Luteic acid
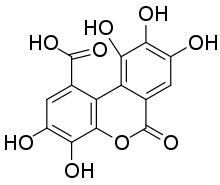
Luteic acid is a natural phenol found in numerous fruits. It is a monolactonized tergalloyl group. Maximilian Nierenstein showed in 1945 that luteic acid was a molecule present in the myrobalanitannin, a tannin found in the fruit of Terminalia chebula and is an intermediary compound in the synthesis of ellagic acid.[1] It can form from hexahydroxydiphenic acid. It is also present in the structure of the tannins alnusiin and bicornin.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3,4,8,9,10-Pentahydroxy-6-oxo-6H-dibenzo[b,d]pyran-1-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Luteolic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H8O9 | |
| Molar mass | 320.21 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Nierenstein, M.; Potter, J. (1945). "The distribution of myrobalanitannin". The Biochemical Journal. 39 (5): 390–392. doi:10.1042/bj0390390. PMC 1258254. PMID 16747927.
- Structures of alnusiin and bicornin, new hydrolyzable tannins having a monolactonized tergalloyl group. Yoshida T, Yazaki K, Memon M.U, Maruyama I, Kurokawa K, Shingu T and Okuda T, Chemical and pharmaceutical bulletin, 1989, volume 37, number 10, pages 2655-2660, INIST:19467830 (abstract)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.