Makkum, Súdwest-Fryslân
Makkum is a village of Súdwest-Fryslân municipality, west of Bolsward on the banks of the lake IJsselmeer in the province Friesland of the Netherlands. It had a population of around 3,460 in January 2017,[3] making it the largest village of the former municipally Wûnseradiel. North and south of Makkum are nature reserves Noardwaard and Súdwaard. Belonging to Makkum is the hamlet Ingwier.
Makkum | |
|---|---|
Village | |
 Waag of Makkum | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
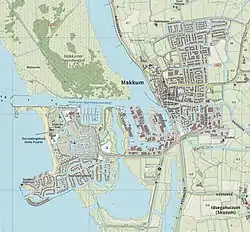 Map of Makkum | |
 Makkum Location in the Netherlands  Makkum Makkum (Netherlands) | |
| Coordinates: 53°3′18″N 5°24′13″E | |
| Country | |
| Province | |
| Municipality | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 6.03 km2 (2.33 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 0.5 m (1.6 ft) |
| Population (2021)[1] | |
| • Total | 3,380 |
| • Density | 560/km2 (1,500/sq mi) |
| Postal code | 8754[1] |
| Dialing code | 0515 |
| Website | Official |
Historically Makkum is a fishing village. In the 20th century it started receiving tourists.
History
The Sint Maarten terp is over a thousand years old. It housed the rural village Mackum with its church. In the 16th century a town arose south of the village called Statum. Here freight ships passing through the locks had to pay tolls. Most of these ships were heading for Bolsward. After the Middle Ages both villages grew together. The current church was built in 1660.
Makkum was known as the gateway to the Zuiderzee for its locks which were owned by the neighboring monastery. This strategic position meant Makkum could develop to an important centre of trade.
The Golden Age of Makkum started in the 17th century and lasted until the 18th century. Makkum became an important center of trade and industry, including brick works, wind-powered saw-, oil-, paper-, and pealing mills, ship yards and seashell lime kilns. The lime kiln industry was the major pillar of Makkums prosperity employing many people. The high quality quicklime produced was amongst others used in house construction in Amsterdam. Transport of base materials and end products was by ship which caused shipping and ship construction to flourish. Seashell fishing was of importance next to common fisheries.
The coat of arms of Makkum shows a golden mermaid carrying a sailing vessel in her right hand and a lime kiln in her left. The 19th century brought economical decline caused by the siltation of the Zuiderzee which made the harbor of Makkum unreachable. Only shipyards and potteries remained.
Lately tourism has developed strongly in Makkum from the attraction of water sports. Recreational area "De Holle Poarte" with its beach, campsite, holiday homes and boulevard attracts many visitors every year.
Besides agriculture, nature plays a large role with thatch cutting in the Makkumerwaard. The nature reserves along the IJsselmeer coast are known for their birdlife and abundance of flora. The Preamke foundation operates a flat bottom boat for tourists. The WON foundation makes an effort for showing the history of sea fishing on the former Zuiderzee.
Places of interest
The rich history of the village is still very visible. The village has a town-like structure dating from the 17th century. At the lock are historic merchant houses and village has a weigh house. The pottery Royal Tichelaar Makkum is one of the oldest companies of the Netherlands.
 Makkum lock
Makkum lock Harbour of Makkum
Harbour of Makkum
 Donia church
Donia church
Community
The organisation for local interests was founded in 1909. The village newspaper is called Makkumer Belboei. In the summer a pop festival is held called Leugenbollepop. Us Stek works on interests in the area of sports and activities. Sint Martinus, It Iepen Stee and De Arke are the three primary schools of the village.
People from Makkum
Cynthia Lenige, (1755–1780), poet in Dutch and Frisian, after whom a street is named
References
- "Kerncijfers wijken en buurten 2021". Central Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 6 April 2022.
- "Postcodetool for 8754AA". Actueel Hoogtebestand Nederland (in Dutch). Het Waterschapshuis. Retrieved 6 April 2022.
- Kerncijfers wijken en buurten 2017 - CBS Statline