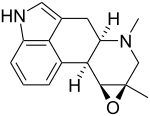
Epoxyagroclavine
Epoxyagroclavine is an ergot alkaloid made by permafrost Penicillium.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
6,8β-Dimethyl-8α,9α-epoxy-10β-ergoline | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1aR,3aR,9bS,9cS)-1a,3-Dimethyl-1a,2,3,3a,4,6,9b,9c-octahydroindolo[4,3-fg]oxireno[2,3-c]quinoline | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H18N2O | |
| Molar mass | 254.327 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Kozlovskiĭ, AG; Zhelifonova, VP; Adanin, VM; Antipova, TV; Ozerskaia, SM; Kochkina, GA; Grafe, U (2003). "[The fungus Penicillium citrinum Thom 1910 VKM FW-800 isolated from ancient permafrost sediments as a producer of the ergot alkaloids agroclavine-1 and epoxyagroclavine-1]". Mikrobiologiia. 72 (6): 816–21. PMID 14768549.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.