Demak Regency
Demak (Javanese: ꦢꦼꦩꦏ꧀) is a regency located in the Indonesian province of Central Java, on the northern coast of the island. It is bordered by Jepara Regency and the Java Sea to the north, Kudus and Grobogan Regencies to the east, Grobogan and Semarang Regencies to the south, while to the west are Semarang Regency and the city of Semarang, to which the districts of Mranggen and Sayung within Demak Regency are essentially suburban. The regency covers an area of 995.32 km2 (384.30 sq mi) and had a population of 1,055,579 at the 2010 Census[3] and 1,203,956 at the 2020 Census;[4] the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 1,223,217 (comprising 617,297 males and 605,920 females).[2] It was originally the centre of the Demak Sultanate, once a dominant power in the region. Due to its strong relation with the spread of Islam in Java and the Wali Sanga, it is sometimes referred to with the nickname Kota Wali.
Demak Regency
Kabupaten Demak | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Coat of arms | |
| Nickname: Kota Wali (city of the saints) | |
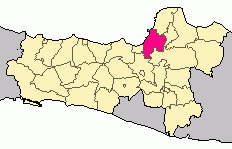 Location of Demak Regency in Central Java | |
| Coordinates: 6°53′41.1″S 110°38′18.5″E | |
| Country | Indonesia |
| Province | Central Java |
| Establishment | 28 March 1503[1] |
| Capital | Demak |
| Government | |
| • Regent | Dr. Hj. Eisti'anah, S.E. |
| • Vice Regent | K.H. Ali Makshun, M.Si |
| Area | |
| • Total | 995.32 km2 (384.30 sq mi) |
| Population (mid 2022 estimate) | |
| • Total | 1,223,217 |
| • Density | 1,200/km2 (3,200/sq mi) |
| [2] | |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (WIB) |
| Area code | +62 291 |
| Website | demakkab.go.id |
History
Precolonial period
The area was a part of the Majapahit Empire during its zenith around the 14th century. The city itself was founded sometime in the late fifteenth century, possibly by a Chinese whose descendant later became the Sultans of Demak. The first Sultan was known as Raden Patah, who was a vassal of Majapahit until 1478.[5] The city was founded as a seaport, next to the now-nonexistent Muria Palaeostrait separating Java from Muria Island (now Mount Muria), although silting has now entirely turned the waterway into land.[6] The Sultanate expanded in the expense of the declining Majapahit and its fragments, conquering the coastal region of Tuban around 1527 and reaching inland areas as far as Malang by 1546.[5] As the capital, the city became an important center for trade and the spread of Islam across the island, and a base of the semi-apocryphal Wali Sanga. Upon the decline of the Sultanate, the region was conquered in turn by the Pajang and Mataram Sultanates.[7] The seaport began to silt sometime in the 17th century, diminishing the region's importance as a seaport.
Dutch East Indies Era
Direct VOC presence in Java started upon their capture of Jayakarta (now Jakarta, then Batavia) on 1619. In the 18th century, a massacre of ethnic Chinese in Batavia triggered a war between VOC and Mataram, resulting in the latter's defeat and cession of the north coast of Java, including Demak, to VOC.[8] Upon the latter's dissolution on late 1799, administration of the area along with the rest of VOC's territory was transferred to the Dutch Government while Mataram was reduced to several fragmented states in the south coast of Java, including Yogyakarta and Surakarta.
As part of Dutch East Indies, Demak was organized with nearby Semarang into Residentie Semarang as the Demak Regency[9] and later into Central Java province upon the independence of Indonesia.
Economy
In 2014, the gross regional domestic product of the regency was Rp 14.078 trillion (US$1.133 billion) or Rp 12.73 million per capita (US$1025),[10]: 369 with the agriculture and manufacturing sectors being the largest contributors. Rice is the most important agricultural produce, with 608,532 tons harvested in 2016 from 69,975 hectares (172,910 acres) of cultivated land.[10]: 212
A 300-hectare (740-acre) industrial park is currently under construction, aimed to boost investment in the regency.[11]
Administrative districts
The Regency comprises fourteen districts (kecamatan), tabulated below with their areas and their populations at the 2010 Census[3] and the 2020 Census,[4] together with the official estimates as at mid 2022.[2] The table also includes the locations of the district administrative centres, the number of administrative villages in each district (totaling 243 rural desa and 6 urban kelurahan - the latter all in Demak District), and its post code.
| Name of District (kecamatan) | Area in km2 | Pop'n Census 2010 | Pop'n Census 2020 | Pop'n Estimate mid 2022 | Admin centre | No. of villages | Post code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mranggen | 77.59 | 157,143 | 175,722 | 177,837 | Mranggen | 19 | 59567 |
| Karangawen | 81.71 | 82,814 | 94,653 | 96,198 | Karangawen | 12 | 59566 |
| Guntur | 64.28 | 72,312 | 86,122 | 88,228 | Guntur | 20 | 59565 |
| Sayung | 85.97 | 96,758 | 105,712 | 106,503 | Sayung | 20 | 59563 |
| Karangtengah | 56.44 | 59,075 | 68,781 | 70,154 | Karangtengah | 17 | 59561 |
| Bonang | 87.06 | 95,796 | 106,712 | 107,915 | Bonang | 21 | 59552 (a) |
| Demak | 63.05 | 98,127 | 110,165 | 111,576 | Demak | 19 | 59511 -59517 |
| Wonosalam | 62.79 | 71,485 | 84,662 | 86,638 | Wonosalam | 21 | 59571 |
| Dempet | 63.94 | 51,092 | 59,689 | 60,921 | Dempet | 16 | 59573 |
| Kebonagung | 44.46 | 37,649 | 41,560 | 41,955 | Kebonagung | 14 | 59583 |
| Gajah | 53.73 | 43,014 | 51,735 | 53,101 | Gajah | 18 | 59581 |
| Karanganyar | 69.87 | 68,182 | 77,535 | 78,723 | Karanganyar | 17 | 59582 |
| Mijen | 55.00 | 50,305 | 58,287 | 59,395 | Mijen | 15 | 59584 |
| Wedung | 129.42 | 71,827 | 82,621 | 84,073 | Wedung | 20 | 59554 |
| Totals | 995.32 | 1,055,579 | 1,203,956 | 1,223,217 | Demak | 249 |
Note: (a) except for desa of Kembangan, which has a post code of 59511.
The first five districts listed above are situated in the southwest part of the Regency (and thus adjacent to Semarang City), with an area of 365.99 km2 and 538,920 inhabitants in mid 2022. The remaining nine districts are situated further away from Semarang, with an area of 629.33 km2 and 684,297 inhabitants in mid 2022.[2]
See also
References
- Almanaf, Rival (29 March 2017). "Peringati Hari Jadi, Bupati Ajak Seluruh Elemen Laksanakan Lima Program Unggulan Demak" (in Indonesian). Tribunnews Jateng. Retrieved 18 August 2017.
- Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2023, Kabupaten Demak Dalam Angka 2023 (Katalog-BPS 1102001.3321)
- Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021.
- Ricklefs, M.C. (2008). A History of Modern Indonesia since C.1200. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 38–39.
- Sunarto (2006). "Geomorphological Development of the Muria Palaeostrait in Relation to the Morphodynamics of the Wulan Delta, Central Java". Indonesian Journal of Geography.
- Soekmono, R. (1981). Pengantar sejarah kebudayaan Indonesia 3 (in Indonesian) (Edisi 3. ed.). Yogyakarta: Penerbit Kanisius. ISBN 9789794132913.
- Setiono, Benny G. (2008). Tionghoa Dalam Pusaran Politik (in Indonesian). Jakarta: TransMedia. p. 161. ISBN 9789797990527. Retrieved 18 August 2017.
- Cribb, Robert. "Administrative divisions in Central Java, 1931". Digital Atlas of Indonesian History. Retrieved 18 August 2017.
- "Demak in Figures 2017" (PDF). BPS Kabupaten Demak (in Indonesian). Statistics Indonesia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 August 2017. Retrieved 18 August 2017.
- Oktaviane, Dwi (24 July 2017). "Demak bangun kawasan industri, siap layani investor" (in Indonesian). Tempo. Retrieved 18 August 2017.
