Portal:Liquor
|
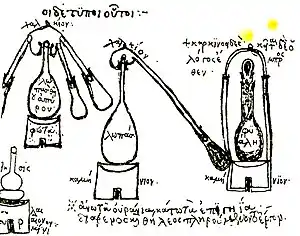
Distilled beverages | Baijiu | Brandies | Fruit brandies | Distilled ciders | Drink distillers | Fermented teas | Fortified wine | Gins | Horilkas | Liqueurs | Neutral grain spirits | Pisco | Rice drinks | Rums | Tequila | Vodkas | Whisky/Whiskey Introduction.svg.png.webp) A cocktail glass  Swan necked copper pot stills in the Glenfiddich distillery Liquor (/ˈlɪkər/ LIK-ər) is an alcoholic drink produced by the distillation of grains, fruits, vegetables, or sugar that have already gone through alcoholic fermentation. Other terms for liquor include: spirit, distilled beverage, spirituous liquor or hard liquor. The distillation process concentrates the liquid to increase its alcohol by volume. As liquors contain significantly more alcohol (ethanol) than other alcoholic drinks, they are considered "harder." In North America, the term hard liquor is sometimes used to distinguish distilled alcoholic drinks from non-distilled ones, whereas the term spirits is more commonly used in the UK. Some examples of liquors include vodka, rum, gin, and tequila. Liquors are often aged in barrels, such as for the production of brandy and whiskey, or are infused with flavorings to form flavored liquors, such as absinthe. While the word liquor ordinarily refers to distilled alcoholic spirits rather than beverages produced by fermentation alone, it can sometimes be used more broadly to refer to any alcoholic beverage (or even non-alcoholic products of distillation or various other liquids). (Full article...) Selected article -Gin (/dʒɪn/) is a distilled alcoholic drink that derives its flavour from juniper berries and other botanical ingredients. Gin originated as a medicinal liquor made by monks and alchemists across Europe. The modern gin was then modified in Flanders and the Netherlands, to provide aqua vita from distillates of grapes and grains. It then became an object of commerce in the spirits industry. Gin became popular in England after the introduction of jenever, a Dutch and Belgian liquor that was originally a medicine. Although this development had been taking place since the early 17th century, gin became widespread after the 1688 Glorious Revolution led by William of Orange and subsequent import restrictions on French brandy. Gin subsequently emerged as the national alcoholic drink of England. Gin today is produced in different ways from a wide range of herbal ingredients, giving rise to a number of distinct styles and brands. After juniper, gin tends to be flavoured with herbs, spices, floral or fruit flavours, or often a combination. It is commonly consumed mixed with tonic water in a gin and tonic. Gin is also often used as a base spirit to produce flavoured, gin-based liqueurs, for example sloe gin, traditionally produced by the addition of fruit, flavourings and sugar. (Full article...)Selected biography -Eva Ekeblad (née De la Gardie; 10 July 1724 – 15 May 1786) was a Swedish countess, salon hostess, agronomist, and scientist. She was widely known for discovering a method in 1746 to make alcohol and flour from potatoes, allowing greater use of scarce grains for food production, significantly reducing Sweden's incidence of famine. Ekeblad was the first female member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences (1748). (Full article...)General articles -Did you know -
|
.png.webp)
.jpg.webp)





















.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)











.svg.png.webp)



.jpg.webp)



.jpg.webp)












.jpg.webp)






