List of presidents of Indonesia
The president is the head of state and also head of government of the Republic of Indonesia. The president leads the executive branch of the Indonesian government and is the commander-in-chief of the Indonesian National Armed Forces. Since 2004, the president and vice president are directly elected to a five-year term.
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of Indonesia |
|---|
 |
The presidency was established during the formulation of the 1945 constitution by the Investigating Committee for Preparatory Work for Independence (BPUPK), a body established by the occupying Japanese 16th Army on 1 March 1945 to work on "preparations for independence in the region of the government of this island of Java".[1] On 18 August 1945, the Preparatory Committee for Indonesian Independence (PPKI), which was created on 7 August to replace the BPUPK, selected Sukarno as the country's first president.
Presidents
| No. | Portrait | Name (Birth–Death) |
Term of office | Political party | Vice president(s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Took office | Left office | Time in office | ||||||
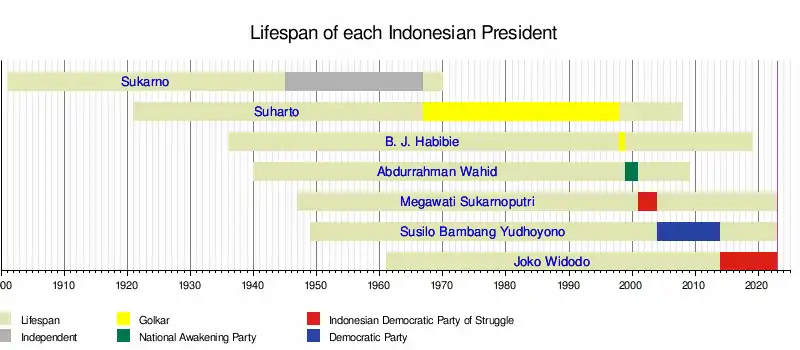
| 1 |  |
Sukarno (1901–1970) |
18 August 1945 | 12 March 1967[2] | 21 years, 206 days | Independent | Mohammad Hatta | |
| Vacant (1 December 1956 – 12 March 1967) | ||||||||
| Declared Indonesia's independence from colonial powers. Presided during the Indonesian National Revolution and the first national elections. One of the founding fathers of the Non-Aligned Movement and hosted the 1955 Bandung Conference. Called for a 'Guided Democracy' following the collapse of 10 governments during the 1950s, with Nasakom as the principle ideology. Acceded Western New Guinea. Opposed the formation of Malaysia and began Konfrontasi. Signed the Supersemar in 1966, following the assassination of 6 generals. Relieved from power in 1967. | ||||||||
| During this interval, Chief of Staff of the Indonesian Army Suharto was the acting President. | ||||||||
| 2 |  |
Suharto (1921–2008) |
27 March 1968 | 21 May 1998 | 30 years, 70 days | Golkar[lower-alpha 1] | ||
| Vacant (27 March 1968 – 23 March 1973) | ||||||||
| Hamengkubuwono IX | ||||||||
| Adam Malik | ||||||||
| Umar Wirahadikusumah | ||||||||
| Sudharmono | ||||||||
| Try Sutrisno | ||||||||
| B. J. Habibie | ||||||||
| The first president from a military background. The longest serving president with an over 30-year tenure. Seized power from Sukarno through Supersemar in 1966. Declared a New Order military dictatorship. Dismantled the Communist Party of Indonesia and oversaw the mass murder and imprisonment of thousands of suspected communists throughout the archipelago. Ended Konfrontasi and initiated friendly relationships with neighbouring countries of Malaysia and Singapore, and Indonesia became a founding member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations and the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation. Severed ties with China and other communist countries in the region. Annexed East Timor. Incorporated Western New Guinea into Indonesia. Oversaw great economic and infrastructural development, but rampant corruption within the bureaucracy and government. Resigned following the collapse of the Indonesian economy during the 1997 Asian financial crisis and the 1998 riots. | ||||||||
| 3 |  |
B. J. Habibie (1936–2019) |
21 May 1998 | 20 October 1999 | 1 year, 152 days | Golkar | Vacant | |
| First, and to date the only, president (aside from acting presidents) who was born outside of Java. First vice president to become president. Took power following Suharto's resignation. Oversaw Indonesia's democratic transition. East Timor declared independence from Indonesia. Released thousands of political prisoners. Decided not to run for a full term. | ||||||||
| 4 |  |
Abdurrahman Wahid (1940–2009) |
20 October 1999 | 23 July 2001 | 1 year, 276 days | National Awakening Party | Vacant (20–21 October 1999) | |
| Megawati Sukarnoputri | ||||||||
| 1999 | ||||||||
| First executive branch officer (president and vice president) to have come from a religious background. Head of Nahdlatul Ulama and grandson of its founder. Term embroiled by a number of scandals and corruption cases. Abolished all remaining legal discrimination against Chinese Indonesians. Attempts to reform the military and remove its political power were not taken kindly by military actors. Attempted to dissolve parliament, but was eventually removed from office by them. | ||||||||
| 5 |  |
Megawati Sukarnoputri (born 1947) |
23 July 2001 | 20 October 2004 | 3 years, 89 days | Indonesian Democratic Party of Struggle | Vacant (23–26 July 2001) | |
| Hamzah Haz | ||||||||
| First female president of Indonesia and the first to be born after the proclamation of independence in 1945. Oldest daughter and second child of President Sukarno, first president born to another president. First female vice president and as of 2021 the only one to be born post-1945. Came to power following the impeachment of Abdurrahman Wahid. Presided during a period of economic growth. Bali was attacked by a major bombing in 2002 by Jemaah Islamiyah. Lost the reelection bid to her former coordinating minister. | ||||||||
| 6 |  |
Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono (born 1949) |
20 October 2004 | 20 October 2014 | 10 years | Democratic Party | Jusuf Kalla | |
| Boediono | ||||||||
| 2004 2009 | ||||||||
| The first president to be directly elected by popular vote. Parts of Sumatra were devastated by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami. Jemaah Islamiyah severely weakened following efforts by Detachment 88. Indonesia classified part of MINT and became a member of the G20. Elected to a second term in 2009. Indonesia formed the Bali Democracy Forum and became a founding member of the Open Government Partnership. Presided over consistent economic growth. During his second term, the Democratic Party suffered a number of corruption scandals. | ||||||||
| 7 |  |
Joko Widodo (born 1961) |
20 October 2014 | Incumbent | 9 years, 8 days | Indonesian Democratic Party of Struggle | Jusuf Kalla | |
| Ma'ruf Amin | ||||||||
| 2014 2019 | ||||||||
| The first president not to have emerged from the country's political elite or to have been an army general.[3] First president to have been a regional politician (mayor for about 7 years, governor for nearly 2 years) and the first to be born after the recognition of independence in December 1949. Initiated the process to move Indonesia's capital from Jakarta to East Kalimantan. Elected to a second term in 2019. During his second term, he hosted the G20 Bali summit in 2022. | ||||||||
By age
| # | President | Born | Age at start of presidency |
Age at end of presidency |
Post-presidency timespan |
Lifespan | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Died | Age | ||||||
| 1 | Sukarno | 6 June 1901 | 44 years, 73 days 18 August 1945 |
65 years, 279 days 12 March 1967[lower-alpha 2] |
3 years, 101 days | 21 June 1970 | 69 years, 15 days |
| 2 | Suharto | 8 June 1921 | 45 years, 277 days 12 March 1967 |
76 years, 347 days 21 May 1998[lower-alpha 3] |
9 years, 251 days | 27 January 2008 | 86 years, 233 days |
| 3 | B. J. Habibie | 25 June 1936 | 61 years, 330 days 21 May 1998 |
63 years, 117 days 20 October 1999 |
19 years, 326 days | 11 September 2019 | 83 years, 78 days |
| 4 | Abdurrahman Wahid | 7 September 1940 | 59 years, 43 days 20 October 1999 |
60 years, 319 days 23 July 2001[lower-alpha 2] |
8 years, 160 days | 30 December 2009 | 69 years, 114 days |
| 5 | Megawati Sukarnoputri | 23 January 1947 | 54 years, 181 days 23 July 2001 |
57 years, 271 days 20 October 2004 |
19 years, 8 days | (living) | 76 years, 278 days |
| 6 | Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono | 9 September 1949 | 55 years, 41 days 20 October 2004 |
65 years, 41 days 20 October 2014 |
9 years, 8 days | (living) | 74 years, 49 days |
| 7 | Joko Widodo | 21 June 1961 | 53 years, 121 days 20 October 2014 |
(incumbent) | (incumbent) | (living) | 62 years, 129 days |
| # | President | Born | Age at start of presidency |
Age at end of presidency |
Post-presidency timespan |
Died | Age |
| Lifespan | |||||||
Notes
- With military support
- Removed from office
- Resigned from office
By time in office
| Rank | President | Length in days | Order of presidency | Number of terms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Suharto | 11,393[lower-alpha 1] | 2nd • 12 March 1967 – 21 May 1998[lower-alpha 2] | Six full terms; resigned 2 months and 11 days into seventh term |
| 2 | Sukarno | 7,876[lower-alpha 3] | 1st • 18 August 1945 – 12 March 1967[lower-alpha 4][2] | De jure: Four full terms; removed 1 year, 6 months, and 22 days into fifth term De facto: Never faced reelection, declared president for life by the Provisional People's Consultative Assembly (MPRS) on 18 May 1963 |
| 3 | Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono | 3,652 | 6th • 20 October 2004 – 20 October 2014 | Two full terms |
| 4 | Joko Widodo | 3,295[lower-alpha 5] | 7th • 20 October 2014 – Incumbent | Serving second term |
| 5 | Megawati Sukarnoputri | 1,185 | 5th • 23 July 2001[lower-alpha 6] – 20 October 2004 | One partial term (3 years, 2 months, and 27 days)[lower-alpha 7] |
| 6 | Abdurrahman Wahid | 642 | 4th • 20 October 1999 – 23 July 2001[lower-alpha 4] | One partial term (1 year, 9 months, and 3 days) |
| 7 | B. J. Habibie | 517 | 3rd • 21 May 1998[lower-alpha 6] – 20 October 1999 | One partial term[lower-alpha 8] (1 year, 4 months, and 29 days) |
| 8 | Assaat | 231 | acting • 27 December 1949[lower-alpha 9] – 15 August 1950 | Acting president[lower-alpha 10] for 7 months and 19 days |
| 9 | Sjafruddin Prawiranegara | 203 | acting • 22 December 1948[lower-alpha 9] – 13 July 1949 | Acting president[lower-alpha 11] for 6 months and 21 days |
Notes
- Suharto was acting president until 27 March 1968 (381 days), when he was made full president
- Resigned from office
- Sukarno was detained by Dutch troops on 19 December 1948 during the Operation Kraai. During this time, the Emergency Government of the Republic of Indonesia, led by Sjafruddin Prawiranegara, acted as the country's government-in-exile until 13 July 1949. As a result, Sukarno's term in office actually had 206 days less. This figure includes his term as the president of the United States of Indonesia (27 December 1949 – 15 August 1950; 231 days), which was coterminous with Assaat being president of the constituent Republic of Indonesia.
- Removed from office
- As of 28 October 2023
- Succeeded to presidency
- Sought election to a full term in 2004, but was defeated.
- Originally assigned to office until 10 March 2003, but due to the accelerated election he was required to face reelection in which he did not contest after his accountability speech was rejected by the MPR.
- Acting president
- President of State of Republic of Indonesia after Dutch–Indonesian Round Table Conference, while Sukarno became president of United States of Indonesia.
- President of emergency government during Indonesian National Revolution, after both Sukarno and Hatta were captured by the Dutch authorities after the second police action.
See also
References
- Kusuma, A.B.; Elson, R.E. (2011), "A note on the sources for the 1945 constitutional debates in Indonesia" (PDF), Bijdragen tot de Taal-, Land- en Volkenkunde, 167 (2–3): 196–209, doi:10.1163/22134379-90003589, ISSN 0006-2294
- Sukarno transferred key presidential powers to Suharto on 11 March 1966 in a vaguely worded letter of authority known as Supersemar and surrendered his powers on 22 February 1967 but he was not formally relieved of his presidential title by the provisional parliament until 12 March 1967.
- Cochrane, Joe (22 July 2014). "A Child of the Slum Rises as President of Indonesia". The New York Times.