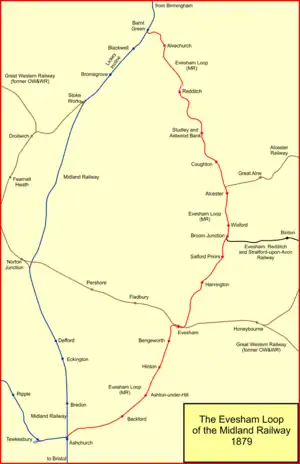
Evesham loop line
The Evesham branch line is a mostly disused English railway line running from Barnt Green via Redditch, Alcester and Evesham to Ashchurch. It was sometimes known as the Gloucester loop line of the Midland Railway.
| Barnt Green–Ashchurch | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Overview | |||
| Status | Operational (Barnt Green–Redditch) | ||
| Owner | Network Rail | ||
| Locale | |||
| Termini | |||
| History | |||
| Opened |
| ||
| Closed | 1962–1963 (Redditch–Ashchurch) | ||
| Technical | |||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) | ||
| |||
Gloucester loop line |
|---|
It opened in stages between 1859 and 1868, built by the Redditch Railway, the Midland Railway and the Evesham and Redditch Railway. All these sections were affiliated to the Midland Railway and amalgamated with it. When complete, the line formed a useful route for goods services avoiding the congested and difficult route via the Lickey Incline. It became more important when a line from Stratford on Avon to Broom was opened in 1879, bringing through goods traffic to the route. Long-distance goods services were diverted away from the line over other routes after 1960, and the line declined steeply. It was closed south of Redditch in stages in 1962 and 1963.
Today the northernmost stretch between Barnt Green and Redditch is still in operation as a branch of the Cross-City Line. This has enjoyed a revival of its passenger services in recent years. At the other end, a very short length of the original line serves an MoD depot at Ashchurch. The remainder of the line is disused.
Birmingham and Gloucester Railway
The Birmingham and Gloucester Railway opened throughout in 1840. With the Bristol and Gloucester Railway, it formed a through route between the dominant manufacturing districts of the West Midlands, and the important port of Bristol. The principal objective of the promoters of the Birmingham and Gloucester Railway was to achieve a trunk route between those important centres, and in devising its route, they paid little heed to the agricultural districts of the Vale of Evesham, ("one of Britain's richest"[1]) and other areas of Worcestershire and Gloucestershire.[1]
Construction
Redditch Railway

Redditch was an important town not far from the Bristol and Gloucester Railway route, but it was not until 23 July 1858 that the Redditch Railway was incorporated. The line was to leave the Midland Railway main line at Barnt Green and run to Brock Hill Lane, Redditch, a distance of about 4+1⁄2 miles. Authorised capital was £35,000 in £10 shares, with the usual addition of loans of £11,500. The line opened to passengers on 19 September 1859, and to goods traffic on 1 October of the same year. There was no other station, until Alvechurch was opened in November 1859. The line was leased and worked from the outset by the Midland Railway.[1][2][3]
The take-up of the £35,000 share issue was disappointing: only £27,120 was taken. Worse, the actual cost of construction of the line amounted to £54,574. The deficit on capital account was £27,000, presumably partly supported by unauthorised loans. The Company went back to Parliament for authorisation for further capital, and an Act of 7 August 1862 allowed the Company to raise fresh share capital to the extent of £15,000, and to take loans of up to £5,000, and to create debenture stock in lieu of loans.[4][5][6]
The company was merged with the Midland Railway in 1863; the change was ratified by the Midland Railway (Additional Powers) Act 1874.[6]
Ashchurch–Evesham (Midland Railway)
The Oxford, Worcester and Wolverhampton Railway opened its main line through Evesham in 1852. The Midland Railway saw the potential of the town, and determined to build its own line to Evesham. It obtained authorisation of a ten-mile Ashchurch and Evesham branch, by the Midland Railway (New Lines) Act of 7 June 1861. It was opened to goods trains on 1 July 1864. The first passenger trains ran on 1 October 1864. The Evesham station was immediately adjacent to the OW&WR station. On weekdays there were four trains in each direction on weekdays and two on Sundays. After a short time there were two trains running through to Gloucester.[4][5][6][1]
Evesham and Redditch Railway

Evesham had two railway lines, but interested parties there saw the advantage of a direct connection to Birmingham, and they supported a proposed Evesham and Redditch Railway. The line was to be 17 miles in length. The Evesham and Redditch Railway was incorporated by the Evesham and Redditch Railway Act of 13 July 1863; authorised capital was £189,600. The company was leased to the Midland Railway on incorporation.[4][5][6][7][8]
Part of the line, from Evesham to Alcester, a distance of nearly ten miles, opened to goods traffic on 16 June 1866. Colonel Yolland for the Board of Trade approved passenger opening, and passenger trains started running on 17 September 1866. Four trains ran daily between Alcester and Evesham, with two on Sundays, and after a short period these were combined with the Ashchurch trains, but the Gloucester through trains had been discontinued.
This opening left 7 miles between Alcester and Redditch to be completed; there was a 330-yard tunnel under the southern end of the town at Redditch. The line was completed on 4 May 1868. The Redditch Railway's terminus station was closed and a through station was opened about a quarter of a mile to the south.[4][5][9][1][8] The new location was more convenient to the town centre. Between Redditch and Evesham the line comprised single track with passing loops; from Evesham to Ashchurch the track was double throughout.[5]
The company was vested in the Midland by the Midland Railway (Additional Powers) Act 1882.[6]
Working arrangements and absorption
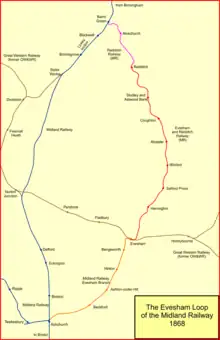
The Evesham branch (from Ashchurch) was part of the Midland Railway; the other two companies forming the through route, the Redditch Railway and the Evesham and Redditch Railway, were worked from their respective openings by the Midland company. The Redditch Railway was absorbed by the Midland Railway from 1 January 1865 (under powers in the Midland Railway (New Lines and Additional Powers) Act of 21 July 1863). The Evesham and Redditch Railway was vested in the Midland Railway from 1 July 1882, and the company was finally dissolved on 25 June 1886.[4]
The Midland Railway had acquired a highly competitive access to Birmingham and to all parts of the country for the Vale of Evesham's fruit and vegetable products; at the same time the OW&WR east-to-west route (by now GWR) had become less strategically important.[5]
The line from Stratford on Avon

A line was built from Stratford-upon-Avon joining the Evesham Loop at Broom: the line was built by the Evesham, Redditch & Stratford-on-Avon Junction Railway. This railway was an extension of a line from Fenny Compton to Stratford-on-Avon, called the East and West Junction Railway. The E&WJR aspired to carry Northamptonshire iron ore to South Wales via Stratford and beyond but had run out of money, and was in the hands of the receiver in 1879 when the Evesham company opened its line.
The line ran from the E&WJR at Stratford to connect with the Evesham Loop line at Broom, between Alcester and Evesham. Its authorising Act gave it running powers over the Midland Railway between Redditch and Evesham, although these were never exercised except for access to the station at Broom. The line opened on 2 June 1879, and was worked by the E&WJR.[10][4][11]
The connection at Broom faced north, away from South Wales; at first the point of junction was in the middle of a Midland Railway staff section on the single line (Wixford to Salford Priors), a highly improper situation. This was rectified soon after the line opened. Broom station was an exchange station only, with no public access, until 1 November 1880.[10][4][11]
The ER&SoAJR itself went into receivership in 1886.[4][11] In 1909 those two companies merged to form the Stratford-on-Avon and Midland Junction Railway.[10]
Alcester Railway
The Alcester Railway company, authorised on 6 August 1872, constructed a branch line from Bearley on the Stratford on Avon Railway to Alcester. In fact it made a junction with the Midland Railway a short distance north of Alcester station; the Alcester Railway had running powers into the Midland Railway station. The branch was opened on 4 September 1876; it was worked by the Great Western Railway. The Alcester Company was finally taken over by the Great Western Railway on 1 July 1883.[12]
Broom south curve
The junction at Broom with the Stratford-upon-Avon and Midland Junction Railway faced north. For a time the Midland Railway used the SoA&MJR line as a through goods link between its system in Northamptonshire and the Gloucestershire network, but the poor facilities of the route and the necessity to reverse at Broom to continue the journey over the Evesham Loop line militated against it.
Nevertheless, during World War II a heavy traffic over that route developed; the track and signalling on the Stratford line was greatly improved for the purpose. The trains still had to reverse at Broom, and the delays involved in doing so with heavy trains became intolerable. To relieve the situation a south curve was built at Broom, creating a triangle. It opened on 27 September 1942.[13][1][14]
Evesham connection
The Midland Railway and the OW&WR (later GWR) were alongside one another at Evesham, and for many years there was only an exchange siding connection between the two. In the 1950s a running connection was made, to enable Honeybourne – Cheltenham services to be diverted that way to Ashchurch.[1]
Passenger services
Passenger services between Redditch and Ashchurch showed little variation over the years, normally consisting of four or five trains in each direction on weekdays at roughly three-hourly intervals. These were a mixture of through trains and trains between Redditch, Evesham and Ashchurch connecting with other services to and from Birmingham. In the early years there were 13 trains in each direction between Birmingham and Redditch on weekdays with an extra late train on Thursdays and Saturdays. After the Second World War, services were reduced, only nine trains running, with some unhelpful gaps.
An hourly diesel service was introduced between Birmingham and Redditch on 25 April 1960. Peak-hour trains and through workings to Evesham and Ashchurch continued to be steam hauled.[4]
Developments from 1960
A frequent regular interval passenger service was introduced between Birmingham and Redditch in April 1960. This greatly reduced the availability of paths for freight trains over the single-track section north of Redditch, and nearly all through freight traffic passing over this section was diverted to the main line via the Lickey Incline. Meanwhile, there was an increase in the Woodford Halse to South Wales traffic from Broom Junction, and in 1960 a double-track east-to-south spur was constructed at Stratford on Avon. This enabled all the Woodford Halse traffic to be diverted to the Honeybourne route, leaving only local goods services, and the Oxford-South Wales freight trains running over the Evesham–Ashchurch section. Broom station was closed on 1 October 1962, a few months after the line from Broom West to Broom East had closed on 1 July 1962.
On 1 October 1962 the Alcester–Evesham section was closed temporarily to all traffic without warning, because of "the unsafe condition of the line". Next the double-track Evesham–Ashchurch section was closed on 9 September 1963, because of the considerable expenditure necessary to maintain the track for heavy freight movements.[4][5] The section between Evesham and Ashchurch soon followed, closing for passengers on 17 June 1963.[5]
In 1962, British Railways announced the intention of withdrawing passenger services on the 28-mile stretch between Redditch and Ashchurch. The proposals originally entailed the complete closure of Harvington and Ashton-under-Hill stations and the retaining of facilities for full wagon loads at Hinton, with all other stations remaining for freight and parcels traffic. But further developments caused all stations on the branch south of Alcester, except Evesham, to be closed completely from 1 July 1963.[4]
These events left the Barnt Green to Redditch section as a short branch of less than 5 miles (8.0 km). This was proposed for closure as part of the Beeching Axe, but was reprieved due to a local campaign, as well as Reddich gaining the designation of a New Town. However in the late 1960s its service was reduced to just four trains daily at peak times. This persisted until 1980, when an hourly service was extended to Redditch on the newly upgraded Cross-City Line. This was upgraded to half-hourly in 1989. In the early-1990s, British Rail electrified the branch. In 2014 a passing loop was constructed on the branch at Alvechurch and this allowed the service to be further upgraded to three trains per hour.[15][16]
Station list
- Barnt Green; opened 1 May 1844; still open;
- Alvechurch; opened 1 November 1859; relocated 19 March 1993; still open;
- Redditch; opened 19 September 1859; relocated 4 May 1868; resited 7 February 1972; still open;
- Studley and Astwood Bank; opened 4 May 1868; closed 1 October 1962;
- Coughton; opened 4 May 1868; closed 30 June 1952;
- Alcester; opened 17 September 1866; closed 1 October 1962;
- Wixford; opened 17 September 1866; original was temporary; replacement date uncertain; closed 2 January 1950;
- Broom (Junction); opened 2 June 1879 unadvertised exchange station; public from 1 November 1880; closed 1 October 1962;
- Salford Priors; opened 17 September 1866; closed 1 October 1962;
- Harvington; opened 17 September 1866; closed 1 October 1962;
- Evesham; opened 1 October 1864; closed 17 June 1963; (former OW&WR station remains open);
- Bengeworth; opened 1 October 1864; closed 8 June 1953;
- Hinton; opened 1 October 1864; closed 17 June 1963;
- Ashton-under-Hill; opened 1 October 1864; closed 17 June 1963;
- Beckford; opened 1 October 1864; closed 17 June 1963;
- Evesham Junction;
- Ashchurch; opened 24 June 1840; closed 15 November 1971; reopened 2 June 1997; still open.[17][18]
References
- Rex Christiansen, A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain: volume 13: Thames and Severn, David & Charles Publishers, Newton Abbot, 1981, 0 7153 8004 4, page 58
- Ernest F. Carter, An Historical Geography of the Railways of the British Isles, Cassell, London, 1959, page 292
- Donald J. Grant, Directory of the Railway Companies of Great Britain, Matador Publishers, Kibworth Beauchamp, 2017, ISBN 978 1785893 537, page 467
- John M. Tolson, Birmingham and Gloucester Loop, in Railway Magazine, November 1964
- Leslie Oppitz, Hereford & Worcester Railways Remembered, Countryside Books, Newbury, 1990, ISBN 1 85306 096 8, pages 31 to 33
- R. J. Essey, An Illustrated History of the Ashchurch to Barnt Green Line: The Evesham Route, Oxford Publishing Co, Hersham, 2002, ISBN 0 86093 562 0, page 21
- Carter, page 344
- Grant, pages 193 and 194
- Essery, pages 21 and 22
- R. C. Riley and Bill Simpson, A History of the Stratford-upon-Avon & Midland Junction Railway, Lamplight Publications, Banbury, 1999, ISBN 1 899246 04 5, page 13
- Essery, page 28
- Essery, page 29
- Essery, page 76
- Riley and Simpson, page 49
- "Milestone marks the end of a railway era". Redditch Standard. Archived from the original on 2 December 2013. Retrieved 16 November 2013.
- "Redditch branch reopened after improvements completed". rail.co.uk. 8 September 2014. Retrieved 29 November 2020.
- Col M. H. Cobb, The Railways of Great Britain: A Historical Atlas, Ian Allan Limited, Shepperton, 2002
- Michael Quick, Railway Passenger Stations in England, Scotland and Wales: A Chronology, the Railway and Canal Historical Society, Richmond, Surrey, 2002