iPAQ
The iPAQ is a discontinued Pocket PC and personal digital assistant which was first unveiled by Compaq in April 2000.
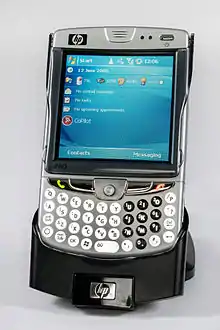



HP's line-up of iPAQ devices included PDA-devices, smartphones and GPS-navigators. A substantial number of devices were outsourced from Taiwanese HTC corporation.
The name was borrowed from Compaq's earlier iPAQ Desktop Personal Computers. Following Hewlett-Packard's acquisition of Compaq, the product has been marketed by HP. The devices use a Windows Mobile interface. In addition to this, there are several Linux distributions that also operate on some of these devices. Earlier units were modular. Sleeve accessories were released called "jackets", which slide around the unit and add functionality such as a card reader, wireless networking, GPS, and extra batteries. Later versions of iPAQs have most of these features integrated into the base device itself, some including GPRS mobile telephony (SIM card slot and radio).
History
The iPAQ was developed by Compaq based on the SA-1110 "Assabet" and SA-1111 "Neponset" reference boards that were engineered by a StrongARM development group located at Digital Equipment Corporation's Hudson Massachusetts facility. At the time when these boards were in development, this facility was acquired by Intel. When the "Assabet" board is combined with the "Neponset" companion processor board they provide support for 32 megabytes of SDRAM in addition to CompactFlash and PCMCIA slots along with an I2S or AC-Link serial audio bus, PS/2 mouse and trackpad interfaces, a USB host controller and 18 additional GPIO pins. Software drivers for a CompactFlash Ethernet device, IDE storage devices such as the IBM Microdrive and the Lucent WaveLAN/IEEE 802.11 Wifi device were also available. An earlier StrongARM SA-1100 based research handheld device call the "Itsy" had been developed at Digital Equipment Corporation's Western Research Laboratory (later to become the Compaq Western Research Laboratory).
The first iPAQ Pocket PC was the H3600 series, released in 2000.[1] It ran Microsoft's Pocket PC 2000 operating system, and featured a 240 x 320 pixel 4096-color LCD, 32 MB of RAM, and 16 MB of ROM.[2][3] Compaq released a similarly-designed H3100 series Pocket PC in January, 2001.[4] It was a lower-priced model[5] with a 15-greyscale monochrome LCD, 16 MB of RAM, and a dark grey D-pad instead of the chrome D-pad of its predecessor.[6][3] The H3600 series was succeeded by the H3800 and H3900 series, which retained the same form factor, but had a different button layout.
Soon after HP's merger with Compaq in 2002, HP discontinued its Jornada line of Microsoft Windows powered Pocket PCs, and continued the iPAQ line that started under Compaq.
In June 2003, HP retired the h3xxx line of iPAQs and introduced the h1xxx line of iPAQs targeted at price conscious buyers, the h2xxx consumer line, and the h5xxx line, targeted at business customers. They were sold pre-installed with the Windows Mobile for Pocket PC 2003 Operating System. The h63xx series of iPAQs running the Phone Edition of Windows Mobile 2003, the hx47xx series and the rz17xx series, both running the Second Edition of Windows Mobile 2003 were introduced in August 2004.
In August 2004, HP released the rz17xx and rx3xxx series of Mobile Media Companions. These devices were aimed at consumers, rather than the traditional corporate audience. Emphasis was placed on media features, like NEVO TV Remote and Mobile Media. They ran on Windows Mobile 2003SE.
In February 2005, the iPAQ Mobile Messenger hw6500 series was introduced to selected media at the 3GSM conference in Cannes, France. It was replaced a year later by the hw6900 series, running on Windows Mobile 5.
In 2007, the iPAQ rx4000 Mobile Media Companion PDA/media devices and rx5000 Travel Companion PDA/GPS devices were released. Both series of iPAQs work on the Windows Mobile 5 Operating System (WM5), as do the hx2000 and hw6900 series. The first HP Windows Mobile 6 device, the iPAQ 500 Series Voice Messenger, with the Windows Mobile 6 Standard Operating System (WM6), and numeric pad, was released in the same year.
The entire iPAQ line was completely revamped by the introduction of five new iPAQ series to complement the introduction of the iPAQ 500 Series Voice Messenger earlier in the year. The models announced were the 100 Series Classic Handheld, the 200 Series Enterprise Handheld, the 300 Series Travel Companion, the 600 Series Business Navigator and the 900 Series Business Messenger. The 100 and 200 Series are regular touchscreen PDAs without phone functionality running WM6. The 300 Series Travel Companion is not a PDA; marketed as a Personal Navigation Device, it is a handheld GPS unit operating on the Windows CE 5.0 core Operating System with a custom user interface. The 600 and 900 series are phones with integrated GPS and 3G capabilities, running the WM6 Professional. The 600 series possesses a numeric pad and the 900 series features a full QWERTY keyboard.
Hewlett-Packard introduced a smartphone iPAQ Pocket PC that looks like a regular cell phone and has VoIP capability. The series is the HP iPAQ 500 Series Voice Messenger.[7]
In December 2009, HP released the iPAQ Glisten, running on Windows Mobile 6.5.
In mid-August 2011, HP announced that they would be discontinuing all webOS devices.[8]
Model list
Jacket-compatible
These older models are compatible with the iPAQ Jacket which can accept 1× CompactFlash, 1× PC Card or 2× PC Card slots.
iPAQ jacket PN 173396-001 PCMCIA (PC port) 1× internal Li-ion battery PN 167648 3.7 V 1500 mAh (upgradable).
| Model (variants) | Release Date | RAM (MiB) | ROM (MiB) | Slots | CPU | CPU Clock
(MHz) |
OS | WiFi | Bluetooth | IrDA | PN 173396-001 | Special Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H3650 (H3630, H3635) | 2000[9] | 32 | 16 | None | SA-1110 | 206 | PPC2000 | None | None | Yes | Yes | 4096-color display [3] |
| H3150 (H3130, H3135) | 2001[4] | 16 | 16 | None | SA-1110 | 206 | PPC2000 | None | None | Yes | 4-bit gray scale display[3] | |
| H3670 (H3660) | 2001[10] | 64 | 16 | None | SA-1110 | 206 | PPC2000 | Yes | Yes | |||
| H3760 | 64 | 32 | None | SA-1110 | 206 | PPC2002 | ||||||
| H3830 (Rosella) | 32 | 32 | 1SD | SA-1110 | 206 | PPC2002 Premium | Yes | |||||
| H3850 | 64 | 32 | 1SD | SA-1110 | 206 | PPC2002 | ||||||
| H3870 | 64 | 32 | 1SD | SA-1110 | 206 | PPC2002 | BT1.1 | Yes | Yes | |||
| H3950 | 64 | 32 | 1SD/IO | PXA250 | 400 | PPC2002 Premium | Yes | NEVO TV Remote Software | ||||
| H3970 | 64 | 48 | 1SD | PXA250 | 400 | PPC2002 Premium | BT1.1 | Yes | Yes | NEVO TV Remote Software | ||
| H5150 | 64 | 32 | 1SD | PXA255 | 400 | WM2003 | BT1.1 | Yes | Yes | NEVO TV Remote Software | ||
| H5400 | 64 | 48 | 1SD | PXA250 | 400 | WM2003 | 802.11b | BT1.1 | Yes | Yes | NEVO TV Remote Software, Biometric Fingerprint reader | |
| H5500 | 128 | 48 | 1SD | PXA255 | 400 | WM2003 | 802.11b | BT1.1 | Yes | Yes | Biometric Fingerprint reader | |
Newer models
- SDIO can support up to 2GB.[11]
| Model | Release Date | RAM (MiB) | ROM (MiB) | Slots | CPU | CPU Clock
(MHz) |
OS | WiFi | Bluetooth | More |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1910 | 2002 | 64 | 16 | 1 SD | PXA250 | 200 | PPC2002 | No | No | No RS-232 Support |
| H1915 | 2002 | 64 | 16 | 1 SD | PXA255 | 200 | PPC2002 | No | No | No RS-232 Support |
| H1930 | 2003 | 64 | 16 | 1 SDIO | S3C2410 | 203 | WM2003 | No | No | No RS-232 Support |
| H1940 | 2003 | 64 | 32 | 1 SDIO | S3C2410 | 266 | WM2003 | No | BT1.1 | No RS-232 Support |
| rx1950 | 2005 | 32 | 64 | 1 SDIO | S3C2442 | 300 | WM5 | 802.11b | No | |
| rx1950 Navigator | 32 | 64 | 1 SDIO | S3C2442 | 300 | WM5 | 802.11b | No | GPS | |
| H2100 | 64 | 64 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA270 | 312 | WM2003 | 802.11b | No | ||
| H2110 | 64 | 64 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA270 | 312 | WM2003SE | No | Yes | ||
| H2210 or H2215[12] | 64 | 32 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA255 | 400 | WM2003 | No | BT1.1 | NEVO TV Remote Software v2.0 | |
| H4150 | October 15, 2003 | 64 | 32 | 1SDIO | PXA255 | 400 | WM2003 | 802.11b | BT1.1 | |
| H4350 | 64 | 32 | 1SDIO | PXA255 | 400 | WM2003 | 802.11b | BT1.1 | Integrated QWERTY keyboard | |
| hx2100 | 64 | 64 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA270 | 312 | WM5 | No | BT | IrDA, USB 2.0 | |
| hx2110 | 64 | 64 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA270 | 312 | WM2003SE | No | BT1.2 | IrDA, USB 1.1 | |
| hx2190b | 64 | 192 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA270 | 312 | WM5 | No | BT1.2 | IrDA, USB 2.0 | |
| hx2200 | 64 | ?? | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA250 | 400 | PPC2003 Premium | Yes | No | ||
| hx2410 | 64 | 64 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA270 | 520 | WM2003SE | 802.11b | BT1.2 | ||
| hx2415 | 64 | 64 | 1CF 1SDIO 1MMC | PXA270 | 520 | WM2003SE | 802.11b | BT1.2 | ||
| hx2490b | 64 | 192 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA270 | 520 | WM5 Premium | 802.11b | BT | IrDA, USB 2.0 | |
| hx2490c | 64 | 512 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA270 | 520 | WM5 Premium | 802.11b | BT | IrDA, USB 2.0 | |
| hx2495b | 64 | 192 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA270 | 520 | WM5 | 802.11b | BT1.7.1 | ||
| hx2750 | 128 | 128 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA270 | 624 | WM2003SE | 802.11b | BT1.2 | ||
| hx2790 | October, 2005 [13] | 64 | 192 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA270 | 624 | WM5 | 802.11b | BT1.7.1 | |
| hx2790b | 2005 | 64 | 320 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA270 | 624 | WM5 | 802.11b | BT1.7.1 | |
| hx2790c | 2005 | 64 | 512 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA270 | 624 | WM5 | 802.11b | BT1.7.1 | |
| hx4700 | 2004 | 64 | 128 | 1CF 1SDIO | PXA270 | 624 | WM2003SE | 802.11b | BT1.2 | VGA, 5.0 officially, may be unofficially
upgraded to WM 6.5 |
| rz1700 | 32 | 32 | 1SDIO | S3C2410 | 203 | WM2003SE | No | No | ||
| rz1710 | 25 | ?? | 1SDIO 1SD/MMC | S3C2410 | 203 | WM2003SE | No | No | Full RS 232, IrDA | |
| rx1950 | 64 | 32 | 1SDIO 1SD/MMC | SC32442 | 300 | WM5.0 | 802.11b | unknown | May be unofficially upgraded to WM 6.1 | |
| rx3100 | 64 | 32 | 1SDIO | S3C2440 | 300 | WM2003SE | 802.11b | BT1.2 | NEVO TV Remote Software v2.0 | |
| rx3115 | 64 | 32 | 1SDIO | S3C2440 | 300 | WM2003SE | 802.11b | BT1.2 | NEVO TV Remote Software v2.0 | |
| rx3415 | 64 | 32 | 1SDIO | S3C2440 | 400 | WM2003SE | 802.11b | BT1.2 | NEVO TV Remote Software v2.0 | |
| rx3417 | 64 | 64 | 1SDIO | S3C2440 | 400 | WM2003SE | 802.11b | BT1.2 | NEVO TV Remote Software v2.0 | |
| rx3700 | 64 | 128 | 1SDIO | S3C2440 | 400 | WM2003SE | 802.11b | BT1.2 | Camera | |
| rx3715 | 64 | 128 | 1SDIO | S3C2440 | 400 | WM2003SE | 802.11b | BT1.2 | IrDA, 1.2 MP Camera,
NEVO TV Remote Software v2.0 | |
| h6300 | 64 | 64 | 1SDIO | TI OMAP | 168 | WM2003 | 802.11b | BT1.1 | GPRS/Camera | |
| h6310 | 64 | 64 | 1SDIO | TI OMAP 1510 | 168 | WM2003 | 802.11b | BT1.1 | GPRS | |
| hw6500 | 64 | 64 | 1SDIO 1miniSD | PXA270 | 312 | WM2003SE | BT1.2 | GPRS/EDGE, GPS | ||
| hw6900 (Sable) | 64 | 64 | 1miniSD | PXA270 | 416 | WM5.0 | 802.11b | BT1.2 | GPRS/EDGE, GPS | |
| rw6800 | 64 | 128 | 1miniSD | PXA270 | 416 | WM5.0 | 802.11b | BT1.2 | GPRS/EDGE | |
| 110 | 64 | 256 | 1SDHC/SDIO | PXA310 | 624 | WM6.0 | 802.11b/g | BT2.0 w/ EDR | ||
| 210/211/214 | 128 | 256 | 1CF 1SDHC/SDIO | PXA310 | 624 | WM6.0 | 802.11b/g | BT2.0 w/ EDR | VGA,USB Host Support | |
| 614c | 128 | 256 | 1SDHC/SDIO | PXA270 | 520 | WM6.0 | 802.11b/g | BT2.0 w/ EDR | QVGA, GPRS/EDGE/3G, GPS | |
| 910c | 128 | 256 | 1microSDHC | PXA270 | 416 | WM6.1 | 802.11b/g | BT2.0 w/ EDR | QVGA, GPRS/EDGE/3G, GPS | |
| Glisten | 256 | 512 | 1microSDHC | Qualcomm MSM7200A | 533 | WM6.5 | 802.11b/g | BT2.0 w/ EDR | QVGA, GSM/UMTS/HSDPA, aGPS |
Alternative operating systems for the iPAQ
OpenEmbedded
The OpenEmbedded distribution is (as of 2016) the only actively maintained Linux distribution for the iPAQ models, by way of the meta-handheld layer.[14]
Familiar Linux
An alternative Linux-based OS available for the iPAQ was Familiar. It stopped being actively maintained in 2007.
It was available with the Opie or GPE GUI environment, or as a base Linux system with no GUI if preferred.
Both Opie and GPE provided the usual PIM suite (calendar, contacts, to do list, and notes) as well as a long list of other applications. Support for handwriting recognition, on-screen keyboard, bluetooth, IrDA and add-on hardware such as keyboards are standard in both environments.
The v0.8.4 (2006-08-20) version supports HP iPAQ H3xxx and H5xxx series of handhelds, and introduced initial support for the HP iPAQ H2200, Hx4700, and H6300 series.[15]
Intimate Linux
On devices with added storage (primarily microdrives) there is a modified port of Debian called Intimate.[16] In addition to a standard X11 desktop, Intimate also offered the Opie, GPE and Qtopia suites. (Qtopia was a QT-based PIM suite with an optional commercial license.)
NetBSD
NetBSD will install and run on iPAQ.
Plan 9 from Bell Labs
Plan 9 from Bell Labs runs on some iPAQs. The nickname of the architecture is "bitsy," after the name of the ARM-based chipsets used in many of the machines. The "Installation on Ipaq" part of the wiki states: "These instructions are for a Compaq Ipaq and have been tested only on models H3630 and H3650 with 32MB of RAM." In regards to iPAQs, the page on the wiki titled "Supported PDAs" only mentions that the "H3630 and H3650 are known to work."
Ångström distribution
Upgrades
The hx2000 series and some later models are upgradeable to newer versions of Windows Mobile. These upgrades could be purchased from HP. Windows Mobile 2003 could be installed on the H3950, H3970, h5450 models and possibly other models of the H3xxx series with sufficient ROM capacity. Other "cooked" (ready to run) roms have been provided by the group known as the xda-developers and are available for the hx2000 series, the hx4700 and others. The upgradeable versions for the hx2000 and hx4700 include Windows Mobile 6.0, 6.1 and 6.5 which are the newest releases of the Windows Mobile platform.
Internal Li-ion battery
iPAQ models 3100–3700 are fitted with internal Li-ion battery PN 167648 3.7 V 1500 mAh which can be replaced with a 2200 mAh unit. The same battery is used in the iPAQ jacket PN 173396-001 PCMCIA (PC port), which may also be upgraded to a 2200 mAh unit. The 3800/3900 series are fitted with a 1700 mAh cell as standard, also upgradeable to 2200 mAh. Compaq presumably upgraded the battery to cope with the faster CPU's power requirements.
RAM upgrades
It is possible to have the internal RAM of an iPAQ H3970 and hx4700 upgraded to 128 MB by using a specialist service to replace the surface-mount BGA RAM chips.
See also
- HP Touchpad
- HP Slate
- Personal digital assistant
- Windows Mobile
- Hewlett-Packard
- Jornada (PDA) – The predecessor of sorts to the iPAQ line.
- HTC HD2
- SuperWaba – Free and open software development kit for Pocket PC and Linux iPAQs
- Pocket PC
- imageon
References
- "iPAQ H3630 Pocket PC". compaq.com. Archived from the original on 2000-08-17.
- "iPAQ H3600 Series Pocket PC specifications". compaq.com. Archived from the original on 2000-08-15.
- "iPAQ H3000 Pocket PC Reference Guide" (PDF). June 2000.
- "Compaq Unveils Monochrome iPAQ Pocket PC Model with Immediate Availability". compaq.com. 2001-01-29. Archived from the original on 2001-04-01.
- "iPAQ H3135 Pocket PC". compaq.com. Archived from the original on 2001-06-06.
- "QuickSpecs - Compaq iPAQ Pocket PC H3100 Series". compaq.com. Archived from the original on 2000-10-27.
- "Filter News Results - HP Newsroom Filter News Results" (PDF). Hp.com. Retrieved 2 May 2017.
- "HP gives up on mobile – what next for webOS? - General - Feature - HEXUS.net". Mobile-device.biz. Archived from the original on 25 September 2011. Retrieved 2 May 2017.
- "Compaq iPAQ H3650 Pocket PC Review – The Gadgeteer". 28 June 2000. Retrieved 2020-09-01.
- "New iPAQ Pocket PC Models and Options Add Memory, Storage, Software and CompactFlash Options (Advisory)". compaq.com. 2001-03-09. Archived from the original on 2001-03-31.
- "La technologie SDIO Now! v2.1 pour les Pocket PC HP hx2200 et hx2700". Génération-NT (in French). 17 November 2005. Retrieved 2020-12-01.
- "REVIEW: HP iPaq h2215 (h2210) Review". Brighthand. Archived from the original on 19 November 2017. Retrieved 17 June 2018.
- "HP iPaq hx2790 FA677T#ABU WiFi/Bluetooth Pocket PC". UsedHandhelds.com, Inc. Retrieved 2020-09-01.
- "meta-handheld git repository". Cgit.openembedded.org. Archived from the original on 14 May 2016. Retrieved 2 May 2017.
- "iPAQ H3900". Sites.google.com. Retrieved 2 May 2017.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-11-14. Retrieved 2012-12-06.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
