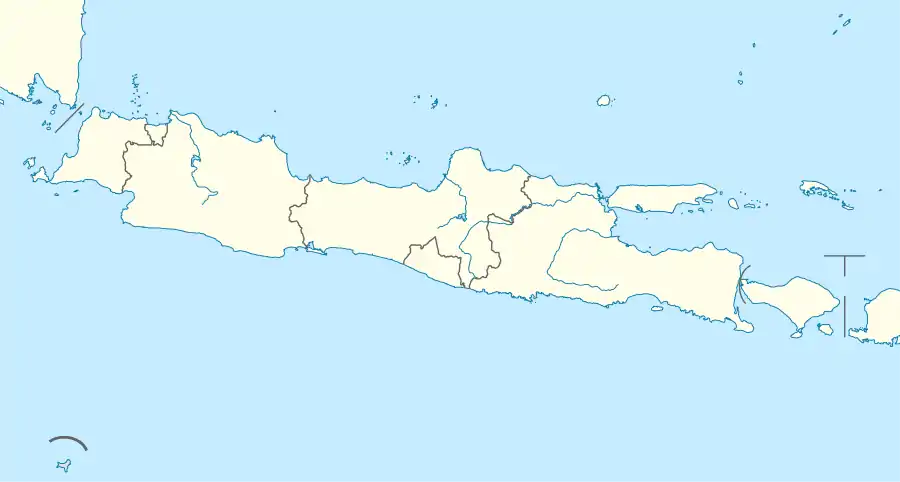
Sukoharjo Regency
Sukoharjo Regency is a regency (Indonesian: kabupaten) in the Central Java province in Indonesia. It covers an area of 493.23 km2 and had a population of 824,238 at the 2010 Census[2] and 907,587 at the 2020 Census;[3] the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 916,627 (comprising 458,483 males and 458,144 females).[1] Its capital is Sukoharjo, about 10 km south from Surakarta. This regency is bordered by the city of Surakarta in the north, Karanganyar Regency in the east, Wonogiri Regency and Yogyakarta in the south as well as Klaten Regency in the west. The regency is part of the metropolitan zone of Surakarta, which is known as Subosukawonosraten.
Sukoharjo Regency
Kabupaten Sukoharjo | |
|---|---|
| Other transcription(s) | |
| • Javanese | ꦑꦧꦸꦥꦠꦺꦤ꧀ꦯꦸꦏꦲꦂꦗ |
 A sign marking the entrance to the Regency | |
 Coat of arms | |
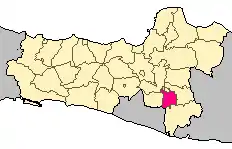 Location within Central Java | |
| Coordinates: 7.6833°S 110.8333°E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Java |
| Province | Central Java |
| Capital | Sukoharjo |
| Government | |
| • Regent | Wardoyo Wijaya |
| • Vice Regent | Purwadi |
| Area | |
| • Total | 493.23 km2 (190.44 sq mi) |
| Population (mid 2022 estimate) | |
| • Total | 916,627 |
| • Density | 1,900/km2 (4,800/sq mi) |
| [1] | |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (IWST) |
| Area code | (+62) 271 |
| Website | sukoharjokab |
Geography
The Solo River (known in Indonesian as Bengawan Solo) "divides" this regency into two parts. The northern part is commonly lowland and wavy, forming the catchment area of Surakarta city, while the southern part is mountainous.
Near the northern border are the suburban areas surrounding Surakarta City such as Grogol, Baki, Gatak and Kartasura, which lie within the metropolitan area of that city. Kartasura is the junction of the Solo-Yogyakarta track with Solo-Semarang.
Sukoharjo Regency is crossed by the Solo-Wonogiri railway, which re-opened in 2004 after being unused for many years. This railway is one of the most "dangerous" ones in Indonesia because it is located beside the main road without any barrier.
Climate
Sukoharjo has a tropical monsoon climate (Am) with moderate to little rainfall from June to October and heavy rainfall from November to May. The following climate data is for the city of Sukoharjo.
| Climate data for Sukoharjo | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 29.9 (85.8) |
30.0 (86.0) |
30.3 (86.5) |
31.3 (88.3) |
30.9 (87.6) |
31.0 (87.8) |
30.6 (87.1) |
31.4 (88.5) |
32.1 (89.8) |
32.5 (90.5) |
31.4 (88.5) |
30.6 (87.1) |
31.0 (87.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.1 (79.0) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.3 (79.3) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.0 (78.8) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.7 (78.3) |
26.6 (79.9) |
27.3 (81.1) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.5 (79.7) |
26.4 (79.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 22.4 (72.3) |
22.4 (72.3) |
22.4 (72.3) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.0 (71.6) |
21.0 (69.8) |
20.2 (68.4) |
20.1 (68.2) |
21.2 (70.2) |
22.1 (71.8) |
22.3 (72.1) |
22.4 (72.3) |
21.7 (71.2) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 316 (12.4) |
317 (12.5) |
297 (11.7) |
209 (8.2) |
142 (5.6) |
74 (2.9) |
49 (1.9) |
40 (1.6) |
45 (1.8) |
111 (4.4) |
201 (7.9) |
264 (10.4) |
2,065 (81.3) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org[4] | |||||||||||||
Administrative districts
Sukoharjo Regency is divided into twelve districts (kecamatan), tabulated below with their areas and their populations at the 2010 Census[2] and the 2020 Census,[3] together with the official estimates as at mid 2022.[1] The table also includes the locations of the district administrative centres, the number of administrative villages in each district (totaling 150 rural desa and 17 urban keluraham), and its post code.
| Name of District (kecamatan) | Area in km2 | Pop'n Census 2010 | Pop'n Census 2020 | Pop'n Estimate mid 2022 | Admin centre | No. of villages | Post code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weru | 45.60 | 49,147 | 54,795 | 55,253 | Ngreco | 13 | 57562 |
| Bulu | 46.40 | 27,813 | 34,104 | 35,028 | Bulu | 12 | 57563 |
| Tawangsari | 39.32 | 47,791 | 52,538 | 52,833 | Lorog | 12 | 57561 |
| Sukoharjo (district) | 46.82 | 88,046 | 97,020 | 97,610 | Joho | 14 (a) | 57511 -57551 |
| Nguter | 57.85 | 42,059 | 52,309 | 53,629 | Nguter | 16 | 57571 |
| Bendosari | 55.72 | 51,940 | 61,563 | 62,818 | Mulur | 14 (b) | 57521 -57528 |
| Polokarto | 66.89 | 73,264 | 83,748 | 84,857 | Mranggen | 17 | 57555 (c) |
| Mojolaban | 38.29 | 86,038 | 96,533 | 97,459 | Bekonang | 15 | 57554 |
| Grogol | 31.33 | 127,886 | 128,193 | 128,352 | Madegondo | 14 | 57552 |
| Baki | 21.40 | 68,386 | 76,422 | 77,096 | Kadilangu | 14 | 57556 |
| Gatak | 19.95 | 46,463 | 54,309 | 55,266 | Blimbing | 14 | 57557 |
| Kartasura | 21.66 | 115,405 | 116,053 | 116,426 | Singopuran | 12 (d) | 57161 -57169 |
| Totals | 493.23 | 824,238 | 907,587 | 916,627 | Sukoharjo | 167 |
Note: (a) all kelurahan. (b) including 1 kelurahan - Jombor. (c) except for the village (desa) of Mranggen, which has a post code of 57513. (d) includes 2 kelurahan - Kartasura and Ngadirejo.
The districts are subdivided into 150 rural desa and 17 urban kelurahan. The administrative center is located in the town of Sukoharjo.
References
- Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2023, Kabupaten Sukoharjo Dalam Angka 2023 (Katalog-BPS 1102001.3311)
- Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021.
- "Climate: Sukoharjo". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved 15 November 2020.