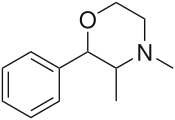
Phendimetrazine
Phendimetrazine (Bontril, Adipost, Anorex-SR, Appecon, Melfiat, Obezine, Phendiet, Plegine, Prelu-2, Statobex) is a stimulant drug of the morpholine chemical class used as an appetite suppressant.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Bontril |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Peak plasma levels occur within 1 to 3 hours. Absorption is usually complete by 4 to 6 hours |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 19-24 hours |
| Excretion | Urinary elimination |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.186 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H17NO |
| Molar mass | 191.274 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Pharmacology
Phendimetrazine functions as a prodrug to phenmetrazine; approximately 30 percent of an oral dose is converted into it. Phendimetrazine can essentially be thought of as an extended-release formulation of phenmetrazine with less potential for abuse. Phendimetrazine is an anorectic drug which acts as a norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agent (NDRA).[3]
As an amphetamine congener, its structure incorporates the backbone of methamphetamine, a potent CNS stimulant. While the addition of an N-methyl group to amphetamine significantly increases its potency and bioavailability, methylation of phenmetrazine renders the compound virtually inactive. However, phendimetrazine is a prodrug for phenmetrazine which acts as the active metabolite. Phendimetrazine possesses preferable pharmacokinetics over phenmetrazine as a therapeutic agent because its metabolization by demethylases produces a more steady and prolonged exposure of active drug within the body. This decreases abuse potential as the peak blood-concentration of active phenmetrazine that's produced from a single dose of phendimetrazine is lower than a single therapeutically equivalent dose of phenmetrazine.
Indicated as a short-term secondary treatment for exogenous obesity, phendimetrazine immediate-release 35mg tablets are typically consumed one hour before meals, not to exceed three doses daily. Phendimetrazine is also manufactured as a 105mg extended-release capsule for once daily dosing, typically consumed 30 to 60 minutes before a morning meal. Whereas the immediate-release formulation has a maximum daily dosage of 210mg (6 tablets), the extended-release capsules have a maximum daily dosage of 105mg (one capsule).
Legality
According to the List of Psychotropic Substances under International Control published by the International Narcotics Control Board, phendimetrazine is a Schedule III controlled substance under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances.[4]
Synthesis
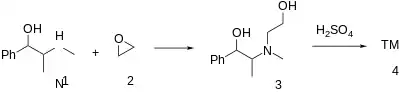
Alkylation of ephedrine (1) with oxirane (2) gives the diol, N-(2-Hydroxyethyl) Pseudoephedrine [54275-43-3] [91688-17-4] (3). (The secondary nature of the amine in 1) eliminates the complication of dialkylation and thus the need to go through the amide.) Cyclization affords phendimetrazine (4).
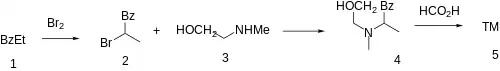
The halogenation of Propiophenone [93-55-0] (1) with bromine gives 2-Bromopropiophenone [2114-00-3] (2). Further reaction with N-Methylethanolamine [109-83-1] (3) goes on to five CID:232614 [902267-47-4] (4). Cyclization with formic acid completed the synthesis of phendimetrazine (5).
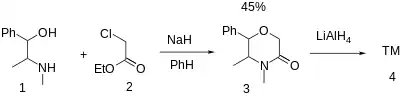
The reaction between Ephedrine [299-42-3] (1) and ethyl chloroacetate [105-39-5] (2) in the presence of sodium hydride gives 4,5-dimethyl-6-phenylmorpholin-3-one, [5493-96-9] (3). The optional reduction of the lactam carbonyl with lithium aluminium hydride.
Additional method:[10]
See also
References
- Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- Landau D, Jackson J, Gonzalez G (2008). "A case of demand ischemia from phendimetrazine". Cases J. 1 (1): 105. doi:10.1186/1757-1626-1-105. PMC 2531092. PMID 18710555.
- Rothman RB, Baumann MH (2006). "Therapeutic potential of monoamine transporter substrates". Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 6 (17): 1845–59. doi:10.2174/156802606778249766. PMID 17017961. Archived from the original on 2017-03-26. Retrieved 2020-05-05.
- "List of psychotropic substances under international control" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-08-31. Retrieved 2005-06-15.
- Otto, W. G. (7 March 1956). "Optisch aktives 2-Phenyl-3,4-dimethyl-morpholin". Angewandte Chemie. 68 (5): 181–182. doi:10.1002/ange.19560680508.
- Werner Heel and Karl Zeile, U.S. Patent 2,997,469 (1961 to Ingelheim, Germany, assignors to C. H. Boehringer Sohn, Ingelheim, Germany, a partnership).
- , GB862198 (1961 to ILSE LIEBRECHT, JULIUS LIEBRECHT, WALTER MAYER LIST, WALTER MAYER-LIST).
- , GB791416 (1958 to ILSE LIEBRECHT, JULIUS LIEBRECHT, WALTER MAYER LIST. WALTER MAYER-LIST).
- Gannon Walter Francis & Poos George Ireland, U.S. Patent 3,308,121 (1967 to Janssen Pharmaceuticals Inc).
- https://eurekamag.com/research/031/845/031845550.php