Valoneic acid dilactone
Valoneic acid dilactone is a hydrolysable tannin that can be isolated from the heartwood of Shorea laevifolia[1] and in oaks species like the North American white oak (Quercus alba) and European red oak (Quercus robur).[2]
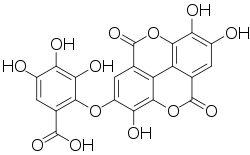 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3,4,5-Trihydroxy-2-[(3,7,8-trihydroxy-5,10-dioxo-5,10-dihydro[1]benzopyrano[5,4,3-cde][1]benzopyran-2-yl)oxy]benzoate | |
| Other names
Valoneic acid bislactone Valoneic acid bilactone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H10O13 | |
| Molar mass | 470.28 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
It shows an inhibitory effect on 5α-reductase,[1] an enzyme involved in steroids metabolism and prostate cancer.
References
- 5A-Reductase inhibitory tannin-related compounds isolated from Shorea laevifolia. Yoshio Hirano, Ryuichiro Kondo and Kokki Sakai, Journal of wood science, Volume 49, Number 4, pp.339-343,doi:10.1007/s10086-002-0481-y
- Analysis of oak tannins by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. Pirjo Mämmelä, Heikki Savolainenb, Lasse Lindroosa, Juhani Kangasd and Terttu Vartiainen, Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 891, Issue 1, 1 September 2000, Pages 75-83, doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00624-5
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.