Philippine Senate elections
Elections to the Senate of the Philippines are done via plurality-at-large voting; a voter can vote for up to twelve candidates, with the twelve candidates with the highest number of votes being elected. The 24-member Senate uses staggered elections, with only one-half of its members up for election at any given time, except for special elections, which are always held concurrently with regularly scheduled elections.[1]

Manner of choosing candidates
With the advent of the nominal multi-party system In 1987, political parties have not been able to muster enough candidates to fill their 12-person slate. This means they have to join coalitions or alliances in order to present a full slate. If a slate is still not complete, "guest candidates" may be invited, even from rival slates. A guest candidate may not be compelled to join the campaign rallies of the slate that invited him/her. A party may even not include their entire ticket to a coalition slate, or assign their candidates to competing slates. A candidate may defect from one slate to another or be unaffiliated with any slate while the campaign is ongoing. The Commission on Elections uses the names of the political parties on the ballot.
Once elected, the parties involved in the different slates may form alliances with one another totally different from the alliances prior to the election.
In Third Republic elections under the nominal two-party system, the Liberal Party and the Nacionalista Party often presented complete 8-person tickets; a party may even exceed the 8-person slate due to perceived popularity. The first instance of having guest candidates was in 1955, when the opposition Liberals adopted Claro M. Recto of the Nacionalista Party, who had also opposed the presidency of Ramon Magsaysay. Parties having guest candidates was seen as a weakness of finding candidates within their ranks.[2]
Manner of election
1916 to 1935
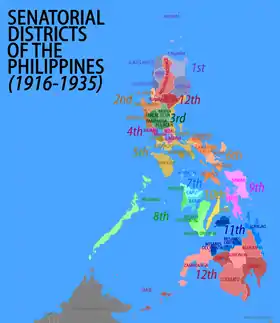
From 1916 to 1934, the country was divided into 12 senatorial districts. Eleven of these districts elected two senators each. In 1916, each district elected two senators (plurality-at-large): one was to serve a six-year term, the other a three-year term. On each election thereafter, one seat per district was up (first past the post). The senators from the 12th district were appointed by the American governor-general for no fixed term.[3]
In 1935, the electorate approved in a plebiscite a new constitution that abolished the Senate and instituted a unicameral National Assembly of the Philippines. The members of the Constitutional Convention originally wanted bicameralism but could not agree on how the senators shall be elected: via the senatorial districts or being nationally elected.[4]
1941 to 1949
The electorate In 1940 approved in a plebiscite amendments to the constitution that restored the bicameral Congress of the Philippines, including the Senate. Elections for the Senate were held on every second Monday of November of every odd-numbered year; however, the old senatorial districts were not used anymore; instead, the 24-member Senate was to be elected on a nationwide at-large basis.[4] As the first election in the new setup, the voters in the 1941 election voted for 24 senators. However, they were also given the option of writing the party's name on the ballot, wherein all of the candidates of the party would receive votes. With the 24 candidates with the most votes winning in the election, the ruling Nacionalista Party won all 24 seats in a landslide victory. The winners included Rafael Martinez, who replaced Norberto Romualdez, who died the day before the election; Martinez won because of voters who had selected the party, rather than specifying a particular candidate.[5]
Due to World War II, Congress was not able to convene until June 1945. President Sergio Osmeña called for special sessions to convene the 1st Congress of the Commonwealth of the Philippines until elections could be organized. Originally, to observe the staggered terms, the eight candidates with the most votes were to serve for eight years, the next eight for four years, and still the next eight for two years. However, several members had died and others were disqualified because they were charged with collaboration with the Japanese, so the Senate conducted a lottery to determine which senators would serve until 1946 and which would serve until 1947.[6] In the 1946 election, voters elected 16 senators; the first eight candidates with the highest number of votes were to serve until 1951, the next eight were to serve until 1949.[3]
1951 to 1971

Electoral reform enacted in 1951 eliminated block voting, which had given voters the option of writing the party's name on the ballot. In a 1951 election, voters voted for eight senators for the first time and each voter had to write at most eight names for senator (writing the party's name would result in a spoiled vote). Noting that after the elimination of block voting, many people voted for a split ticket, political scientist David Wurfel has remarked that "The electoral reform of 1951 was thus one of the most important institutional changes in the postwar Philippines, making the life of the opposition easier."[5]
On September 23, 1972, President Ferdinand Marcos declared martial law and assumed legislative powers. In a 1973 plebiscite, the electorate approved a new constitution that abolished Congress and replaced it with a unicameral National Assembly, which would ultimately be the Batasang Pambansa (parliament).[3]
1987 to present

Marcos was overthrown as a result of the 1986 People Power Revolution. The new president, Corazon Aquino, appointed a Constitutional Commission to write a new constitution. The electorate approved the constitution in 1987, restoring the bicameral Congress. Instead of electing 8 senators every two years, the new constitution provided that 12 senators would be elected every three years. As part of the transitory provisions, the voters elected 24 senators in the 1987 election, to serve until 1992. In the 1992 election, the voters still voted for 24 candidates, but the first 12 candidates with the most votes were to serve until 1998, while the next 12 were to serve only until 1995. Thereafter, 12 candidates are elected every second Monday of May every third year since 1995.[7]
Summary
| Elections | Elected | Seats per district | Districts | Total seats |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1916 | 22 | 2 | 11 | 24 |
| 1919 | 11 | 1 | 11 | 24 |
| 1922 | 11 | 1 | 12 | 24 |
| 1925 | 11 | 1 | 12 | 24 |
| 1928 | 11 | 1 | 12 | 24 |
| 1931 | 11 | 1 | 12 | 24 |
| 1934 | 11 | 1 | 12 | 24 |
| Senate abolished from 1935 to 1941. Senators elected in 1941 will not serve until 1945. | ||||
| 1941 | 24[lower-alpha 1] | 24 | 1 | 24 |
| 1946 | 16[lower-alpha 2] | 16 | 1 | 24 |
| 1947 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 24 |
| 1949 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 24 |
| 1951 | 8+1 special[lower-alpha 3] | 9 | 1 | 24 |
| 1953 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 24 |
| 1955 | 8+1 special[lower-alpha 4] | 9 | 1 | 24 |
| 1957 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 24 |
| 1959 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 24 |
| 1961 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 24 |
| 1963 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 24 |
| 1965 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 24 |
| 1967 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 24 |
| 1969 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 24 |
| 1971 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 24 |
| Senate abolished from 1972 to 1987. | ||||
| 1987 | 24 | 24 | 1 | 24 |
| 1992 | 24[lower-alpha 5] | 24 | 1 | 24 |
| 1995 | 12 | 12 | 1 | 24 |
| 1998 | 12 | 12 | 1 | 24 |
| 2001 | 12+1 special[lower-alpha 6] | 13 | 1 | 24 |
| 2004 | 12 | 12 | 1 | 24 |
| 2007 | 12 | 12 | 1 | 24 |
| 2010 | 12 | 12 | 1 | 24 |
| 2013 | 12 | 12 | 1 | 24 |
| 2016 | 12 | 12 | 1 | 24 |
| 2019 | 12 | 12 | 1 | 24 |
| 2022 | 12 | 12 | 1 | 24 |
- Out of the 24 senators-elect, the first eight candidates with the highest number of votes will serve for six years, the next eight for four years, and the next eight for two years. However, this was not followed due to the intervention of World War II. The senators in 1945 drew lots on who would be serving until 1946, and until 1947.
- Out of the 16 senators-elect, the first eight candidates with the highest number of votes will serve for six years, and the next eight for four years.
- A special election for the seat vacated by Fernando Lopez who was elected vice president in 1949 was held.
- A special election for the seat vacated by Carlos P. Garcia who was elected vice president in 1953 was held.
- Out of the 24 senators-elect, the first twelve candidates with the highest number of votes will serve for six years, and the next twelve for three years.
- Teofisto Guingona, Jr. was appointed vice president on 2001; the thirteenth-placed candidate in the election will serve for Guingona's unexpired term of three years.[8]
List of results
Senatorial districts era
| Election | Nacionalista | Progresista | Democrata | Collectivista | Pro- Independencia | Consolidato | Independents | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1916 | 22 | 1 | 1 | 24 | ||||
| 1919 | 21 | 1 | 2 | 24 | ||||
| 1922 | 12 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 24 | |||
| 1925 | 5 | 8 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 24 | ||
| 1928 | 24 | 0 | 3 | 24 | ||||
| 1931 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 12 | ||||
| 1934 | 6 | 17 | 1 | 24 |
At-large era
In this table, the "administration" ticket is the ticket supported by the sitting president. In 1992, Corazon Aquino who was nominally supporting the LDP, supported the presidential candidacy of Fidel V. Ramos of Lakas, making the "administration ticket" ambiguous.
| Election | Seats won (Party/coalition totals)[9] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Administration ticket | Primary opposition ticket | Others | |
| 1941 | 24 Nacionalistas | ||
| 1946 | 7 Nacionalistas | 8 Nacionalistas (Liberal wing) | 1 Popular Front |
| 1947 | 6 Liberals | 2 Nacionalistas | |
| 1949 | 8 Liberals | ||
| 1951 | 0 Liberals | 9 Nacionalistas | |
| 1953 | 0 Liberals | 5 Nacionalistas | 2 Democrats 1 Citizens' |
| 1955 | 9 Nacionalistas | 0 Liberals | |
| 1957 | 6 Nacionalistas | 2 Liberals | |
| 1959 | 5 Nacionalistas | 2 Liberals | 1 NCP |
| 1961 | 2 Nacionalistas | 4 Liberals | 2 Progressives |
| 1963 | 4 Liberals | 4 Nacionalistas | |
| 1965 | 2 Liberals | 5 Nacionalistas | 1 NCP |
| 1967 | 6 Nacionalistas | 1 Liberal | 1 Independent |
| 1969 | 6 Nacionalistas | 2 Liberals | |
| 1971 | 2 Nacionalistas | 6 Liberals | |
| 1987 | 22 LABAN | 2 GAD | |
| 1992 | 16 LDP | 5 NPC | 2 Lakas 1 Liberal/PDP-Laban |
| 1995 | 9 Lakas-Laban | 3 NPC | |
| 1998 | 5 Lakas | 7 LAMMP | |
| 2001 | 8 PPC | 4 Puwersa ng Masa | 1 Independent |
| 2004 | 7 K-4 | 5 KNP | |
| 2007 | 2 Team Unity | 8 GO | 2 Independents |
| 2010 | 2 Lakas-Kampi | 3 Liberals | 2 Nacionalistas 2 PMP 1 PRP 1 NPC 1 Independent |
| 2013 | 9 Team PNoy | 3 UNA | |
| 2016 | 7 KDM | 4 PGP | 1 UNA |
| 2019 | 9 HNP | 0 Otso Diretso | 1 Independent 1 NPC 1 UNA |
| 2022 | 1 TNP | 1 TRoPa | 4 UniTeam 4 shared candidates 1 Lacson–Sotto slate 1 Independent |
Top-notcher
Since the at-large era, a high-scoring winner can be seen as a strong contender for a future presidential or vice-presidential bid.[1]
Senate composition
These are at the start of each Congress. A senator may change parties or leave office mid-term.
| Election | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1941 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1946 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1947 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1949 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1951 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1953 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1955 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1957 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1959 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1961 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1963 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1965 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1967 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1969 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1971 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1987 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1992 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1995 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1998 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2001 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2004 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2022 |
Latest elections
2022
- Guest candidate of UniTeam Alliance
- Guest candidate of the Lacson–Sotto slate
- Guest candidate of the MP3 Alliance
- Guest candidate of Tuloy na Pagbabago
- Guest candidate of Team Robredo–Pangilinan
- Guest candidate of Labor and Ecology Advocates for Democracy
- Withdrew
- Guest candidate of Aksyon Demokratiko
2019
| # | Candidate | Coalition | Party | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cynthia Villar | HNP | Nacionalista | 25,283,727 | 53.46% | ||
| 2. | Grace Poe | Independent | 22,029,788 | 46.58% | |||
| 3. | Bong Go | HNP | PDP–Laban | 20,657,702 | 42.35% | ||
| 4. | Pia Cayetano | HNP | Nacionalista | 19,789,019 | 41.84% | ||
| 5. | Ronald dela Rosa | HNP | PDP–Laban | 19,004,225 | 40.18% | ||
| 6. | Sonny Angara | HNP | LDP | 18,161,862 | 38.40% | ||
| 7. | Lito Lapid | NPC | 16,965,464 | 35.87% | |||
| 8. | Imee Marcos | HNP | Nacionalista | 15,882,628 | 33.58% | ||
| 9. | Francis Tolentino | HNP | PDP–Laban | 15,510,026 | 32.79% | ||
| 10. | Koko Pimentel | HNP | PDP–Laban | 14,668,665 | 31.01% | ||
| 11. | Bong Revilla | HNP | Lakas | 14,624,445 | 30.92% | ||
| 12. | Nancy Binay | UNA | UNA | 14,504,936 | 30.67% | ||
| 13. | JV Ejercito | HNP | NPC | 14,313,727 | 30.26% | ||
| 14. | Bam Aquino | Otso Diretso | Liberal | 14,144,923 | 29.91% | ||
| 15. | Jinggoy Estrada | HNP | PMP | 11,359,305 | 24.02% | ||
| 16. | Mar Roxas | Otso Diretso | Liberal | 9,843,288 | 20.81% | ||
| 17. | Serge Osmeña | Independent | 9,455,202 | 19.99% | |||
| 18. | Willie Ong | Lakas | 7,616,265 | 16.12% | |||
| 19. | Dong Mangudadatu | HNP | PDP–Laban | 7,499,604 | 15.86% | ||
| 20. | Jiggy Manicad | HNP | Independent | 6,896,889 | 14.58% | ||
| 21. | Chel Diokno | Otso Diretso | Liberal | 6,342,939 | 13.41% | ||
| 22. | Juan Ponce Enrile | PMP | 5,319,298 | 11.25% | |||
| 23. | Gary Alejano | Otso Diretso | Liberal | 4,726,652 | 9.99% | ||
| 24. | Neri Colmenares | Labor Win | Makabayan | 4,683,942 | 9.90% | ||
| 25. | Samira Gutoc | Otso Diretso | Liberal | 4,345,252 | 9.19% | ||
| 26. | Romulo Macalintal | Otso Diretso | Independent | 4,007,339 | 8.47% | ||
| 27. | Erin Tañada | Otso Diretso | Liberal | 3,870,529 | 8.18% | ||
| 28. | Larry Gadon | KDP | KBL | 3,487,780 | 7.37% | ||
| 29. | Florin Hilbay | Otso Diretso | Aksyon | 2,757,879 | 5.83% | ||
| 30. | Freddie Aguilar | Independent | 2,580,230 | 5.46% | |||
| 31. | Glenn Chong | KDP | KDP | 2,534,335 | 5.36% | ||
| 32. | Rafael Alunan III | Bagumbayan | 2,059,359 | 4.35% | |||
| 33. | Faisal Mangondato | KKK | Independent | 1,988,719 | 4.20% | ||
| 34. | Agnes Escudero | KKK | Independent | 1,545,985 | 3.27% | ||
| 35. | Diosdado Padilla | PFP | 1,095,337 | 2.32% | |||
| 36. | Ernesto Arellano | Independent | 937,713 | 2.30% | |||
| 37. | Allan Montaño | Labor Win | Independent | 923,419 | 2.25% | ||
| 38. | Leody de Guzman | Labor Win | PLM | 893,506 | 2.17% | ||
| 39. | Melchor Chavez | WPP | WPP | 764,473 | 2.06% | ||
| 40. | Vanjie Abejo | KKK | Independent | 656,006 | 2.00% | ||
| 41. | Edmundo Casiño | KDP | KDP | 580,853 | 1.97% | ||
| 42. | Abner Afuang | WPP | WPP | 559,001 | 1.92% | ||
| 43. | Shariff Ibrahim Albani | WPP | WPP | 496,855 | 1.87% | ||
| 44. | Dan Roleda | UNA | UNA | 469,840 | 1.80% | ||
| 45. | Conrado Generoso | KKK | Independent | 449,785 | 1.75% | ||
| 46. | Nur-Ana Sahidulla | KDP | KDP | 444,096 | 1.68% | ||
| 47. | Abraham Jangao | Independent | 434,697 | 1.65% | |||
| 48. | Marcelino Arias | WPP | WPP | 404,513 | 1.59% | ||
| 49. | Richard Alfajora | KKK | Independent | 404,513 | 1.57% | ||
| 50. | Sonny Matula | Labor Win, WPP | WPP | 400,339 | 1.50% | ||
| 51. | Elmer Francisco | PFP | 395,427 | 1.45% | |||
| 52. | Joan Sheelah Nalliw | KKK | Independent | 390,165 | 1.38% | ||
| 53. | Gerald Arcega | WPP | WPP | 383,749 | 1.30% | ||
| 54. | Butch Valdes | KDP | KDP | 367,851 | 1.20% | ||
| 55. | Jesus Caceres | KKK | Independent | 358,472 | 0.90% | ||
| 56. | Bernard Austria | PDSP | 347,013 | 0.70% | |||
| 57. | Jonathan Baldevarona | Independent | 310,411 | 0.67% | |||
| 58. | Emily Mallillin | KKK | Independent | 304,215 | 0.64% | ||
| 59. | Charlie Gaddi | KKK | Independent | 286,361 | 0.50% | ||
| 60. | RJ Javellana | KDP | KDP | 258,538 | 0.47% | ||
| 61. | Junbert Guigayuma | WPP | WPP | 240,306 | 0.40% | ||
| 62. | Luther Meniano | WPP | WPP | 159,774 | 0.30% | ||
| Total turnout | 47,296,442 | 74.31% | |||||
| Total votes | 362,179,156 | N/A | |||||
| Registered voters | 63,643,263 | 100.0% | |||||
| Source: COMELEC | |||||||
2016
| # | Candidate | Coalition | Party | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Franklin Drilon | KDM | Liberal | 18,607,391 | 41.52% | ||
| 2. | Joel Villanueva | KDM, PRP | Liberal | 18,459,222 | 41.39% | ||
| 3. | Tito Sotto | PGP, UNA | NPC | 17,200,371 | 38.51% | ||
| 4. | Panfilo Lacson | KDM, UNA | Independent | 16,926,152 | 37.82% | ||
| 5. | Dick Gordon | PGP, UNA | Independent | 16,719,322 | 37.28% | ||
| 6. | Migz Zubiri | PGP, UNA | Independent | 16,119,165 | 35.87% | ||
| 7. | Manny Pacquiao | UNA, PRP | UNA | 16,050,546 | 35.67% | ||
| 8. | Francis Pangilinan | KDM | Liberal | 15,955,949 | 35.56% | ||
| 9. | Risa Hontiveros | KDM | Akbayan | 15,915,213 | 35.53% | ||
| 10. | Win Gatchalian | PGP, WPP | NPC | 14,953,768 | 33.58% | ||
| 11. | Ralph Recto | KDM, PGP, PRP | Liberal | 14,271,868 | 31.79% | ||
| 12. | Leila de Lima | KDM | Liberal | 14,144,070 | 31.55% | ||
| 13. | Francis Tolentino | PRP | Independent | 12,811,098 | 28.64% | ||
| 14. | Serge Osmeña | Independent | 12,670,615 | 28.20% | |||
| 15. | Martin Romualdez | UNA | Lakas | 12,325,824 | 27.60% | ||
| 16. | Isko Moreno | PGP, PRP | PMP | 11,126,944 | 24.95% | ||
| 17. | TG Guingona | KDM | Liberal | 10,331,157 | 22.92% | ||
| 18. | Jericho Petilla | KDM, PRP | Liberal | 7,046,580 | 15.77% | ||
| 19. | Mark Lapid | KDM | Aksyon | 6,594,190 | 14.71% | ||
| 20. | Neri Colmenares | PGP | Makabayan | 6,484,985 | 14.48% | ||
| 21. | Edu Manzano | PGP, PRP | Independent | 5,269,539 | 11.69% | ||
| 22. | Roman Romulo | PGP | Independent | 4,824,484 | 10.79% | ||
| 23. | Susan Ople | PGP, PRP, UNA, WPP | Nacionalista | 2,775,191 | 6.07% | ||
| 24. | Alma Moreno | UNA | UNA | 2,432,224 | 5.42% | ||
| 25. | Greco Belgica | Independent | 2,100,985 | 4.62% | |||
| 26. | Rafael Alunan III | Independent | 2,032,362 | 4.45% | |||
| 27. | Larry Gadon | PRP | KBL | 1,971,327 | 4.40% | ||
| 28. | Rey Langit | UNA, WPP | UNA | 1,857,630 | 4.12% | ||
| 29. | Lorna Kapunan | PGP | Aksyon | 1,838,978 | 4.03% | ||
| 30. | Dionisio Santiago | PRP, WPP | Independent | 1,828,305 | 4.02% | ||
| 31. | Samuel Pagdilao | PGP, WPP | Independent | 1,755,949 | 3.91% | ||
| 32. | Melchor Chavez | WPP | WPP | 1,736,822 | 3.85% | ||
| 33. | Getulio Napeñas | UNA | UNA | 1,719,576 | 3.82% | ||
| 34. | Ina Ambolodto | KDM | Liberal | 1,696,558 | 3.62% | ||
| 35. | Allan Montaño | UNA, WPP | UNA | 1,605,073 | 3.56% | ||
| 36. | Walden Bello | Independent | 1,091,194 | 2.41% | |||
| 37. | Jacel Kiram | UNA | UNA | 995,673 | 2.12% | ||
| 38. | Shariff Ibrahim Albani | WPP | Independent | 905,610 | 1.94% | ||
| 39. | Jovito Palparan | Independent | 855,297 | 1.87% | |||
| 40. | Cresente Paez | KDM | Independent | 808,623 | 1.80% | ||
| 41. | Sandra Cam | WPP | PMP | 805,756 | 1.77% | ||
| 42. | Dante Liban | Independent | 782,249 | 1.72% | |||
| 43. | Ramon Montaño | Independent | 759,263 | 1.68% | |||
| 44. | Aldin Ali | WPP | WPP | 733,838 | 1.56% | ||
| 45. | Romeo Maganto | PRP | Lakas | 731,021 | 1.60% | ||
| 46. | Godofredo Arquiza | Independent | 680,550 | 1.50% | |||
| 47. | Levito Baligod | Independent | 596,583 | 1.31% | |||
| 48. | Diosdado Valeroso | Independent | 527,146 | 1.16% | |||
| 49. | Ray Dorona | Independent | 495,191 | 1.09% | |||
| 50. | Eid Kabalu | Independent | 379,846 | 0.81% | |||
| Total turnout | 44,979,151 | 80.69% | |||||
| Total votes | 319,308,507 | N/A | |||||
| Registered voters | 55,739,911 | 100% | |||||
| Reference: Commission on Elections sitting as the National Board of Canvassers.[10][11] | |||||||
2013
- Guest candidate of Makabayan
2010
2007
| Rank | Candidate | Coalition | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Loren Legarda | GO | NPC | 18,501,734 | 62.7% | |
| 2. | Francis Escudero | GO | NPC | 18,265,307 | 61.9% | |
| 3. | Panfilo Lacson | GO | UNO | 15,509,188 | 52.6% | |
| 4. | Manny Villar | GO | Nacionalista | 15,338,412 | 52.0% | |
| 5. | Francis Pangilinan | Liberal | 14,534,678 | 49.3% | ||
| 6. | Benigno Aquino III | GO | Liberal | 14,309,349 | 48.5% | |
| 7. | Edgardo Angara | TEAM Unity | LDP | 12,657,769 | 42.9% | |
| 8. | Joker Arroyo | TEAM Unity | KAMPI | 11,803,107 | 40.0% | |
| 9. | Alan Peter Cayetano | GO | Nacionalista | 11,787,679 | 40.0% | |
| 10. | Gregorio Honasan | Independent | 11,605,531 | 39.3% | ||
| 11. | Antonio Trillanes | GO | UNO | 11,189,671 | 37.9% | |
| 12. | Koko Pimentel | GO | PDP–Laban | 10,898,786 | 37.3% | |
| 13. | Migz Zubiri1 | TEAM Unity | Lakas | 10,640,620 | 37.2% | |
| 14. | Ralph Recto | TEAM Unity | Lakas | 10,721,252 | 36.3% | |
| 15. | Mike Defensor | TEAM Unity | Lakas | 9,938,995 | 33.7% | |
| 16. | Prospero Pichay Jr. | TEAM Unity | Lakas | 9,798,622 | 33.2% | |
| 17. | Sonia Roco | GO | Aksyon | 8,457,748 | 28.7% | |
| 18. | Cesar Montano | TEAM Unity | Lakas | 7,800,451 | 26.4% | |
| 19. | Tito Sotto | TEAM Unity | NPC | 7,638,361 | 25.9% | |
| 20. | John Henry Osmeña | GO | UNO | 7,267,048 | 24.6% | |
| 21. | Vicente Magsaysay | TEAM Unity | Lakas | 6,357,905 | 21.4% | |
| 22. | Nikki Coseteng | GO | Independent | 5,274,682 | 17.9% | |
| 23. | Tessie Aquino-Oreta | TEAM Unity | NPC | 4,362,065 | 14.8% | |
| 24. | Chavit Singson | TEAM Unity | Lakas | 4,353,644 | 14.8% | |
| 25. | Richard Gomez | Independent | 2,725,664 | 9.2% | ||
| 26. | Jamalul Kiram III | TEAM Unity | PDSP | 2,488,994 | 8.4% | |
| 27. | Melchor Chavez | KBL | 843,702 | 2.9% | ||
| 28. | Martin Bautista | Ang Kapatiran | 761,165 | 2.6% | ||
| 29. | Zosimo Paredes | Ang Kapatiran | 713,817 | 2.4% | ||
| 30. | Joselito Pepito Cayetano | KBL | 510,366 | 1.7% | ||
| 31. | Adrian Sison | Ang Kapatiran | 402,331 | 1.4% | ||
| 32. | Oliver Lozano | KBL | 305,647 | 1.0% | ||
| 33. | Antonio Estrella | KBL | 285,488 | 1.0% | ||
| 34. | Victor Wood | KBL | 283,036 | 1.0% | ||
| 35. | Felix Cantal | PGRP | 123,608 | 0.4% | ||
| 36. | Eduardo Orpilla | KBL | 107,532 | 0.4% | ||
| 37. | Ruben Enciso | KBL | 100,523 | 0.3% | ||
| Total turnout | 29,498,660 | 65.51% | ||||
| Total votes | 268,664,477 | N/A | ||||
| Registered voters | 45,029,443 | 100.0% | ||||
| Note: 37 candidates ran for senator. | Source: COMELEC.gov.ph website | |||||
- ^1 replaced by Koko Pimentel as a result of an election protest.
References
- John Gray Geer, ed. (2004). Public opinion and polling around the world: a historical encyclopedia, Volume 1. ABC-CLIO, Inc. p. 690. ISBN 1-57607-911-2.
- Quezon, Manuel L. III (May 11, 2013). "The Great Divide: The midterm election of 2013 (Part 1)". Manuel L. Quezon III. Retrieved May 20, 2021.
- "History of the Senate". Official website of the Senate. Retrieved December 31, 2012.
- Quezon, Manuel III (June 15, 2009). "Reviewing the prewar plebiscites". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Archived from the original on March 26, 2012. Retrieved January 14, 2011.
- Quezon, Manuel III (November 20, 2006). "Block voting". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Archived from the original on March 26, 2012. Retrieved December 31, 2012.
- Quezon, Manuel III (April 10, 2008). "Senate the victim of a design flaw". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Archived from the original on March 26, 2012. Retrieved January 13, 2011.
- R., Lazo (2009). Philippine governance and the 1987 constitution. Rex Bookstore, Inc. ISBN 978-971-23-4546-3.
- Araneta, Sandy (July 24, 2001). "It's final: Honasan is No. 13". The Philippine Star. Retrieved January 13, 2011.
- Dieter Nohlen; Florian Grotz; Christof Hartmann, eds. (2001). Elections in Asia and the Pacific: South East Asia, East Asia, and the South Pacific. Oxford University Press. pp. 223–224. ISBN 978-0-19-924959-6.
- Commission on Elections en banc sitting as the National Board of Canvassers (May 19, 2016). "NBOC Resolution No. 007-16" (PDF). Retrieved May 22, 2016.
- Commission on Elections en banc sitting as the National Board of Canvassers (May 19, 2016). "2016 Official Senatorial Election Results". Rappler. Retrieved May 22, 2016.
- Commission on Elections en banc sitting as the National Board of Canvassers (July 5, 2019). "NBOC Resolution No. 0010-13". Retrieved July 14, 2019.
