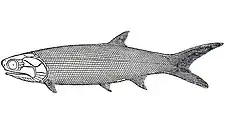
Tanyrhinichthys
Tanyrhinichthys is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish with a lengthened rostrum that lived during the Kasimovian (Missourian) age (Upper Pennsylvanian, Upper Carboniferous) in what is now New Mexico, United States.[1] Fossils were recovered from Tinajas Member of the Atrasado Formation (Kinney Brick Quarry).[1]
| Tanyrhinichthys Temporal range: Kasimovian ~ | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | †Tanyrhinichthys Gottfried, 1987 |
| Binomial name | |
| †Tanyrhinichthys mcallisteri Gottfried, 1987 | |
Ecology and evolution
Tanyrhinichthys had an elongated rostrum equipped with sensory canals, which allowed it to find prey organisms hidden in the substrate, similar to modern sturgeons. It is one of the first actinopterygians to independently evolve an elongate rostrum during the Paleozoic Era, along with Tegeolepis and Phanerorhynchus.[1]
References
- Stack, Jack; Hodnett, John-Paul; Lucas, Spencer G.; Sallan, Lauren (2021). "Tanyrhinichthys mcallisteri, a long-rostrumed Pennsylvanian ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii) and the simultaneous appearance of novel ecomorphologies in Late Palaeozoic fishes". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 191 (2): 347–374. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlaa044.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.