1976 United States Senate election in Pennsylvania
The 1976 United States Senate election in Pennsylvania was held on November 2, 1976. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator and Minority Leader Hugh Scott decided to retire. Republican John Heinz won the open seat.[1]
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
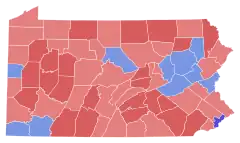 County results Heinz: 50–60% 60–70% Green: 50–60% 70–80% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Pennsylvania |
|---|
 |
|
|
Background
In December 1975, U.S. senator Hugh Scott announced that he would not seek re-election in 1976 at the age of 75 after serving in Congress for 33 years. Scott listed personal reasons and several "well-qualified potential candidates" for the seat among the reasons of his decision to retire. Other reasons, including his support for Richard Nixon and accusations that he had illegally obtained contributions from Gulf Oil were alleged to have contributed to the decision.[2]
Republican primary
Candidates
- C. Homer Brown
- Mary Ellen Foltz
- John Heinz, U.S. Representative from Pittsburgh since 1971[3]
- George Packard, former managing editor of the Philadelphia Bulletin[4]
- Arlen Specter, former District Attorney of Philadelphia[5][6]
- Francis Worley, former State Representative from Adams County
Results
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | H. John Heinz III | 358,715 | 37.73% | |
| Republican | Arlen Specter | 332,513 | 34.98% | |
| Republican | George Packard | 160,379 | 16.87% | |
| Republican | C. Homer Brown | 46,828 | 4.93% | |
| Republican | Mary Ellen Foltz | 29,160 | 3.07% | |
| Republican | Francis Worley | 20,421 | 2.15% | |
| Write-in | 2,665 | 0.28% | ||
| Total votes | 950,681 | 100.00% | ||
Democratic primary
Candidates
- Bill Green, U.S. Representative from Philadelphia[7]
- Jeanette Reibman, State Senator from Easton[5]
Results
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | William J. Green III | 762,733 | 68.71% | |
| Democratic | Jeanette Reibman | 345,264 | 31.10% | |
| Write-in | 2,058 | 0.19% | ||
| Total votes | 1,110,055 | 100.00% | ||
General election
Candidates
- William Green, U.S. Representative from Philadelphia (Democratic)
- John Heinz, U.S. Representative from Pittsburgh (Republican)
- Frank Kinces (Communist)
- Bernard Salera (Labor)
- Frederick W. Stanton (Socialist Workers)
- Andrew J. Watson (Constitution)
Campaign
Heinz was the victor in all but nine counties, defeating opponent William Green, who had a 300,000 vote advantage in his native Philadelphia area. Heinz and Green spent $2.5 million and $900,000, respectively, during the ten-month campaign. Much of the money Heinz spent on his campaign was his own, leading to accusations from Green that he was "buying the seat". Heinz replied to this by claiming that the spending was necessary to overcome the Democratic voter registration advantage.[9]
Results
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | H. John Heinz III | 2,381,891 | 52.39% | ||
| Democratic | William J. Green III | 2,126,977 | 46.79% | ||
| Constitution | Andrew J. Watson | 26,028 | 0.57% | ||
| Socialist Workers | Frederick W. Stanton | 5,484 | 0.12% | ||
| Labor Party | Bernard Salera | 3,637 | 0.08% | ||
| Communist Party | Frank Kinces | 2,097 | 0.05% | ||
| N/A | Other | 239 | 0.00% | N/A | |
| Total votes | 4,546,353 | 100.00% | |||
| Republican hold | Swing | ||||
See also
References
- "Statistics of the Congressional and Presidential Election of November 2, 1976" (PDF). Office of the Clerk of the U.S. House. Retrieved July 9, 2014.
- "Senate Republican leader Hugh Scott won't run in 1976". St. Petersburg Times. December 5, 1975. Retrieved August 14, 2011.
- "Heinz, Henry John III (1938–1991)". Biographical Directory of the U.S. Congress. Retrieved August 13, 2011.
- "Biography of H. John Heinz III". Archives: Biographies. Carnegie Mellon University. Retrieved August 7, 2012.
- "PA US Senate - R Primary". Our Campaigns. Retrieved August 14, 2011.
- "Specter, Arlen (born 1930)". Biographical Directory of the U.S. Congress. Retrieved August 14, 2011.
- "GREEN, William Joseph, (born 1938)". Biographical Directory of the U.S. Congress. Retrieved August 13, 2011.
- "PA US Senate - D Primary". Our Campaigns. Retrieved August 14, 2011.
- "John Heinz". Gettysburg Times. November 3, 1976. Retrieved August 14, 2011.

