| 8 June 14:00:05 |
|||||||
| US Air Force/STP | Low Earth | Technology | 31 January 1982 | Successful | |||
| Final flight of Thor LV-2F Burner II | |||||||
| 11 June 10:00[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 23 June[3] | Successful | ||||
| 15 June 18:41 |
|||||||
| NRO | Low Earth | Optical imaging | 6 August | Successful | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | Film return | 20 June[19] | Partial spacecraft failure | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | Film return | 26 June[20] | Successful | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | Film return | 10 July[20] | Spacecraft failure | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | Film return | 15 July[20] | Successful | |||
| Maiden flight of Titan IIID, first Hexagon satellite. SRV-1 recovered from water, SRV-3 lost due to parachute failure | |||||||
| 20 June 22:45 |
|||||||
| US Air Force | Suborbital | Target | 20 June | Successful | |||
| 24 June 07:59[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 6 July[3] | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | 13 July[3] | Successful | |||||
| 25 June | |||||||
| Intended: Low Earth | Optical imaging | 25 June[3] | Launch failure | ||||
| 26 June 23:15:08[6] |
|||||||
| Intended: Highly elliptical | Test flight | +51 seconds | Launch failure | ||||
| Intended: Highly elliptical | Test flight | ||||||
| Loss of roll control, vehicle disintegrated at max Q | |||||||
| 29 June 10:12 |
|||||||
| US Air Force | Suborbital | REV test | 29 June | Successful | |||
July | |||||||
| 8 July 22:58:00 |
|||||||
| NASA | Low Earth | Solar | 15 December 1979 | Successful | |||
| 16 July 01:41:36[1] |
|||||||
| Sun-synchronous | Weather | 27 August 1991[3] | Successful | ||||
| 16 July 10:50 |
|||||||
| NRO | Low Earth | ELINT | 31 August 1978 | Successful | |||
| 20 July 10:00[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 2 August[3] | Successful | ||||
| 21 July 16:00 |
|||||||
| NASA | Suborbital | Test flight | 21 July | Launch failure | |||
| 22 July | |||||||
| Intended: Low Earth | ELINT | 22 July | Launch failure | ||||
| Failed to orbit | |||||||
| 23 July 11:00[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 5 August[3] | Successful | ||||
| 26 July 13:34 |
|||||||
| NASA | Selenocentric | Lunar orbiter | 7 August 20:45:53 | Successful | |||
| NASA | Selenocentric | Lunar lander | 30 July 22:16:29 | Successful | |||
| NASA | Selenocentric | Magnetospheric | 1974 | Successful | |||
| Crewed flight with three astronauts, fourth crewed lunar landing and first use of Lunar Roving Vehicle, subsatellite deployed on 4 August at 20:13 UTC | |||||||
| 28 July 03:29[1] |
|||||||
| Molniya | Communications | 19 July 1977[3] | Successful | ||||
| 30 July 08:29[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 11 August[3] | Successful | ||||
August | |||||||
| 3 August 11:00:00[4] |
|||||||
| Intended: Low Earth | Calibration | +204 seconds | Launch failure | ||||
| Second stage malfunction, failed to orbit[10] | |||||||
| 5 August 10:00[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 18 August[3] | Successful | ||||
| 7 August 00:11 |
|||||||
| US Air Force | Low Earth | Ionospheric | 29 August | Successful | |||
| US Air Force | Low Earth | Ionospheric | 29 August | Successful | |||
| US Air Force | Low Earth | Air density | 31 January 1972 | Successful | |||
| US Air Force | Low Earth | Air density | 19 September | Successful | |||
| US Air Force | Low Earth | Air density | In orbit | Operational | |||
| US Air Force | Low Earth | Technology | 2 November 1979 | Successful | |||
| US Air Force | Low Earth | Technology | 18 March 1979 | Successful | |||
| US Air Force | Low Earth | Technology | 11 June 1972 | Successful | |||
| US Air Force | Low Earth | Air density | 1 September 1981 | Successful | |||
| Two OV1 satellites deployed by independent upper stages, LOADS-2 shared upper stage with OV1-20, other payloads shared with OV1-21. All payloads passive other than OV1s. | |||||||
| 8 August 23:45[9] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | FOBS test | 9 August | Successful | ||||
| Final flight of R-36OM, and FOBS programme | |||||||
| 12 August 05:30[1] |
|||||||
| Deployed: Low Earth Final: Medium Earth |
Test flight | 23 August 1981[3] | Successful | ||||
| Final flight of Soyuz-L | |||||||
| 12 August 15:30 |
|||||||
| NRO | Low Earth | Optical imaging | 3 September | Successful | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | Film return | August | Successful | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | Film return | September | Successful | |||
| Maiden flight of Titan III(24)B | |||||||
| 16 August 18:39:00 |
|||||||
| CNES | Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | |||
| Maiden flight of Scout B-1 | |||||||
| 19 August | |||||||
| Intended: Low Earth | Optical imaging | 19 August | Launch failure | ||||
| Failed to achieve orbit | |||||||
| 27 August 10:54:56[4] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Calibration | 28 January 1972[3] | Successful | ||||
| 28 August 02:22 |
|||||||
| US Air Force | Suborbital | Target | 28 August | Successful | |||
September | |||||||
| 1 September | |||||||
| US Air Force | Suborbital | REV test | 1 September | Successful | |||
| 2 September 13:40:40[13] |
|||||||
| Highly elliptical | Lunar sample return | 11 September | Spacecraft failure | ||||
| Failed to achieve soft landing, instead impacting the moon[22] | |||||||
| 4 September 13:52 |
|||||||
| NASA | Suborbital | Plasma physics | 4 September | Successful | |||
| 5 September 13:44 |
|||||||
| NASA | Suborbital | Plasma physics | 5 September | Successful | |||
| 7 September 01:15[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | ELINT | 4 January 1980 | Successful | ||||
| 10 September 03:37[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | ELINT | 29 March 1980 | Successful | ||||
| 10 September 21:33 |
|||||||
| NRO | Low Earth | Optical imaging | 5 October | ||||
| NRO | Low Earth | ELINT | 3 February 1976 | ||||
| 10 September | |||||||
| Suborbital | Test flight | 10 September | Successful | ||||
| Maiden flight of Dongfeng 5 | |||||||
| 14 September 13:00[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 23 June[3] | Successful | ||||
| 21 September 12:00[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 2 October[3] | Successful | ||||
| 24 September 10:30:00[4] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Radar target | 29 October 1972[3] | Successful | ||||
| 28 September 04:00:00 |
|||||||
| ISAS | Low Earth | Solar Ionospheric | In orbit | Successful | |||
| 28 September 07:40[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 10 October[3] | Successful | ||||
| 28 September 10:00:22[13] |
|||||||
| Selenocentric | Lunar orbiter | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| 29 September 09:45:00 |
|||||||
| NASA | Low Earth | Solar | 9 July 1974 | Successful | |||
| NASA | Low Earth | Tracking target | 19 September 1978 | Successful | |||
| 29 September 11:30[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 12 October[3] | Successful | ||||
October | |||||||
| 7 October 12:30[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 19 October[3] | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | 30 October | Successful | |||||
| 13 October 13:41[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| 14 October 07:51:17 |
|||||||
| US Air Force | Low Earth | Weather | In orbit | Successful | |||
| Maiden flight of Thor LV-2F Burner IIA | |||||||
| 14 October 09:00[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 27 October[3] | Successful | ||||
| 17 October 13:36 |
|||||||
| STP | Low Earth | Technology | In orbit | Successful | |||
| 19 October 12:40:01[4] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Calibration | 19 March 1972[3] | Successful | ||||
| 21 October 11:32:00 |
|||||||
| NOAA | Intended: Low Earth | Weather | 21 October | Launch failure | |||
| Final flight of Delta N6, oxidiser leak led to premature second stage cutoff. Debris reached orbit, however payload did not | |||||||
| 23 October 17:01 |
|||||||
| NRO | Low Earth | Optical imaging | 17 November | Successful | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | Film return | October/November | Successful | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | Film return | November | Successful | |||
| 28 October 04:09:29 |
|||||||
| RAE | Low Earth | Technology | In orbit | Successful | |||
| First and only successful British orbital launch, final flight of Black Arrow and last orbital launch from Woomera | |||||||
November | |||||||
| 2 November 14:25[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 16 November[3] | Successful | ||||
| 3 November 03:09:06 |
|||||||
| US Air Force | Geosynchronous | Communications | In orbit | Successful | |||
| US Air Force | Geosynchronous | Communications | In orbit | ||||
| 5 November 13:00 |
|||||||
| ELDO | Intended: Geosynchronous transfer | Technology | 5 November | Launch failure | |||
| Third stage structural failure. Only flight of Europa II, and final flight of Europa family. Final launch conducted by ELDO, first launch from BEC (later ELA-1 and ELV) | |||||||
| 15 November 05:52:00 |
|||||||
| NASA | Medium Earth | Magnetospheric | 10 January 1992 | Successful | |||
| Final flight of Scout B | |||||||
| 17 November 11:09:48[4] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Calibration | 9 April 1972[3] | Successful | ||||
| 19 November 12:00[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 2 December[3] | Successful | ||||
| 20 November 18:00[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Geodesy | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| 24 November 09:30[1] |
|||||||
| Molniya | Communications | 10 May 1976[3] | Successful | ||||
| 29 November 10:09:56[4] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Calibration | 20 April 1972[3] | Successful | ||||
| 29 November 17:30:00[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | ASAT target | 3 December (destroyed) | Successful | ||||
| Destroyed by Kosmos 462 | |||||||
| 30 November 16:39[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | ELINT | 5 March 1980 | Successful | ||||
December | |||||||
| 2 December 08:25:14[4] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | 7 April 1972[3] | Successful | |||||
| 2 December 17:30:01[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Micrometeoroid detection gamma-ray astronomy | 21 February 1979[3] | Successful | ||||
| Ceased operations on 14 December 1972 | |||||||
| 3 December 13:19[9] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | ASAT test | 4 April 1975 | Successful | ||||
| Intercepted and destroyed Kosmos 459 | |||||||
| 3 December | |||||||
| Intended: Low Earth | Optical imaging | 3 December[3] | Launch failure | ||||
| Intended: Low Earth | |||||||
| 4 December 22:33 |
|||||||
| US Air Force | Intended: Geosynchronous | ELINT | 4 December | Launch failure | |||
| First stage malfunctioned, failed to orbit | |||||||
| 5 December 16:20 |
|||||||
| CNES | Intended: Low Earth | Ionospheric | 5 December | Launch failure | |||
| Second stage malfunction, failed to orbit | |||||||
| 6 December 09:50[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 11 December[3] | Successful | ||||
| 10 December 11:00[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 16 December[3] | Successful | ||||
| 11 December 20:47:01 |
|||||||
| SRC | Low Earth | Ionospheric | 12 December 1978 | Successful | |||
| 14 December 12:13 |
|||||||
| NRO | Low Earth | ELINT | In orbit | Successful | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | ELINT | In orbit | Successful | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | ELINT | In orbit | Successful | |||
| NRO | Low Earth | ELINT | In orbit | Successful | |||
| Final flight of Thorad SLV-2G Agena-D | |||||||
| 15 December 04:31[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Navigation | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| 16 December 09:39[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 18 August[3] | Successful | ||||
| 17 December 10:39:58[4] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Calibration | 18 April 1972[3] | Successful | ||||
| 17 December 13:00[8] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Communications | In orbit | Successful | ||||
| 19 December 22:50[1] |
|||||||
| Molniya | Communications | 13 April 1977[3] | Successful | ||||
| 20 December 01:10:04 |
|||||||
| Intelsat | Geosynchronous | Communications | In orbit | Successful | |||
| 25 December 11:30[9] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Ocean surveillance | 9 February 1972 | Successful | ||||
| BES-5 nuclear reactor ejected, and remains in orbit | |||||||
| 27 December 14:04[1] |
|||||||
| Low Earth | Optical imaging | 6 January 1972[3] | Successful | ||||
| Maiden flight of Soyuz-M | |||||||
| 27 December 19:00:00[8] |
|||||||
| OKB-586/CNES | Medium Earth | Magnetospheric | In orbit | Successful | |||
| 29 December 10:50:01[1] |
|||||||
| Sun-synchronous | Weather | In orbit | Successful | ||||
Launches from the Moon
| Date and time (UTC) | Rocket | Flight number | Launch site | LSP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Payload (⚀ = CubeSat) |
Operator | Orbit | Function | Decay (UTC) | Outcome | ||
| Remarks | |||||||
| 6 February 18:48 |
Fra Mauro (Luna) | ||||||
| NASA | Selenocentric (CSM) | Crewed | 7 February 00:46 | Successful | |||
| Carrying two astronauts back to CSM after lunar landing | |||||||
| 2 August 17:11 |
Hadley-Apennine (Luna) | ||||||
| NASA | Selenocentric (CSM) | Crewed | 3 August 03:04 | Successful | |||
| Carrying two astronauts back to CSM after lunar landing | |||||||
Deep space rendezvous in 1971
| Date (UTC) | Spacecraft | Event | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 February | Apollo 14 | Entered selenocentric orbit | ||
| 5 February 09:18:11 |
Apollo 14 LM | Landing on the Moon | Landed in Fra Mauro region, returned 43 kg of rocks | |
| 29 July | Apollo 15 | Entered selenocentric orbit | ||
| 30 July 22:16:29 |
Apollo 15 LM | Landing on the Moon; first crewed lunar rover | Landed in Hadley Rille region, returned 77 kg of rocks | |
| 11 September | Luna 18 | Impacted the Moon | In Mare Fecunditatis, failed lander | |
| 3 October | Luna 19 | Entered selenocentric orbit | ||
| 14 November | Mariner 9 | Entered areocentric orbit | First orbiter of Mars and of another planet | |
| 27 November | Mars 2 orbiter | Entered areocentric orbit | ||
| Mars 2 lander | First Mars impact | Failed soft lander | ||
| 27 November | Mars 3 orbiter | Entered areocentric orbit | ||
| Mars 3 lander | First soft landing on Mars | |||
EVAs
| Start Date/Time | Duration | End Time | Spacecraft | Crew | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 February 14:42 |
4 hours 48 minutes[25] |
19:30 | Apollo 14 Apollo LM-8 Antares |
Shepard and Mitchell deployed several experiments on the lunar surface near the landing site, such as the Solar Wind Composition Experiment and the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP). The crew also took a contingency sample and planted a U.S. flag at the site.[26] | |
| 6 February 8:11 |
4 hours 34 minutes |
12:45 | Apollo 14 Apollo LM-8 Antares |
Planned as a traverse to Cone Crater, however the astronauts were unable to find the rim of the crater amid rolling terrain. The crew also took panoramic pictures and set up additional experiments. Shepard famously hit a golf ball on the lunar surface, using a six iron golf club head attached to the handle of an excavation tool. | |
| 31 July 00:16 |
33 minutes | 00:49 | Apollo 15 Apollo LM-10 Falcon |
Scott stood on the lander's ascent engine cover to survey the landing site through the vehicle's docking hatch and take panoramic photography. | |
| 31 July 13:13 |
6 hours 32 minutes[27] |
19:45 | Apollo 15 Apollo LM-10 Falcon |
Scott and Irwin visited Elbow Crater near the rim of Hadley Rille using the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), marking the first time humans traveled in a wheeled vehicle on another world. The crew also deployed an ALSEP on their return to the landing site.[28] | |
| 1 August 11:48 |
7 hours 12 minutes |
19:01 | Apollo 15 Apollo LM-10 Falcon |
Scott and Irwin drove the LRV 12.5 miles along the base of the Apennine Mountains, visiting several craters, collecting samples and taking panoramic photography. The crew also took a deep core sample of lunar soil and planted a U.S. flag. | |
| 2 August 08:52 |
4 hours 49 minutes |
13:42 | Apollo 15 Apollo LM-10 Falcon |
Scott and Irwin traveled to Scarp Crater then northwest along the rille, collecting samples. The crew also retrieved the core sample drilled during the previous EVA. | |
| 5 August 15:31 |
39 minutes | 16:10 | Apollo 15 Apollo CSM-112 Endeavour |
First spacewalk in deep space, conducted during the return trip to Earth. Worden retrieved exposed film from the Scientific Instrument Module (SIM) bay of the Service Module, while Irwin stood in the hatch. |
Orbital launch summary
By country
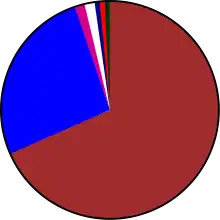 |
| |||||||||||||||
| Orbital launch attempts by country in 1971 | ||||||||||||||||
| Country | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 91 | 82 | 9 | 0 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Last and only successful launch | |
| 35 | 31 | 4 | 0 |
By family
| Family | Country | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atlas | 6 | 4 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Black Arrow | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Diamant | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Europa | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Kosmos (R-12/14) | 34 | 31 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Long March | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Mu | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| N | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| R-7 | 44 | 40 | 4 | 0 | ||
| R-36 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Saturn | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Titan | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Thor | 14 | 12 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Scout | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Universal Rocket | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 | ||
By type
| Rocket | Country | Family | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atlas E/F | Atlas | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Atlas-Agena | Atlas | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Atlas-Centaur | Atlas | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Black Arrow | Black Arrow | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Diamant B | Diamant | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Delta | Delta | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Europa | Europa | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Kosmos-2 | Kosmos | 14 | 12 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Kosmos-3 | Kosmos | 20 | 19 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Long March 1 | Long March | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Molniya | R-7 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Mu-3 | Mu | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| N1 | N | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Proton | Universal Rocket | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| R-36OM | R-36 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Saturn V | Saturn | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Scout B | Scout | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Soyuz | R-7 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Thor-Burner | Thor | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Thorad-Agena | Thor | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Titan IIIB | Titan | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Titan IIIC | Titan | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Titan IIID | Titan | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Tsyklon | R-36 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Voskhod | R-7 | 31 | 27 | 4 | 0 | ||
| Vostok | R-7 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | ||
By configuration
| Rocket | Country | Type | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atlas E/F-OV1-PM | Atlas E/F | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Atlas SLV-3A Agena-D | Atlas-Agena | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Atlas SLV-3C Centaur-D | Atlas-Centaur | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Black Arrow | Black Arrow | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Diamant B | Diamant B | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Delta E1 | Delta | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Delta M | Delta | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Delta M6 | Delta | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Only flight | |
| Delta N | Delta | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Delta N6 | Delta | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Europa II | Europa | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Only flight | |
| Kosmos-2I | Kosmos-2 | 14 | 12 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Kosmos-3M | Kosmos-3 | 20 | 19 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Long March 1 | Long March | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Molniya-M/ML | Molniya | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Mu-3S | Mu-3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| N1 | N1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Proton-K | Proton | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Proton-K/D | Proton | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0 | ||
| R-36OM | R-36O | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Saturn V | Saturn V | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Scout B | Scout B | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Scout B-1 | Scout B | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Soyuz | Soyuz | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Soyuz-L | Soyuz | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Soyuz-M | Soyuz | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Thor LV-2F Burner II | Thor-Burner | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Thor LV-2F Burner IIA | Thor-Burner | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Thorad SLV-2G Agena-D | Thorad-Agena | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Thorad SLV-2H Agena-D | Thorad-Agena | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Titan III(23)B | Titan III | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Final flight | |
| Titan III(24)B | Titan III | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Titan III(33)B | Titan III | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Titan III(23)C | Titan III | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Titan III(23)D | Titan III | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight | |
| Tsyklon-2 | Tsyklon | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Voskhod | Voskhod | 31 | 27 | 4 | 0 | ||
| Vostok-2M | Vostok | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | ||
By launch site
| Site | Country | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cape Kennedy | 10 | 5 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Baikonur | 31 | 28 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Jiuquan | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Kapustin Yar | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Kennedy | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Kagoshima | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Kourou | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Plesetsk | 58 | 53 | 5 | 0 | ||
| San Marco | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Operated by Italy | |
| Vandenberg | 19 | 17 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Wallops | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Woomera | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Final orbital launch | |
By orbit
| Orbital regime | Launches | Achieved | Not Achieved | Accidentally achieved |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Failed to orbit | N/A | N/A | N/A | 12 | |
| Low Earth | 109 | 100 | 9 | 1 | Two to Salyut 1 |
| Medium Earth | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Geosynchronous/transfer | 7 | 5 | 2 | ||
| High Earth | 10 | 9 | 1 | 0 | Including highly elliptical and Molniya orbits and trans-lunar trajectories. |
| Heliocentric | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
References
- McDowell, Jonathan. "R-7". Orbital and Suborbital Launch Database. Archived from the original on 22 June 2008. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- Krebs, Gunter. "Zenit-4M (Rotor, 11F691)". Gunter's Space Page. Archived from the original on 11 April 2021. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- McDowell, Jonathan. "Satellite Catalog". Jonathan's Space Page. Archived from the original on 18 October 2018. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- McDowell, Jonathan. "R-12". Orbital and Suborbital Launch Database. Archived from the original on 19 October 2012. Retrieved 3 June 2012.
- Krebs, Gunter. "Meteor-1". Gunter's Space Page. Archived from the original on 3 June 2012. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- McDowell, Jonathan. "Launch Log". Jonathan's Space Page. Archived from the original on 23 January 2018. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- Krebs, Gunter. "Zenit-2M (Gektor, 11F690)". Gunter's Space Page. Archived from the original on 11 April 2021. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- McDowell, Jonathan. "R-14". Orbital and Suborbital Launch Database. Archived from the original on 12 February 2012. Retrieved 3 June 2012.
- McDowell, Jonathan. "R-36". Orbital and Suborbital Launch Database. Archived from the original on 26 June 2012. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- Wade, Mark. "Kosmos 11K63". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 4 November 2016. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- Krebs, Gunter. "Tselina-D (11F619, Ikar)". Gunter's Space Page. Archived from the original on 10 May 2012. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- Krebs, Gunter. "Tselina-D (11F619, Ikar)". Gunter's Space Page. Archived from the original on 10 May 2012. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- McDowell, Jonathan. "Proton". Orbital and Suborbital Launch Database. Archived from the original on 5 September 2004. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- Anikeev, Alexander. "Spacecraft "Soyuz-10"". Crewed Astronautics: Figures and Facts. Archived from the original on 4 September 2011. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- Wade, Mark. "Mars M-71". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 18 June 2012. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- Anikeev, Alexander. "Spacecraft "Soyuz-11"". Crewed Astronautics: Figures and Facts. Archived from the original on 31 August 2011. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- Krebs, Gunter. "Voskhod (11A57)". Gunter's Space Page. Archived from the original on 24 September 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- The Hexagon Story (PDF), US National Reconnaissance Office, archived from the original (PDF) on 16 September 2012, retrieved 4 June 2012
- The Hexagon Story (PDF), US National Reconnaissance Office, archived from the original (PDF) on 16 September 2012, retrieved 4 June 2012
- Perry, Robert (November 1973), A History of Satellite Reconnaissance (PDF), vol. IIIB, US National Reconnaissance Office, archived from the original (PDF) on 16 September 2012, retrieved 4 June 2012
- Wade, Mark. "Molniya-1". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 16 May 2008. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- Wade, Mark. "Luna Ye-8-5". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 25 February 2002. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- Wade, Mark. "Molniya-2". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 2 June 2012. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- Wade, Mark. "Molniya-2". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 2 June 2012. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- "Apollo 14 Timeline". NASA. Archived from the original on 27 May 2013. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
- "Apollo 14 Surface Operations Overview". Lunar and Planetary Institute. Archived from the original on 5 April 2015. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
- "Apollo 15 Timeline". NASA. Archived from the original on 9 March 2021. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
- "Apollo 15 Surface Operations Overview". Lunar and Planetary Institute. Archived from the original on 28 March 2015. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.