Control Yuan
The Control Yuan is the supervisory and auditory branch of the government of Taiwan.[1]
| 監察院 Jiānchá Yuàn (Mandarin) Kàm-tshat Īnn (Taiwanese) Kam-chhat Yen (Hakka) | |
.svg.png.webp) Seal of the Control Yuan | |
| Agency overview | |
|---|---|
| Formed |
|
| Preceding |
|
| Jurisdiction | |
| Headquarters | Taipei, Taiwan |
| Agency executives | |
| Key document |
|
| Website | www.cy.gov.tw |
Control Yuan 監察院 | |
|---|---|
| Type | |
| Type | |
| History | |
| Founded | 4 June 1948 |
| Disbanded | 1 February 1993 |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 178 |
Length of term | 6 years |
| Authority | Constitution of the Republic of China |
| Elections | |
| Indirect election | |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Control Yuan Building, Nanking (1948-1950) Control Yuan Building, Taipei, Taiwan | |
| Constitution | |
| Constitution of the Republic of China | |
| Control Yuan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 監察院 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 监察院 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
|
Designed as a hybrid of auditor and ombudsman by Taiwanese law, the Control Yuan holds the following powers:[2]
- Impeachment: The Control Yuan has the power to impeach government officials. Successfully impeached cases then go to the Disciplinary Court of the Judicial Yuan for adjudication.[3] Impeachment of the President and the Vice President of the Republic follows a different procedure and does not go through the Control Yuan.
- Censure: The Control Yuan also has the power to censure a government official. The censure is sent to the official's superior officer.[4]
- Audit: The Executive Yuan (cabinet) presents the annual budget to the Control Yuan each year for audit.
- Corrective Measures: The Control Yuan, after investigating the work and facilities of the Executive Yuan and its subordinate organs, may propose corrective measures to the Executive Yuan or its subordinate organs for improvement after these measures are examined and approved by the relevant committees.
According to the current Constitution, the Control Yuan shall consist of 29 members. One member shall be the President of the Control Yuan, and another shall be the Vice President. All members, including the President and Vice President of Control Yuan, shall be nominated by the President of Taiwan and approved by Legislative Yuan (the parliament of Taiwan). Members serve with a term limit of six years.
Prior to constitutional reforms in the 1990s, the Control Yuan, along with National Assembly (electoral college) and the Legislative Yuan (lower house) formed the national tricameral parliament. It functioned similarly to an upper house of a bicameral legislature, though it formed its own separate branch and was indirectly elected by provincial or municipal legislatures with 178 senators elected.[5]
Structure
Members composition
The Control Yuan consists of a council with 29 members, including a President and a Vice President and the National Audit Office. All 29 members and the auditor-general are nominated by the President of the Republic and approved by Legislative Yuan for 6-year terms. The incumbent 6th Control Yuan was nominated by President Tsai Ing-wen on June 22, 2020 [6] and later confirmed by Legislative Yuan on July 17, 2020.[7] Members inaugurated on August 1, 2020 and their terms expire on July 31, 2026.
| President | Vice President |
|---|---|
| Chen Chu | Post Vacant |
| Members | |
| National Human Rights Commission members | Other members |
| 9 members | 17 members, 1 seat vacant |
Council and committees
The council of the Yuan, chaired by the Yuan President, is divided into a number of committees to exercise the Yuan's supervision power. No member of the Control Yuan can hold another public office or profession while serving in the branch (according to Article 103 of the constitution), and members must be able to perform absent of partisan control or influence. Members can vote in no more than three committees and can join additional committees as non-voting members. Each committee can have up to 14 members and usually elects a convenor amongst themselves to chair committee meetings.
| Standing committees | Special committees |
|---|---|
|
|
The following responsibilities were also assigned by various acts.
- Anti-Corruption: The Anti-Corruption Committee is a seven-member committee, which cannot include the President of Vice President of the Control Yuan, which deals with asset declarations by government officials, recusals due to conflict of interest, and political donations.[8]
- Examination Invigilation: The Control Yuan also appoints proctors to supervise examinations for civil servants.[9]
National Human Rights Commission
The National Human Rights Committee is a ten-member committee under the Control Yuan which investigates human rights abuses, proposes human rights laws, compiles an annual report and promotes human rights education. The President of the Control Yuan must be a member of the committee. The committee was established by the National Human Rights Committee Organic Law on 10 December 2019.[10]
Administrative Appeal Committee
An Administrative Appeal Committee, operated under the aegis of the Control Yuan but consisting of both members and non-members of the Control Yuan, considers administrative appeals which are inappropriate to both the Control Yuan proper and the Ministry of Audit.
National Audit Office
The National Audit Office is headed by an auditor-general who is nominated by the President of the Republic and appointed with consent of Legislative Yuan (parliament), exercises the Control Yuan's power of audit. It consists of five departments:
- General public affairs audit department
- National defense expenditures audit department
- Special public affairs audit department
- State-run corporations and government-owned businesses audit department
- Financial affairs audit department (also in charge of supervising local government audits)
In addition, most local governments have established the Audit Divisions/Offices, these serve as the subordinate agencies of the National Audit Office. Currently, 21 local governments of the 22 administrative divisions of Taiwan have Audit Divisions/Offices (except Lienchiang County).
Impeachment procedure and notable cases
The Control Yuan is responsible to investigate possible violations on laws and regulations of public servants and raise impeachments if needed. Investigations are initiated by at least two members, and investigation committees must consist of at least nine members of the Control Yuan. The impeachment cases would be determined by a majority vote by members of investigation committee. Successful impeachment cases will then be forwarded to the Disciplinary Court (懲戒法院) under the Judicial Yuan for adjudication. However, the impeachment of the President or Vice President shall be initiated by Legislative Yuan (parliament) and adjudicate by the Constitutional Court under the Judicial Yuan. Details regarding impeachment proceedings are stipulated in the Enforcement Rules of the Control Act.[11]
- On 19 February 2020, the Control Yuan impeached five military personnel which it deemed responsible for a F-16 Fighter aircraft crash on June 4, 2018 that killed all on board. The case was forwarded to the Public Functionary Disciplinary Sanction Commission in the Judicial Yuan to determine the punishment.[12]
- On 4 June 2019, Hsieh Kung-ping (謝公秉), a top aide of former Hualien County commissioner Fu Kun-chi, Lin Chin-hu (林金虎), a county government employee, and media section chief Huang Wei-jun (黃微鈞), were impeached for bribery using $5.26 million in public funds.[13][14] Both were found guilty on 18 February 2020; Hsieh was given two demerits and fined $100,000 NTD, Lin was handed a 10% pay reduction for a year, and Huang was given one demerit and fined $100,000 NTD.[15]
- On 15 January 2019, Kuan Chung-ming, the president of National Taiwan University, was impeached for violating a law prohibiting public servants from working other jobs. The case was forwarded to the Public Functionary Disciplinary Sanction Commission in the Judicial Yuan to determine whether he was guilty and the appropriate punishment.[16] Kuan was found guilty on 2 September 2019 and officially reprimanded.[17]
History
Constitutional theory
The concept of Control Yuan was introduced by Sun Yat-sen's Three Principles of the People. The theory proposed a separation of powers into five branches (五院; wǔyuàn; gō͘-īⁿ). Sun Yat-sen demonstrated the benefit of separating the supervision and auditing power from the legislature by the designation of the state organs of the Imperial China. He quotes the long tradition of supervision used in past dynasties, ranging from the Censor (御史) established by the Qin (秦) and Han (漢) dynasties to the tái (臺) and jiàn (諫) offices established under the Sui (隋) and Tang (唐) dynasties (tai were selected to supervise civil officials and military officers, while jian were selected to counsel the emperor on supervisory matters) to the Board of Public Censors (都察院) selected under the Ming (明) and Qing (清) dynasties. Most of these offices also operated local and provincial branches to supervise local governments. Under the Qing dynasty, the Board of Public Censors consisted of forty or fifty members, and two presidents, one of Manchu ancestry and the other of Chinese ancestry.[18][19] They were, in theory, allowed to send one censor to participate in the meetings of all government boards. The Board's powers were minimized by the time of political flux which preceded the end of the Empire.
However, the 1947 Constitution of the Republic of China has many influence from the resolutions of the Political Consultative Assembly held between the Chinese Nationalist Party (Kuomintang) and the Chinese Communist Party. Carsun Chang, the major author of the Constitution draft in the Political Consultative Assembly, considered the fact that the supervision and auditing power is traditionally held by the legislature, and also the proposal of federalism from the Communist Party in the drafting process. He designed the Control Yuan to be a chamber of parliament that is indirectly elected by the provincial legislatures of China. The Control Yuan has some similarities to the United States Senate, which allocated a similar number of seats to each province of China and holds the power to confirm many important public positions in the Judicial Yuan and Examination Yuan appointed by the President of the Republic.[20]
In the 1947 constitution, the Control Yuan, together with National Assembly and Legislative Yuan, thus formed chambers of a tricameral parliament according to the Judicial Yuan's interpretation number 76 of the Constitution in 1957.[21] The Control Yuan was given the power to request documents from other government agencies and investigate them for violations of law or neglect as under Sun Yat-sen's ideology. The auditor-general was considered elected by the Control Yuan, who shall be nominated by the President of the Republic with consent of the Legislative Yuan, who was responsible for submitting reports on government budgets.[22] Finally, the Control Yuan had confirmation power for the President, Vice President and members of the Judicial Yuan and Examination Yuan.[23][24]
Establishment and relocation to Taiwan

In the early republican era, the Beiyang government was in favor of the traditional three-branch form of separation of powers. However, a weak culture of republicanism and, later, the Warlord Era suppressed the implementation of this constitutional ideology.
After a successful Northern Expedition campaign, the Kuomintang secured its leadership in China and started to build the Nationalist government according to Sun Yat-sen's ideology. Five branches (Yuans) were created under the Kuomintang's party-state administration. During this time, the Auditing Yuan (Chinese: 審計院; pinyin: Shěnjì Yuàn) was established in February 1928, but in February 1931, the Control Yuan was established and the Auditing Yuan was downgraded to the current ministry-level National Audit Office within the Control Yuan.[25] The creation of Control Yuan on 16 February 1931 was the last establishment of the five-Yuans.[26]
However, the 1947 Constitution of the Republic of China, although retaining the architecture of the five-branch government, changed the Control Yuan to be a parliament chamber. Under the constitution, members of the Yuan (by now senators de facto) were elected from regional legislatures: 5 from each province, 2 from each direct-administered municipality, 8 from Mongolia (by 1948 only the Inner Mongolian provinces were represented), 8 from Tibet, and 8 from the overseas Chinese communities. As originally envisioned both the President and Vice President of the Control Yuan were to be elected by and from the members like the speaker of many other parliamentary bodies worldwide. Following the promulgation of the Constitution, the 178 first Control Yuan members elected by the regional legislatures convened in Nanking on June 4, 1948.[25] The first Control Yuan then confirmed the leaders and members of the first Judicial Yuan and Examination Yuan. The transition from one-party state Nationalist government to constitutional government was hence completed.
However, a year later, the Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China lost the Chinese Civil War and retreated to Taiwan in December 1949. Taiwan was under Japanese rule before August 15, 1945. As a result of World War II, the Republic of China Armed Forces occupied Taiwan on behalf of the Allies. The government established Taiwan Province to mark its annexation of Taiwan. There were 104 members who retreated to Taiwan with the government, including 5 deputies from Taiwan. The Control Yuan occupied the former governmental building of Taihoku Prefecture in Japanese era. The term of the retreated members was extended indefinitely until "re-election is possible in their original electoral district." During this era, the first Control Yuan members continued to conduct sessions in Taipei until they were ordered to retire by the Judicial Yuan (Constitutional Court) in 1991.
With the reduction of members due to age, elections were held from 1969 to 1986 to elect new members to the Yuan from Taiwan.
Until 1993, the Control Yuan's legislative work was limited to helping to audit the national budget, which would then be presented to the Legislative Yuan. The other actions the then chamber took were its impeachment, confirmation and censure powers, applied whenever necessary.
Democratization
Democratization took place in Taiwan starting late 1980s; the movement resulted in a series of constitutional amendment known as the Additional Articles of the Constitution. On May 27, 1992, the second amendment removed the Control Yuan from parliament chambers and its members removed from their legislative duties. Decision process of leaders and members of the Control Yuan follows a similar pattern of Judicial Yuan and Examination Yuan. These officials were nominated by the President of the Republic and confirmation by the National Assembly. The National Assembly was another parliament chamber that can hold the confirmation process to maintain the separation of powers.[27]
On 18 July 1997, by the 4th constitutional amendment, the procedure to impeach the President and Vice President of the Republic was transferred out from the Control Yuan. In this amendment, presidential impeachment shall be initiated by Legislative Yuan and voted by the National Assembly.[28] However, the later political developments in Taiwan has inclined to simplify the parliament to one chamber. The Legislative Yuan was the surviving chamber and the National Assembly was then abolished.[29] Since 25 April 2000, confirmation of leaders and members of the Control Yuan are transferred to Legislative Yuan, together with the confirmation of similar officials of Judicial Yuan and Examination Yuan.[30]
At the end of 2004, President Chen Shui-bian sent a list of nominees to positions in the Control Yuan to the Legislative Yuan for approval. The coalition of Kuomintang and People First Party, which then held a majority in the Legislative Yuan, refused to ratify President Chen's nominees and demanded that he submit a new list. The political deadlock that resulted stopped the Control Yuan from functioning from February 2005 to July 2008. The situation resolved after Kuomintang's candidate Ma Ying-jeou was elected as the President in 2008 Taiwanese presidential election and Kuomintang won the supermajority of Legislative Yuan seats in 2008 Taiwanese legislative election. Mr. Wang Chien-shien was then appointed to be its President under the Ma Ying-jeou administration.
In 2016, Democratic Progressive Party's candidate Tsai Ing-wen was elected as the President in 2016 Taiwanese presidential election and Democratic Progressive Party won the majority of Legislative Yuan seats in 2016 Taiwanese legislative election. On 10 December 2019, the Legislative Yuan passed the National Human Rights Committee Organic Law (國家人權委員會組織法), which established the National Human Rights Committee under the Control Yuan. Its duties include investigating human rights abuses, proposing human rights laws, compiling an annual report, and educational promotion of human rights, in accordance with the Paris Principles.[31] The committee will consist of 10 members, one of which is the President of the Control Yuan who heads the committee.[10] It launched on August 1, 2020, with former democracy activist Chen Chu as president.[32] Kuomintang member Justin Huang was discussed as a potential vice-president, but he declined the position after receiving criticism from both the KMT for crossing party lines without consultation and the DPP for his role in the construction of the Taitung Miramar Resort while he was county magistrate, for which the county government was censured by the Control Yuan.[33][34]
Elections and terms
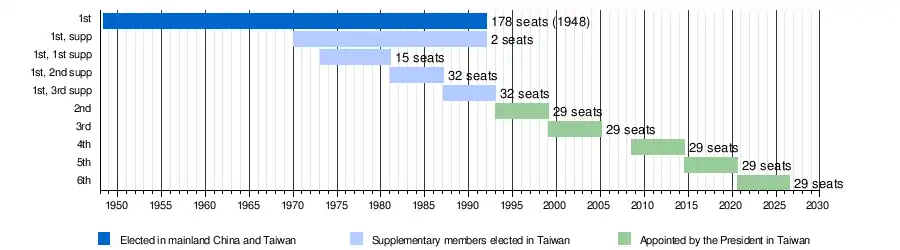
The Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China retreated to Taiwan in 1949, the year following the elections after the enactment of the 1947 constitution. As the Kuomintang government continues to claim sovereignty over mainland China, the term limit of the original Members of the Control Yuan was extended until "re-election is possible in their original electoral districts." In response to the increasing democracy movement in Taiwan, limited supplementary elections were held in the Free Area (Taiwan) starting 1969. Members elected in these supplementary elections served together with those who were elected in 1948. This situation remained until a Constitutional Court (Judicial Yuan) ruling on June 21, 1991 that ordered the retirement of all members with extended terms by the end of 1991.[36]
| Term | Length | Actual length | Election/Appointment | Seats | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | Initially 6 years, then limit removed by Temporary Provisions | Jun 4, 1948-Jan 31, 1993 (See Note column for detailed terms) |
1947-48 elections | 178 | The only election held in mainland China. 5 seats were elected in Taiwan. 104 members retreated to Taiwan with the government; served until the end of 1991. |
| 1969 supp | 2 | Elected in Taipei, terms equal to the 1948-elected members | |||
| 1973 1st supp | 15 | Elected in Taiwan with 6-year terms; then extended to 8 years | |||
| 1980 2nd supp | 32 | Elected in Taiwan with 6-year terms | |||
| 1987 3rd supp | 32 | Elected in Taiwan with 6-year terms; served until Jan 31, 1993 | |||
| 2nd | 6 years | Feb 1, 1993-Jan 31, 1999 | Presidential nomination with National Assembly confirmation |
29 | Changed to a non-parliamentary institution; elections stopped |
| 3rd | Feb 1, 1999-Jan 31, 2005 | ||||
| 4th | Aug 1, 2008-Jul 31, 2014 | Presidential nomination with Legislative Yuan confirmation |
Vacancy due to Legislative Yuan's refusal to initiate the confirmation process | ||
| 5th | Aug 1, 2014-Jul 31, 2020 | ||||
| 6th | Aug 1, 2020-Jul 31, 2026 | Incumbent |
Timeline of Control Yuan elections and terms
President and Vice President of the Control Yuan

Before the 1947 Constitution
The President and Vice President of the Control Yuan in the Nationalist government era were appointed by the Kuomintang (Nationalist Party).
| President | Vice President |
|---|---|
|
|
1947 Constitution
The Control Yuan was a chamber of parliament under the 1947 Constitution of the Republic of China. The President and Vice President of the Control Yuan were elected by and from the members like the speaker of many other parliamentary bodies.
| Order | Date | President | Vice President | Note | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jun 9, 1948–Jan 6, 1954 | Yu Yu-jen | 于右任 | Liu Che | 劉哲 | Inaugurated in Nanking and moved to Taipei |
| Jan 7, 1954–Aug 17, 1954 | Post vacant | Vice President Liu Che died in office | ||||
| Aug 18, 1954–Jul 11, 1957 | Liang Shang-tung | 梁上棟 | ||||
| Jul 12, 1957–Apr 11, 1958 | Post vacant | Vice President Liang Shang-tung died in office | ||||
| Apr 12, 1958–Nov 9, 1964 | Li Shih-tsung | 李嗣璁 | ||||
| Nov 10, 1964–Aug 16, 1965 | Vice President as Acting President | President Yu Yu-jen died in office | ||||
| 2 | Aug 17, 1965–May 14, 1972 | Li Shih-tsung | 李嗣璁 | Chang Wei-han | 張維翰 | |
| May 15, 1972–Mar 18, 1973 | Vice President as Acting President | President Li Shih-tsung died in office | ||||
| 3 | Mar 19, 1973–Mar 23, 1981 | Yu Chun-hsien | 余俊賢 | Chou Pai-lien | 周百鍊 | |
| Mar 24, 1981–Mar 11, 1987 | Huang Tzuen-chiou | 黃尊秋 | ||||
| 4 | Mar 12, 1987–Dec 29, 1991 | Huang Tzuen-chiou | 黃尊秋 | Ma Kung-chun | 馬空群 | |
| Dec 30, 1991–Feb 19, 1992 | Post vacant | Vice President Ma Kung-chun retired at end of 1991 | ||||
| Feb 20, 1992–Jan 31, 1993 | Lin Rong-san | 林榮三 | ||||
1992 Constitution amendment
Since the 1992 ratification of the constitutional amendment, the Control Yuan was reorganized from a chamber of parliament to an independent agency that still performs most of its designated constitutional powers. Since the 4th term, the President and Vice President of the Control Yuan, together with other members, were nominated by the President of the Republic and approved by the Legislative Yuan (the now-unicameral parliament of Taiwan).
| Term | Date | President | Vice President | Note | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd | Feb 1, 1993–Sep 22, 1995 | Chen Li-an | 陳履安 | Cheng Shuei-chih | 鄭水枝 | |
| Sep 23, 1995–Aug 31, 1996 | Vice President as Acting President | President Chen Li-an resigned to run for 1996 Taiwanese presidential election | ||||
| Sep 1, 1996–Jan 31, 1999 | Wang Tso-yung | 王作榮 | ||||
| 3rd | Feb 1, 1999–Jan 31, 2005 | Fredrick Chien | 錢復 | Cheng Meng-lin | 陳孟鈴 | |
| — | Feb 1, 2005–Jul 31, 2008 | Post vacant | Post vacant | Vacant due to Executive-Legislative conflict | ||
| 4th | Aug 1, 2008–Jul 31, 2014 | Wang Chien-shien | 王建煊 | Chen Jinn-lih | 陳進利 | |
| 5th | Aug 1, 2014–Jul 31, 2020 | Chang Po-ya | 張博雅 | Sun Ta-chuan | 孫大川 | |
| 6th | Aug 1, 2020–present | Chen Chu | 陳菊 | Lee Hung-chun | 李鴻鈞 | Vice presidency vacant from Aug 1, 2020 to May 30, 2022 |
Comparable agencies in other countries
| Country | Agency |
|---|---|
| National Supervisory Commission (国家监察委员会) | |
| European Court of Auditors | |
| State Comptroller (מבקר המדינה, مراقب الدولة) | |
| Board of Audit (会計検査院) | |
| Office of the Ombudsman and Commission on Audit | |
| Board of Audit and Inspection (감사원、監査院) | |
| National Audit Office | |
| Government Accountability Office |
See also
References
- Jacobs, Andrew (2009-08-23). "Taiwan's Leader Faces Anger Over Storm Response". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 2020-08-17. Retrieved 2020-08-16.
- See Additional Articles of the Constitution art. 7, available at "Additional Articles of the Constitution of the Republic of China (Taiwan)". July 10, 2005. Archived from the original on August 14, 2022. Retrieved September 14, 2020.
- "公務員懲戒法" [Public Functionary Disciplinary Act]. Article 23, Act of 20 May 2015 (in Chinese). Legislative Yuan. Archived 9 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine
- "Censure". The Control Yuan of the Republic of China. Archived from the original on 9 June 2020. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- Ma, Herbert H. P. (1963). "Chinese Control Yuan: An Independent Supervisory Organ of the State". Washington University Law Review. 1963 (4): 26. Archived from the original on 2021-04-21. Retrieved 2021-04-01.
- "【監委提名】27位被提名人平均62.6歲 男性15名、女性12名". Archived from the original on 2022-01-20. Retrieved 2020-09-14.
- "影/游錫堃宣布:陳菊將任監察院長 27個監委名單全過關". Archived from the original on 2020-08-24. Retrieved 2020-09-14.
- "Regulations Governing the Establishment of the Control Yuan Committee on Anti-Corruption". Article 2, Act of 28 July 2004. Archived 10 June 2020 at the Wayback Machine
- "Examination Invigilation Act". Act of 26 October 1950. Archived 10 June 2020 at the Wayback Machine
- Wang, Yang-yu; Mazzetta, Matthew (10 December 2019). "Bill passed to establish Human Rights Committee under Control Yuan". Central News Agency (Taiwan). Archived from the original on 8 June 2020. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- "Enforcement Rules of the Control Act". Act of 11 February 2009. Legislative Yuan. Archived 28 July 2020 at the Wayback Machine
- Ku, Chuan; Yu, Matt; Yeh, Joseph (19 February 2020). "Five military personnel impeached over negligence in F-16 crash". Central News Agency (Taiwan). Archived from the original on 11 March 2020. Retrieved 9 June 2020.
- Pan, Jason (5 June 2019). "Control Yuan impeaches former Hualien official". Taipei Times. Archived from the original on 9 June 2020. Retrieved 9 June 2020.
- 賴品瑀 (4 June 2019). "花蓮縣政府花公帑收買當地14家媒體 監委批:嚴重傷害新聞信賴". Taro News. Archived from the original on 9 June 2020. Retrieved 9 June 2020.
- 王宏舜 (19 February 2020). "花蓮縣府「買新聞」 謝公秉遭記過2次、罰款10萬元". United Daily News. Archived from the original on 9 June 2020. Retrieved 9 June 2020.
- Yu, Hsiang; Ku, Chuan; Chen, Chih-chung; Wang, Yang-yu; Fan, Cheng-hsiang; Chen, Chun-hua; Elizabeth, Hsu (15 January 2019). "Control Yuan passes motion to impeach new NTU president". Central News Agency (Taiwan). Archived from the original on 9 June 2020. Retrieved 9 June 2020.
- Maxon, Ann (3 September 2019). "Commission reprimands NTU's Kuan". Taipei Times. Archived from the original on 9 June 2020. Retrieved 9 June 2020.
- Hawke's Bay Herald. Volume XXXV, Issue 11595. Monday, July 23, 1900. Page 2.
- The Statesman's year-book, Volume 47. Page 685.
- Constitution of the Republic of China – Chapter IX, Article 91: "The Control Yuan shall be composed of Members who shall be elected by Provincial and Municipal Councils, the local Councils of Mongolia and Tibet, and Chinese citizens residing abroad. Their numbers shall be determined in accordance with the following provisions:
- Five Members from each province;
- Two Members from each municipality under the direct jurisdiction of the Executive Yuan;
- Eight Members from Mongolian Leagues and Banners
- Eight Members from Tibet; and
- Eight Members from Chinese citizens residing abroad."
- 司法院釋字第76號解釋, Judicial Yuan interpretation number 76 (English translation) Archived 2019-01-05 at the Wayback Machine
- Article 90-106, Section IX of the Constitution of the Republic of China (1947)
- Article 79, Section VI of the Constitution of the Republic of China (1947)
- Article 84, Section VII of the Constitution of the Republic of China (1947)
- "The Control Yuan of the Republic of China". Archived from the original on 2016-06-11. Retrieved 2016-05-24.
- Ma, Herbert Han-pao. "The Chinese Control Yuan: An Independent Supervisory Organ of the State". Washington University Law Review. 1963 (4): 402.
- Second Amendment of the Constitution of the Republic of China (1992)
- Fourth Amendment of the Constitution of the Republic of China (1997)
- Sixth Amendment of the Constitution of the Republic of China (1997)
- Seventh Amendment of the Constitution of the Republic of China (1997)
- Shih, Hsiu-chuan (11 December 2018). "Control Yuan may be made National Human Rights Institution". Central News Agency (Taiwan). Archived from the original on 22 June 2020. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- Lin, Sean (2 August 2020). "Human Rights Commission launched". Taipei Times. Archived from the original on 25 January 2021. Retrieved 10 March 2021.
- "Control Yuan nominees confirmed". Taipei Times. 23 June 2020. Archived from the original on 3 March 2021. Retrieved 10 March 2021.
- "監院副院長 提名回扣案黃健庭 立委譁然". Liberty Times. 19 June 2020. Archived from the original on 20 June 2020. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- "Our History". Archived from the original on 2022-05-16. Retrieved 2022-05-02.
- "中央選舉委員會歷次選舉摘要-監察委員選舉". Archived from the original on 2021-02-02. Retrieved 2020-08-31.