Pante Macassar
Pante Macassar (Portuguese: Pante Macassar, Tetum: Pante-Makassár) is a city in the Pante Macassar administrative post on the north coast of East Timor, 152 kilometres or 94 miles to the west of Dili, the nation's capital. It has a population of 4,730 (Stand 2006). It is the capital of the Oecusse exclave (former Oecussi-Ambeno).
Pante Macassar
| |
|---|---|
City | |
 | |
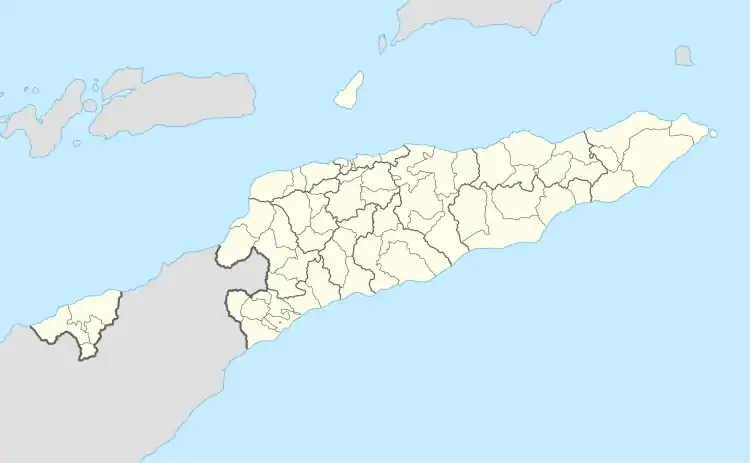 Pante Macassar Location in East Timor | |
| Coordinates: 9°12′S 124°23′E | |
| Country | |
| Municipality | |
| Administrative post | Pante Macassar |
| Area | |
| • Total | 357.30 km2 (137.95 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 189 m (620 ft) |
| Population (2015 census) | |
| • Total | 12,352 |
| • Density | 35/km2 (90/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (TLT) |
| Climate | Aw |
The name literally means "beach of Makassar," alluding to the erstwhile trade with Makassar in Sulawesi (South Celebes).[1] Locally Pante Macassar is known also as "Oecussi," which is commonly translated as "water pot",[1] and was the name of one of the two original kingdoms that form the exclave. The other was Ambeno. During the Portuguese colonisation, the city was also known as Vila Taveiro.
Lifau, in the outskirts of the present city, was the place where the Portuguese first disembarked on Timor and was the first capital of Portuguese Timor. It continued as capital until 1769, when that was transferred to Dili because of constant attacks from the Topasses.
Due to its distance from the remainder of East Timor, Oecussi-Ambeno, and specifically Pante Macassar, became the first territory occupied by Indonesia on 29 November 1975.
In 1999, in the tumult that accompanied the referendum for independence, Pante Macassar was particularly affected by the destructiveness of the pro-integration militias, supported by the Indonesian army. Sixty-five civilian supporters of independence were hanged, and 90 percent of the buildings were burned down.
Twice a week, a ferry boat from Dili arrives, for a journey that takes 12 hours (which is half a day).
Climate
As is typical of the north coast of Timor, Pante Macassar has a tropical savanna climate (Köppen Aw) with a wet season from December to March and a long dry season from April to November.
| Climate data for Pante Macassar | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 29.9 (85.8) |
29.4 (84.9) |
29.9 (85.8) |
30.7 (87.3) |
30.9 (87.6) |
30.4 (86.7) |
29.8 (85.6) |
29.6 (85.3) |
29.6 (85.3) |
30.0 (86.0) |
30.7 (87.3) |
30.3 (86.5) |
30.1 (86.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 27.3 (81.1) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.2 (79.2) |
25.3 (77.5) |
25.0 (77.0) |
25.2 (77.4) |
26.3 (79.3) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.7 (81.9) |
26.5 (79.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 24.7 (76.5) |
23.8 (74.8) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.9 (73.2) |
22.0 (71.6) |
20.8 (69.4) |
20.5 (68.9) |
20.9 (69.6) |
22.6 (72.7) |
24.8 (76.6) |
25.1 (77.2) |
22.9 (73.2) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 260 (10.2) |
214 (8.4) |
150 (5.9) |
57 (2.2) |
37 (1.5) |
18 (0.7) |
17 (0.7) |
7 (0.3) |
1 (0.0) |
12 (0.5) |
48 (1.9) |
167 (6.6) |
988 (38.9) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org[2] | |||||||||||||
References
- Hull, Geoffrey (2002), The Languages of East Timor: Some Basic Facts (Revised 9.2.2002) (PDF), Independently published, archived from the original (PDF) on 1 October 2009, retrieved 20 April 2022
- "Climate: Pante Macassar". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved 16 April 2020.
Further reading
- Ministry of Infrastructure (September 2011). TIM: District Capitals Water Supply Project – The Expansion, Rehabilitation and Operation and Maintenance of Pante Macasar Water Supply Systems – Initial Environmental Examination (PDF) (Report). Asian Development Bank. District Capitals Water Supply Project (RRP TIM 44130-02). Retrieved 14 July 2022.
External links
![]() Media related to Pante Macassar Vila at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Pante Macassar Vila at Wikimedia Commons