Ulanhot
Ulanhot (Mongolian: ᠤᠯᠠᠭᠠᠨᠬᠣᠲᠠ; Chinese: 乌兰浩特), alternatively Ulaγanqota (Red City) in Classical Mongolian, is a county-level city and the administrative center of Hinggan League in the east of the Inner Mongolia, China. Formerly known as Wangin Süm (Wang-un Süme, Wangyehmiao, Wangyemiao, ᠸᠠᠩ ᠤᠨ ᠰᠦᠮᠡ, Chinese: 王爺廟), the city became the first capital of Inner Mongolia, the first autonomous region in China, on 1 May 1947,[3] until the regional capital moved to Zhangjiakou in late December 1949; the regional capital moved again in June 1952 to Hohhot, which remains the capital to this day.[4]
Ulanhot
乌兰浩特市 • ᠤᠯᠠᠭᠠᠨᠬᠣᠲᠠ | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) Ulanhot Airport main terminal building | |
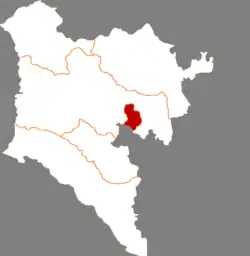 Ulanhot in Hinggan | |
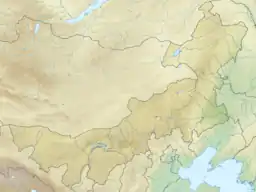 Ulanhot Location of the city center in Inner Mongolia  Ulanhot Ulanhot (China) | |
| Coordinates (Ulanhot municipal government): 46°04′20″N 122°05′36″E | |
| Country | China |
| Autonomous region | Inner Mongolia |
| League | Hinggan |
| Municipal seat | Heping Subdistrict |
| Area | |
| • County-level city | 772.0 km2 (298.1 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 86.10 km2 (33.24 sq mi) |
| Population (2020)[2] | |
| • County-level city | 356,035 |
| • Density | 460/km2 (1,200/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 265,600 |
| • Urban density | 3,100/km2 (8,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 137400 |
| Area code | 0482 |
| Website | www |
| Ulanhot | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 乌兰浩特 | ||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 烏蘭浩特 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||
| Mongolian Cyrillic | Улаан хот | ||||||
| Mongolian script | ᠤᠯᠠᠭᠠᠨᠬᠣᠲᠠ | ||||||
| |||||||
| Former name | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alternative Chinese name | |||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 王爺廟 | ||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 王爷庙 | ||||||
| Literal meaning | prince temple | ||||||
| |||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||
| Mongolian Cyrillic | Вангийн сүм | ||||||
| Mongolian script | ᠸᠠᠩ ᠤᠨ ᠰᠦᠮᠡ | ||||||
| |||||||
The city is connected to Baicheng, Jilin by the Baicheng–Arxan railway (Chinese: 白阿铁路), which runs through the pass south of Ulanhot. China's National Highway 302 runs from Tumen, Jilin to Ulanhot. In the 7918 Network of Highways it will be on the route from Hunchun to Ulanhot . The city is also served by Ulanhot Yilelite Airport (ICAO code ZBUL, IATA code HLH). Routes flown by Air China and Hainan Airlines connect Ulanhot with Beijing Capital International Airport and Hohhot.
Just outside the city is a tomb from the Yuan dynasty and a temple dedicated to Genghis Khan. The temple was constructed in 1940. In the year 2002 it received funds for significant expansion.[5]
Administrative divisions
Ulanhot is divided into 10 subdistricts and 4 towns.
| Name | Simplified Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Mongolian (Hudum Script) | Mongolian (Cyrillic) | Administrative division code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subdistricts | |||||
| Aiguo Subdistrict | 爱国街道 | Àiguó Jiēdào | ᠠᠢ ᠭᠦᠸᠧ ᠵᠡᠭᠡᠯᠢ ᠭᠤᠳᠤᠮᠵᠢ | Ай хве зээл гудамж | 152201001 |
| Heping Subdistrict | 和平街道 | Hépíng Jiēdào | ᠾᠧ ᠫᠢᠩ ᠵᠡᠭᠡᠯᠢ ᠭᠤᠳᠤᠮᠵᠢ | Ге пин зээл гудамж | 152201002 |
| Xing'an Subdistrict | 兴安街道 | Xīng'ān Jiēdào | ᠬᠢᠩᠭᠠᠨ ᠵᠡᠭᠡᠯᠢ ᠭᠤᠳᠤᠮᠵᠢ | Хянган зээл гудамж | 152201003 |
| Shengli Subdistrict | 胜利街道 | Shènglì Jiēdào | ᠱᠧᠩᠯᠢ ᠵᠡᠭᠡᠯᠢ ᠭᠤᠳᠤᠮᠵᠢ | Шенли зээл гудамж | 152201004 |
| Tiexi Subdistrict | 铁西街道 | Tiěxī Jiēdào | ᠲᠡᠮᠦᠷ ᠵᠠᠮ ᠤᠨ ᠪᠠᠷᠠᠭᠤᠨᠳ᠋ᠠᠬᠢ ᠵᠡᠭᠡᠯᠢ ᠭᠤᠳᠤᠮᠵᠢ | Дамар замын баруунтах зээл гудамж | 152201005 |
| Dulin Subdistrict | 都林街道 | Dūlín Jiēdào | ᠳᠡᠭᠦᠯᠢᠨ ᠵᠡᠭᠡᠯᠢ ᠭᠤᠳᠤᠮᠵᠢ | Дүүлэн зээл гудамж | 152201006 |
| Wuyi Subdistrict | 五一街道 | Wǔyī Jiēdào | ᠡᠦ ᠢ ᠵᠡᠭᠡᠯᠢ ᠭᠤᠳᠤᠮᠵᠢ | Үү И зээл гудамж | 152201007 |
| Chengjiao Subdistrict | 城郊街道 | Chéngjiāo Jiēdào | ᠬᠣᠲᠠ ᠶᠢᠨ ᠲᠡᠭᠦᠷᠭᠡᠨ ᠵᠡᠭᠡᠯᠢ ᠭᠤᠳᠤᠮᠵᠢ | Хотын дүүргэн зээл гудамж | 152201008 |
| Xincheng Subdistrict | 新城街道 | Xīnchéng Jiēdào | ᠰᠢᠨᠡ ᠬᠣᠲᠠ ᠵᠡᠭᠡᠯᠢ ᠭᠤᠳᠢᠮᠵᠢ | Шинэ хот зээл гудимж | 152201009 |
| Tianjiao Subdistrict | 天骄街道 | Tiānjiāo Jiēdào | ᠲᠢᠶᠠᠨ ᠵᠢᠶᠣᠤ ᠵᠡᠭᠡᠯᠢ ᠭᠤᠳᠤᠮᠵᠢ | Даяан жяо зээл гудамж | 152201010 |
| Towns | |||||
| Ulan Had Town | 乌兰哈达镇 | Wūlánhādá Zhèn | ᠤᠯᠠᠭᠠᠨᠬᠠᠳᠠ ᠪᠠᠯᠭᠠᠰᠤ | Улаанахта балгас | 152201100 |
| Gegensüm Town | 葛根庙镇 | Gěgēnmiào Zhèn | ᠭᠡᠭᠡᠨᠰᠦ᠋ᠮᠡ ᠪᠠᠯᠭᠠᠰᠤ | Хээнсм балгас | 152201101 |
| Tabin Ortoo Town | 太本站镇 | Tàiběnzhàn Zhèn | ᠲᠠᠪᠢᠨ ᠥᠷᠲᠡᠭᠡ ᠪᠠᠯᠭᠠᠰᠤ | Тавин өртөө балгас | 152201102 |
| Ilalt Town | 义勒力特镇 | Yìlèlìtè Zhèn | ᠢᠯᠠᠯᠲᠠ ᠪᠠᠯᠭᠠᠰᠤ | Ялалт балгас | 152201103 |
Others:
- Hoh Horse Herding Pasture (呼和马场)
- Ulanhot Green Industrial Park (乌兰浩特绿色产业园)
- Hinggan League Economic-Technological Development Area (兴安盟经济技术开发区)
Climate
Ulan Hot has a monsoon-influenced humid continental climate (Köppen Dwa). Winters are long, cold and dry, while summers are very warm. The monthly 24-hour mean temperature ranges from −15.0 °C (5.0 °F) in January to 22.9 °C (73.2 °F) in July, and the annual mean is 5.03 °C (41.1 °F). Over two-thirds of the annual rainfall occurs from May to August.
| Climate data for Ulan Hot (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1971–2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 6.0 (42.8) |
11.7 (53.1) |
23.5 (74.3) |
31.7 (89.1) |
38.3 (100.9) |
40.3 (104.5) |
39.7 (103.5) |
37.1 (98.8) |
32.5 (90.5) |
29.9 (85.8) |
18.9 (66.0) |
7.7 (45.9) |
40.3 (104.5) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −8.1 (17.4) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
5.1 (41.2) |
15.0 (59.0) |
22.7 (72.9) |
27.3 (81.1) |
29.1 (84.4) |
27.5 (81.5) |
22.3 (72.1) |
13.3 (55.9) |
1.1 (34.0) |
−7.1 (19.2) |
12.1 (53.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −14.1 (6.6) |
−9.5 (14.9) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
8.3 (46.9) |
16.2 (61.2) |
21.5 (70.7) |
23.9 (75.0) |
22.0 (71.6) |
15.7 (60.3) |
6.7 (44.1) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
−12.5 (9.5) |
6.0 (42.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −18.6 (−1.5) |
−14.9 (5.2) |
−7.5 (18.5) |
1.6 (34.9) |
9.5 (49.1) |
15.7 (60.3) |
19.0 (66.2) |
16.8 (62.2) |
9.6 (49.3) |
1.1 (34.0) |
−9.0 (15.8) |
−16.7 (1.9) |
0.6 (33.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −33.7 (−28.7) |
−31.2 (−24.2) |
−25.4 (−13.7) |
−13.6 (7.5) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
2.9 (37.2) |
10.4 (50.7) |
6.0 (42.8) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
−17.4 (0.7) |
−26.4 (−15.5) |
−32.9 (−27.2) |
−33.7 (−28.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 1.5 (0.06) |
2.0 (0.08) |
4.2 (0.17) |
17.1 (0.67) |
40.9 (1.61) |
87.5 (3.44) |
134.8 (5.31) |
81.8 (3.22) |
38.8 (1.53) |
13.4 (0.53) |
4.1 (0.16) |
3.6 (0.14) |
429.7 (16.92) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 2.4 | 1.8 | 3.0 | 3.9 | 7.6 | 11.9 | 12.7 | 10.8 | 7.1 | 3.5 | 3.2 | 3.4 | 71.3 |
| Average snowy days | 4.2 | 3.0 | 4.6 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 1.1 | 4.4 | 5.3 | 24.5 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 52 | 43 | 37 | 34 | 40 | 55 | 66 | 66 | 56 | 48 | 50 | 54 | 50 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 202.5 | 216.2 | 266.2 | 261.4 | 271.5 | 252.0 | 244.0 | 255.8 | 249.9 | 230.0 | 184.0 | 177.3 | 2,810.8 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 72 | 73 | 71 | 64 | 58 | 54 | 52 | 59 | 67 | 69 | 66 | 66 | 64 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration[6][7] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China[8] | |||||||||||||
References
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, ed. (2019). China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook 2017. Beijing: China Statistics Press. p. 48. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- Inner Mongolia: Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties
- Wang, Zhanyi (王占义); Shi, Ye (史叶) (2017-07-06). 1947年内蒙古自治政府在兴安盟成立-中国社会科学网. Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. Retrieved 2020-05-12.
- 内蒙古统一的民族区域自治的实现. Xinhua Inner Mongolia. Retrieved 2020-05-12.
- "China Plans New Investment to Expand Genghis Khan Temple". People's Daily. 2002-09-04.
- 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- 乌兰浩特 - 气象数据 -中国天气网 (in Chinese). Weather China. Retrieved 10 October 2023.