It will give you a clear visual perception of the gap between mathematics ... (and) your computer calculations. Lynn Wienck[1]
perturbation and aproximation
- how solution of the problem is altered for non-zero but small perturbation ( usually denoted as an espilon)
- problem can not be solved explicitely ( using symbolic methods), only numericla aproximation can be found
Convergence
" ... methods of acceleration of convergence. Suppose you have a slowly convergent series, and want to know its sum (numerically). Just by summing x_1 + x_2 + ... + x_{1000} + ... x_{1000000} + ... + x_{1000000000} + ... you will get the required accuracy after 100 years. If you fit your x_n to c_2/n^2 + c_3/n^3 + (a few more terms), you will get the same accuracy of the sum in 1 second." Andrey (theoretical high energy physicist) [2]
Above problem you can find in parabolic Julia sets.
" your sequence was generated as ... the output of a fixed point iteration . ... The Levin transformation[3] ... uses forward differences successively to remove error terms of an alternating series."[4]
Examples:
- GSL library[5][6]
- "checking for when the series approximation starts to deviate from the result of running it through the Levin u-transform available in the gnu scientific library. so far in my tests this is taking me right up to the event horizon of what will end up being the lowest iteration, even in locations that used to cause the other methods to bail on the series approximation way sooner, but it also does not seem to be going too far so as to cause glitchy artifacts. it seems to be just right, across the board, which i find to be rather exciting! " ( quaz0r about Mandelbrot )[7]
- series calulator [8]
Precision
How to deal with lack of floating point precision:[9]
- implement higher precision arithmetic than your hardware natively supports
- software emulation ( emulating a double with two floats, fixed points numbers , ...)[10]
- use algorithms that are more numerically stable
Libraries :
- Arb by Fredrik Johansson[11]
See how arb library can be used for checking and adjusting precision :
/*
from arb/examples/logistic.c
public domain.
Author: Fredrik Johansson.
*/
goal = digits * 3.3219280948873623 + 3;
for (prec = 64; ; prec *= 2)
{
flint_printf("Trying prec=%wd bits...", prec);
fflush(stdout);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// computation
if (arb_rel_accuracy_bits(x) < goal)
{
flint_printf("ran out of accuracy at step %wd\n", i);
break;
}
}
if (i == n)
{
flint_printf("success!\n");
break;
}
}
How many decimal digits are there in n bits ?
One digit of binary number needs one bit : there are 2 binary digits ( 0 and 1) and bits have 2 states. One digit of decimal number needs aproximately 3.4 bits.[12] There are 10 decimal numbers, 3 bits have 8 states which is not enough, 4 bits have 16 states which is too much.
| type | Total bits | Bits precision | Number of significant decimal digits |
|---|---|---|---|
| float | 32 | 24 | 6 |
| double | 64 | 53 | 15 |
| long double | 80 | 64 | 18[13] |
| mpfr_t[14] | 142 | 41 | |
| mpfr_t | 1000 | 294 |
See also: decimal-precision-of-binary-floating-point-numbers by RIck Regan
Rules
Rounding
- "compute with two more significant figures than your ultimate answer
- Round only after the last step in calculation. Never do further calculations with rounded numbers.
- for multiplying and dividing find the number of significant digits in each factor. The result will have the smaller number of significant digits.
- For powers and roots, the answer should have the same number of significant digits as the original" [15]
- "When you add (or subtract), you keep as many decimal places as there are in the least accurate number.
- When you multiply (or divide), you keep as many significant digits as there are in the least accurate number."[16]
Examples of numerical computings
Seed value
standard images ( without zoom)
External rays
Parameter rays
The Wolf Jung test : The external parameter rays for angles (in turns)
- 1/7 (period 3)
- 321685687669320/2251799813685247 (period 51)
- 321685687669322/2251799813685247 ( period 51 )
Angles differ by about , but the landing points of the corresponding parameter rays are about 0.035 apart.[19]
Dynamic rays
number type
angle precision
For rotational number ( internal angle) 1/34 ray for external angle :
lands on the alfa fixed point :
It is not a ray for angle :
which land on the point :[20]
Difference between external angles of the rays is :
and between landing points of the rays points is :
/* Maxima CAS code */ (%i1) za:0.491486549841951 +0.091874758908285*%i; (%o1) 0.091874758908285 %i + 0.491486549841951 (%i2) zb:-0.508513450158049 +0.091874758908285*%i; (%o2) 0.091874758908285 %i - 0.508513450158049 (%i3) abs(za-zb); (%o3) 1.0
Escaping test
This test was introduced by by John Milnor.[21] See also analysis by Mark Braverman [22] and roundoff error by Robert P. Munafo[23]
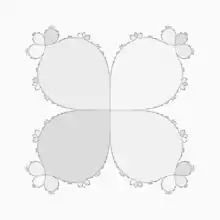
Comment by Mark McClure :[24] " an escape time algorithm would take forever to generate that type of image, since the dynamics are so slow there. If you want resolution of 1/100, it would take roughly 2*10^8 iterates to move the point z0=0.01 to z=2 by iterating f(z)=z+z5 "
Cases
Nonparabolic case
Lets take simple hyperbolic case where parameter c is :
Here repelling fixed point z_f is :
Parabolic case
Lets take simple parabolic case where parameter c is :[25]
Here parabolic fixed point z_f is :
Test
Lets take point z of exterior of Julia set but lying near fixed point :
where n is a positive integer
Check how many iterates i needs point z to reach target set ( = escape) :
where ER is Escape Radius
Show relationship between :
- n
- Last Iteration
- type of numbers used for computations ( float, double, long double, extended, arbitrary precision )
Programs
See FractalForum for evaldraw script[26]
| C source code for CPU one thread - hyperbolic case and float numbers . Click on the right to view |
|---|
/*
gcc -lm -Wall p.c
./a.out
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h> /* pow () */
#include <time.h>
float GiveLastIteration (float Zx, float Zy, float Cx, float Cy, int ER2)
{
float Zx2, Zy2; /* Zx2 = Zx * Zx; Zy2 = Zy * Zy */
float i = 0.0;
Zx2 = Zx * Zx;
Zy2 = Zy * Zy;
while (Zx2 + Zy2 < ER2) /* ER2 = ER * ER */
{
Zy = 2 * Zx * Zy + Cy;
Zx = Zx2 - Zy2 + Cx;
Zx2 = Zx * Zx;
Zy2 = Zy * Zy;
i += 1.0;
}
return i;
}
int main ()
{
float distance;
int n;
/* fixed point zf = zfx = zfy*I = 1.0 for c=0 */
float zfx = 1.0;
float zfy = 0.0;
/* z1 = z1x + z1y * I = point of exterior of Julia set but near parabolic fixed point zp */
float z1x;
float z1y = zfy;
float cx= 0.0;
float cy= 0.0;
/* Escape Radius ; it defines target set = { z: abs(z) > ER}
all points z in the target set are escaping to infinity */
float ER = 2.0;
float ER2;
float LastIteration;
time_t start, end;
float dif;
ER2 = ER * ER;
printf ("Using c with float and Escape Radius = %f \n", ER);
for (n = 1; n < 101; n++)
{
time (&start);
distance = pow (2.0, -n);
printf ("n= %3d distance = %e = %.20f ", n, distance, distance);
z1x = zfx + distance;
LastIteration = GiveLastIteration (z1x, z1y, cx, cy, ER2);
time (&end);
dif = difftime (end, start);
printf ("LI = %3.0f time = %2.0lf seconds\n", LastIteration, dif);
}
return 0;
}
|
| C source code for CPU one thread - hyperbolic case and double numbers . Click on the right to view |
|---|
/*
gcc -lm -Wall p.c
./a.out
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h> /* pow () */
#include <time.h>
double GiveLastIteration(double Zx, double Zy, double Cx, double Cy, int ER2)
{
double Zx2, Zy2; /* Zx2 = Zx * Zx; Zy2 = Zy * Zy */
double i = 0.0;
Zx2 = Zx * Zx;
Zy2 = Zy * Zy;
while (Zx2 + Zy2 < ER2) /* ER2 = ER * ER */
{
Zy = 2 * Zx * Zy + Cy;
Zx = Zx2 - Zy2 + Cx;
Zx2 = Zx * Zx;
Zy2 = Zy * Zy;
i += 1.0;
}
return i;
}
int main ()
{
double distance;
int n;
// fixed point zf = zfx = zfy*I = 1.0 for c=0
double zfx = 1.0;
double zfy = 0.0;
// z1 = z1x + z1y*I = point of exterior of Julia set but near parabolic fixed point zp
double z1x;
double z1y = zfy;
double cx= 0.0;
double cy= 0.0;
// Escape Radius ; it defines target set = { z: abs(z)>ER}
// all points z in the target set are escaping to infinity
double ER = 2.0;
double ER2;
double LastIteration;
time_t start,end;
double dif;
ER2 = ER * ER;
printf ("Using c with double and Escape Radius = %f \n", ER);
for (n = 1; n < 101; n++)
{
time (&start);
distance = pow (2.0, -n);
printf("n= %3d distance = %e = %.20f ", n, distance, distance);
z1x = zfx + distance;
LastIteration = GiveLastIteration (z1x, z1y, cx, cy, ER2);
time (&end);
dif = difftime (end, start);
printf("LI = %3.0f time = %2.0lf seconds\n", LastIteration, dif);
}
return 0;
}
|
| C source code for CPU one thread - hyperbolic case and long double numbers . Click on the right to view |
|---|
/*
gcc -lm -Wall p.c
./a.out
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h> /* pow () */
#include <time.h>
long double GiveLastIteration (long double Zx0, long double Zy0, long double Cx, long double Cy, int ER2)
{
long double Zx2, Zy2; /* Zx2 = Zx * Zx; Zy2 = Zy * Zy */
long double Zx = Zx0;
long double Zy = Zy0;
long double i = 0.0;
Zx2 = Zx * Zx;
Zy2 = Zy * Zy;
while (Zx2 + Zy2 < ER2) /* ER2 = ER * ER */
{
Zy = 2 * Zx * Zy + Cy;
Zx = Zx2 - Zy2 + Cx;
Zx2 = Zx * Zx;
Zy2 = Zy * Zy;
i += 1.0;
}
return i;
}
int main ()
{
long double distance;
int n;
/* fixed point zp = zpx = zpy * I = 1.0 for c = 0 */
long double zpx = 1.0;
long double zpy = 0.0;
/* z1 = z1x + z1y * I = point of exterior of Julia set but near parabolic fixed point zp */
long double z1x;
long double z1y = zpy;
long double cx = 0.0;
long double cy = 0.0;
/* Escape Radius ; it defines target set = { z: abs(z) > ER}
all points z in the target set are escaping to infinity */
long double ER = 2.0;
long double ER2;
long double LastIteration;
time_t start,end;
long double dif;
ER2 = ER * ER;
printf ("Using c with long double and Escape Radius = %Lf \n", ER);
for (n = 1; n < 101; n++)
{
time (&start);
distance = pow (2.0, -n);
z1x = zpx + distance;
LastIteration = GiveLastIteration (z1x, z1y, cx, cy, ER2);
time (&end);
dif = difftime (end, start);
printf("n= %3d distance = %Le = %.10Lf LI = %10.0Lf log2(LI) = %3.0Lf time = %2.0Lf seconds\a\n", n, distance, distance, LastIteration, log2l (LastIteration), dif);
}
return 0;
}
|
| C source code for CPU one thread - parabolic case and float numbers . Click on the right to view |
|---|
/*
gcc -lm -Wall p.c
./a.out
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h> /* pow () */
#include <time.h>
float GiveLastIteration (float Zx0, float Zy0, float Cx, float Cy, int ER2)
{
float Zx2, Zy2; /* Zx2=Zx*Zx; Zy2=Zy*Zy */
float Zx = Zx0;
float Zy = Zy0;
float i = 0.0;
Zx2 = Zx * Zx;
Zy2 = Zy * Zy;
while (Zx2 + Zy2 < ER2) /* ER2 = ER * ER */
{
Zy = 2 * Zx * Zy + Cy;
Zx = Zx2 - Zy2 + Cx;
Zx2 = Zx * Zx;
Zy2 = Zy * Zy;
i += 1.0;
}
return i;
}
int main ()
{
float distance;
int n;
// parabolic fixed point zp = zpx = zpy*I = 0.5 for c=1/4
float zpx = 0.5;
float zpy = 0.0;
// z1 = z1x + z1y*I = point of exterior of Julia set but near parabolic fixed point zp
float z1x;
float z1y = zpy;
float cx = 0.25;
float cy = 0.0;
/* Escape Radius ; it defines target set = { z: abs(z) > ER}
all points z in the target set are escaping to infinity */
float ER = 2.0;
float ER2;
float LastIteration;
time_t start, end;
float dif;
ER2= ER*ER;
printf ("Using c with float and Escape Radius = %f \n", ER);
for (n = 1; n < 101; n++)
{
time (&start);
distance = pow (2.0, -n);
z1x = zpx + distance;
LastIteration = GiveLastIteration (z1x, z1y, cx, cy, ER2);
time (&end);
dif = difftime (end, start);
printf("n= %3d distance = %e = %.10f LI = %10.0f log2(LI) = %3.0f time = %2.0lf seconds\n", n, distance, distance, LastIteration, log2 (LastIteration), dif);
}
return 0;
}
|
| C source code for CPU one thread - parabolic case and double numbers . Click on the right to view |
|---|
/*
* gcc -lm -Wall p.c
* ./a.out
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h> /* pow () */
#include <time.h>
double
GiveLastIteration(double Zx0, double Zy0, double Cx, double Cy, int ER2)
{
double Zx2 , Zy2; /* Zx2 = Zx * Zx; Zy2 = Zy * Zy */
double Zx = Zx0;
double Zy = Zy0;
double i = 0.0;
Zx2 = Zx * Zx;
Zy2 = Zy * Zy;
while (Zx2 + Zy2 < ER2) { /* ER2 = ER * ER */
Zy = 2 * Zx * Zy + Cy;
Zx = Zx2 - Zy2 + Cx;
Zx2 = Zx * Zx;
Zy2 = Zy * Zy;
i += 1.0;
}
return i;
}
double
max(double a, double b)
{
if (a > b)
return a;
else
return b;
}
int
main()
{
double distance;
int n;
//parabolic fixed point zp = zpx = zpy * I = 0.5 for c = 1 / 4
double zpx = 0.5;
double zpy = 0.0;
//z1 = z1x + z1y * I = point of exterior of Julia set but near parabolic fixed point zp
double z1x;
double z1y = zpy;
double cx = 0.25;
double cy = 0.0;
//Escape Radius; it defines target set = {z:abs(z) > ER}
//all points z in the target set are escaping to infinity
double ER = 2.0;
double ER2;
double LastIteration;
time_t start , end;
double dif;
ER2 = ER * ER;
for (n = 1; n < 101; n++) {
time(&start);
distance = pow(2.0, -n);
z1x = zpx + distance;
LastIteration = GiveLastIteration(z1x, z1y, cx, cy, ER2);
time(&end);
dif = difftime(end, start);
printf("n= %3d distance = %e = %.10f LI = %10.0f log2(LI) = %3.0f time = %2.0lf seconds\n",
n, distance, distance, LastIteration, log2(LastIteration), dif);
}
return 0;
}
|
| C source code for CPU one thread - parabolic case and long double numbers . Click on the right to view |
|---|
/*
* gcc -lm -Wall p.c
* ./a.out
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h> /* pow () */
#include <time.h>
long double
GiveLastIteration(long double Zx0, long double Zy0, long double Cx, long double Cy, int ER2)
{
long double Zx2, Zy2; /* Zx2 = Zx * Zx; Zy2 = Zy * Zy */
long double Zx = Zx0;
long double Zy = Zy0;
long double i = 0.0;
Zx2 = Zx * Zx;
Zy2 = Zy * Zy;
while (Zx2 + Zy2 < ER2) { /* ER2 = ER * ER */
Zy = 2 * Zx * Zy + Cy;
Zx = Zx2 - Zy2 + Cx;
Zx2 = Zx * Zx;
Zy2 = Zy * Zy;
i += 1.0;
}
return i;
}
int
main()
{
long double distance;
int n;
//parabolic fixed point zp = zpx = zpy * I = 0.5 for c = 1 / 4
long double zpx = 0.5;
long double zpy = 0.0;
//z1 = z1x + z1y * I = point of exterior of Julia set but near parabolic fixed point zp
long double z1x;
long double z1y = zpy;
long double cx = 0.25;
long double cy = 0.0;
//Escape Radius; it defines target set = {z:abs(z) > ER}
//all points z in the target set are escaping to infinity
long double ER = 2.0;
long double ER2;
long double LastIteration;
time_t start , end;
long double dif;
ER2 = ER * ER;
for (n = 1; n < 101; n++) {
time(&start);
distance = pow(2.0, -n);
z1x = zpx + distance;
LastIteration = GiveLastIteration(z1x, z1y, cx, cy, ER2);
time(&end);
dif = difftime(end, start);
printf("n= %3d distance = %Le = %.10Lf LI = %10.0Lf log2(LI) = %3.0Lf time = %2.0Lf seconds\a\n", n, distance, distance, LastIteration, log2l(LastIteration), dif);
}
return 0;
}
|
| C source code for CPU one thread - parabolic case and GSL library . Click on the right to view |
|---|
/*
* http://www.gnu.org/software/gsl/
*
* gcc -L/usr/lib -lgsl -lgslcblas -lm -Wall pgsl.c
* ./a.out
*
* or
* GSL_IEEE_MODE="extended-precision" ./a.out
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h> /* pow () */
#include <gsl/gsl_complex.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_complex_math.h>
#include <time.h>
long double
GiveLastIteration(gsl_complex z, gsl_complex c, int ER2)
{
long double i = 0.0;
while (gsl_complex_abs2(z) < ER2) { /* ER2 = ER * ER */
z = gsl_complex_add(c, gsl_complex_mul(z, z));
i += 1.0;
}
return i;
}
int
main()
{
//long double distance;
int n;
//parabolic fixed point zp = zpx = zpy * I = 0.5 for c = 1 / 4
gsl_complex zp = gsl_complex_rect(0.5, 0.0);
//long double zpx = 0.5;
//long double zpy = 0.0;
//z1 = z1x + z1y * I = point of exterior of Julia set but near parabolic fixed point zp
gsl_complex z1;
//long double z1x;
//long double z1y = zpy;
//
gsl_complex c = gsl_complex_rect(0.25, 0.0);
//long double cx = 0.25;
//long double cy = 0.0;
//Escape Radius; it defines target set = {z:abs(z) > ER}
//all points z in the target set are escaping to infinity
long double ER = 2.0;
long double ER2;
long double LastIteration;
time_t start , end;
long double dif;
ER2 = ER * ER;
for (n = 1; n < 101; n++) {
time(&start);
z1 = gsl_complex_rect(GSL_REAL(zp) + pow(2.0, -n), 0.0);
LastIteration = GiveLastIteration(z1, c, ER2);
time(&end);
dif = difftime(end, start);
printf("n= %3d LI = %10.0Lf log2(LI) = %3.0Lf time = %2.0Lf seconds\a\n", n, LastIteration, log2l(LastIteration), dif);
}
return 0;
}
|
| C source code for CPU one thread - parabolic case and mpfr library . Click on the right to view |
|---|
/*
* gcc -lm -lmpfr -lgmp -Wall -O2 pmpfr.c ./a.out
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h> // log2
#include <gmp.h>
#include <mpfr.h>
#include <time.h>
// MPFR general settings
mpfr_prec_t precision = 12;
//the number of bits used to represent the significand of a floating - point number
mpfr_rnd_t RoundMode = MPFR_RNDD;
//the way to round the result of a floating - point operation, round toward minus infinity(roundTowardNegative in IEEE 754 - 2008),
double
GiveLastIteration_mpfr (mpfr_t zx,
mpfr_t zy, mpfr_t cx, mpfr_t cy, mpfr_t ER2)
{
double i = 0.0;
mpfr_t temp;
//temporary variable
mpfr_t zx2;
//zx ^ 2
mpfr_t zy2;
//zy ^ 2
// initializes MPFR variables with default_prec
mpfr_inits (temp, zx2, zy2, (mpfr_ptr) 0);
mpfr_mul (zy2, zy, zy, RoundMode); /* zy2 = zy * zy; */
mpfr_mul (zx2, zx, zx, RoundMode); /* zx2 = zx * zx; */
mpfr_add (temp, zx2, zy2, RoundMode);
//temp = zx2 + zy2
while (mpfr_greater_p (ER2, temp))
//while (Zx2 + Zy2 < ER2
{
/* zy = 2.0*zx*zy + cy; */
mpfr_mul (temp, zx, zy, RoundMode);
//temp = zx * zy
mpfr_mul_ui (temp, temp, 2.0, RoundMode);
//temp = 2 * temp = 2 * zx * zy
mpfr_add (zy, temp, cy, RoundMode);
/* zx = zx^2 - zy^2 + cx; */
mpfr_sub (temp, zx2, zy2, RoundMode);
//temp = zx ^ 2 - zy ^ 2
mpfr_add (zx, temp, cx, RoundMode);
//temp = temp + cx
mpfr_mul (zy2, zy, zy, RoundMode); /* zy2 = zy * zy; */
mpfr_mul (zx2, zx, zx, RoundMode); /* zx2 = zx * zx; */
mpfr_add (temp, zx2, zy2, RoundMode);
//temp = zx2 + zy2
i += 1.0;
}
mpfr_clears (temp, zx2, zy2, (mpfr_ptr) 0);
return i;
}
int
main (void)
{
//declares variables
double LastIteration;
time_t start, end;
double dif;
int n;
mpfr_t zpx, zpy;
//parabolic fixed point zp = zpx + zpy * I = 0.5 for c = 1 / 4 mpfr_t zx, zy;
//point z = zx + zy * I
mpfr_t distance;
//between zp and z
mpfr_t cx, cy;
//point c = cx + cy *
mpfr_t base;
mpfr_t ER;
/*
* Escape Radius; it defines target set = {z:abs(z) > ER}; all points
* z in the target set are escaping to infinity
*/
mpfr_t ER2;
/* ER2 = ER * ER */
mpfr_set_default_prec (precision);
//initializes MPFR variables with default_prec
mpfr_inits (ER, ER2, zpx, zpy, zx, zy, distance, cx, cy, base,
(mpfr_ptr) 0);
//Assignment Functions
mpfr_set_ld (zpx, 0.5, RoundMode);
mpfr_set_ld (zpy, 0.0, RoundMode);
mpfr_set_ld (zy, 0.0, RoundMode);
mpfr_set_ld (cx, 0.25, RoundMode);
mpfr_set_ld (cy, 0.0, RoundMode);
mpfr_set_ld (base, 2.0, RoundMode);
mpfr_set_ld (ER, 2.0, RoundMode);
//computations
mpfr_mul (ER2, ER, ER, RoundMode);
mpfr_printf
("Using MPFR-%s with GMP-%s with precision = %u bits and Escape Radius = %Rf \n",
mpfr_version, gmp_version, (unsigned int) precision, ER);
for (n = 1; n <= 60; n++)
{
time (&start);
mpfr_pow_si (distance, base, -n, RoundMode);
mpfr_add (zx, zpx, distance, RoundMode);
LastIteration = GiveLastIteration_mpfr (zx, zy, cx, cy, ER2);
time (&end);
dif = difftime (end, start);
mpfr_printf
("n = %3d distance = %.10Re LI = %10.0f log2(LI) = %3.0f; time = %2.0f seconds \n",
n, distance, LastIteration, log2 (LastIteration), dif);
}
//free the space used by the MPFR variables
mpfr_clears (ER, ER2, zpx, zpy, zx, zy, distance, cx, cy, base,
(mpfr_ptr) 0);
mpfr_free_cache (); /* free the cache for constants like pi */
return 0;
}
|
Results
| float (24) | double (53) | long double (64) | MPFR (80) | MPFR (100) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hyperbolic | 23 | 52 | 63 | 79 | 99 |
| parabolic | 12 | 26 | 32 |
The results for standard C types ( float, double, long double) and MPFR precision are the same for the same precision
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 24 | 53 | 64 | 80 | 100 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hyperbolic | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 24 | 53 | 64 | 80 | 100 |
| parabolic | 3 | 5 | 10 | 19 | 35 | 16 778 821 |
Relation between number of iterations and time of computation in hyperbolic case :
Using MPFR-3.0.0-p8 with GMP-4.3.2 with precision = 128 bits and Escape Radius = 2.000000 n = 1 distance = 5.0000000000e-01 LI = 1 log2(LI) = 0; time = 0 seconds n = 2 distance = 2.5000000000e-01 LI = 2 log2(LI) = 1; time = 0 seconds n = 3 distance = 1.2500000000e-01 LI = 3 log2(LI) = 2; time = 0 seconds n = 4 distance = 6.2500000000e-02 LI = 4 log2(LI) = 2; time = 0 seconds n = 5 distance = 3.1250000000e-02 LI = 5 log2(LI) = 2; time = 0 seconds n = 6 distance = 1.5625000000e-02 LI = 6 log2(LI) = 3; time = 0 seconds n = 7 distance = 7.8125000000e-03 LI = 7 log2(LI) = 3; time = 0 seconds n = 8 distance = 3.9062500000e-03 LI = 8 log2(LI) = 3; time = 0 seconds n = 9 distance = 1.9531250000e-03 LI = 9 log2(LI) = 3; time = 0 seconds n = 10 distance = 9.7656250000e-04 LI = 10 log2(LI) = 3; time = 0 seconds n = 11 distance = 4.8828125000e-04 LI = 11 log2(LI) = 3; time = 0 seconds n = 12 distance = 2.4414062500e-04 LI = 12 log2(LI) = 4; time = 0 seconds n = 13 distance = 1.2207031250e-04 LI = 13 log2(LI) = 4; time = 0 seconds n = 14 distance = 6.1035156250e-05 LI = 14 log2(LI) = 4; time = 0 seconds n = 15 distance = 3.0517578125e-05 LI = 15 log2(LI) = 4; time = 0 seconds n = 16 distance = 1.5258789062e-05 LI = 16 log2(LI) = 4; time = 0 seconds n = 17 distance = 7.6293945312e-06 LI = 17 log2(LI) = 4; time = 0 seconds n = 18 distance = 3.8146972656e-06 LI = 18 log2(LI) = 4; time = 0 seconds n = 19 distance = 1.9073486328e-06 LI = 19 log2(LI) = 4; time = 0 seconds n = 20 distance = 9.5367431641e-07 LI = 20 log2(LI) = 4; time = 0 seconds n = 21 distance = 4.7683715820e-07 LI = 21 log2(LI) = 4; time = 0 seconds n = 22 distance = 2.3841857910e-07 LI = 22 log2(LI) = 4; time = 0 seconds n = 23 distance = 1.1920928955e-07 LI = 23 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 24 distance = 5.9604644775e-08 LI = 24 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 25 distance = 2.9802322388e-08 LI = 25 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 26 distance = 1.4901161194e-08 LI = 26 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 27 distance = 7.4505805969e-09 LI = 27 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 28 distance = 3.7252902985e-09 LI = 28 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 29 distance = 1.8626451492e-09 LI = 29 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 30 distance = 9.3132257462e-10 LI = 30 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 31 distance = 4.6566128731e-10 LI = 31 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 32 distance = 2.3283064365e-10 LI = 32 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 33 distance = 1.1641532183e-10 LI = 33 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 34 distance = 5.8207660913e-11 LI = 34 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 35 distance = 2.9103830457e-11 LI = 35 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 36 distance = 1.4551915228e-11 LI = 36 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 37 distance = 7.2759576142e-12 LI = 37 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 38 distance = 3.6379788071e-12 LI = 38 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 39 distance = 1.8189894035e-12 LI = 39 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 40 distance = 9.0949470177e-13 LI = 40 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 41 distance = 4.5474735089e-13 LI = 41 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 42 distance = 2.2737367544e-13 LI = 42 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 43 distance = 1.1368683772e-13 LI = 43 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 44 distance = 5.6843418861e-14 LI = 44 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 45 distance = 2.8421709430e-14 LI = 45 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 46 distance = 1.4210854715e-14 LI = 46 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 47 distance = 7.1054273576e-15 LI = 47 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 48 distance = 3.5527136788e-15 LI = 48 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 49 distance = 1.7763568394e-15 LI = 49 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 50 distance = 8.8817841970e-16 LI = 50 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 51 distance = 4.4408920985e-16 LI = 51 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 52 distance = 2.2204460493e-16 LI = 52 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 53 distance = 1.1102230246e-16 LI = 53 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 54 distance = 5.5511151231e-17 LI = 54 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 55 distance = 2.7755575616e-17 LI = 55 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 56 distance = 1.3877787808e-17 LI = 56 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 57 distance = 6.9388939039e-18 LI = 57 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 58 distance = 3.4694469520e-18 LI = 58 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 59 distance = 1.7347234760e-18 LI = 59 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 60 distance = 8.6736173799e-19 LI = 60 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 61 distance = 4.3368086899e-19 LI = 61 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 62 distance = 2.1684043450e-19 LI = 62 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 63 distance = 1.0842021725e-19 LI = 63 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 64 distance = 5.4210108624e-20 LI = 64 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 65 distance = 2.7105054312e-20 LI = 65 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 66 distance = 1.3552527156e-20 LI = 66 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 67 distance = 6.7762635780e-21 LI = 67 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 68 distance = 3.3881317890e-21 LI = 68 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 69 distance = 1.6940658945e-21 LI = 69 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 70 distance = 8.4703294725e-22 LI = 70 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 71 distance = 4.2351647363e-22 LI = 71 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 72 distance = 2.1175823681e-22 LI = 72 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 73 distance = 1.0587911841e-22 LI = 73 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 74 distance = 5.2939559203e-23 LI = 74 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 75 distance = 2.6469779602e-23 LI = 75 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 76 distance = 1.3234889801e-23 LI = 76 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 77 distance = 6.6174449004e-24 LI = 77 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 78 distance = 3.3087224502e-24 LI = 78 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 79 distance = 1.6543612251e-24 LI = 79 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 80 distance = 8.2718061255e-25 LI = 80 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 81 distance = 4.1359030628e-25 LI = 81 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 82 distance = 2.0679515314e-25 LI = 82 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 83 distance = 1.0339757657e-25 LI = 83 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 84 distance = 5.1698788285e-26 LI = 84 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 85 distance = 2.5849394142e-26 LI = 85 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 86 distance = 1.2924697071e-26 LI = 86 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 87 distance = 6.4623485356e-27 LI = 87 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 88 distance = 3.2311742678e-27 LI = 88 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 89 distance = 1.6155871339e-27 LI = 89 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 90 distance = 8.0779356695e-28 LI = 90 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 91 distance = 4.0389678347e-28 LI = 91 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 92 distance = 2.0194839174e-28 LI = 92 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 93 distance = 1.0097419587e-28 LI = 93 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 94 distance = 5.0487097934e-29 LI = 94 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 95 distance = 2.5243548967e-29 LI = 95 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 96 distance = 1.2621774484e-29 LI = 96 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 97 distance = 6.3108872418e-30 LI = 97 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 98 distance = 3.1554436209e-30 LI = 98 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 99 distance = 1.5777218104e-30 LI = 99 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 100 distance = 7.8886090522e-31 LI = 100 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 101 distance = 3.9443045261e-31 LI = 101 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 102 distance = 1.9721522631e-31 LI = 102 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 103 distance = 9.8607613153e-32 LI = 103 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 104 distance = 4.9303806576e-32 LI = 104 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 105 distance = 2.4651903288e-32 LI = 105 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 106 distance = 1.2325951644e-32 LI = 106 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 107 distance = 6.1629758220e-33 LI = 107 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 108 distance = 3.0814879110e-33 LI = 108 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 109 distance = 1.5407439555e-33 LI = 109 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 110 distance = 7.7037197775e-34 LI = 110 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 111 distance = 3.8518598888e-34 LI = 111 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 112 distance = 1.9259299444e-34 LI = 112 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 113 distance = 9.6296497219e-35 LI = 113 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 114 distance = 4.8148248610e-35 LI = 114 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 115 distance = 2.4074124305e-35 LI = 115 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 116 distance = 1.2037062152e-35 LI = 116 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 117 distance = 6.0185310762e-36 LI = 117 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 118 distance = 3.0092655381e-36 LI = 118 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 119 distance = 1.5046327691e-36 LI = 119 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 120 distance = 7.5231638453e-37 LI = 120 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 121 distance = 3.7615819226e-37 LI = 121 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 122 distance = 1.8807909613e-37 LI = 122 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 123 distance = 9.4039548066e-38 LI = 123 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 124 distance = 4.7019774033e-38 LI = 124 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 125 distance = 2.3509887016e-38 LI = 125 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 126 distance = 1.1754943508e-38 LI = 126 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 127 distance = 5.8774717541e-39 LI = 127 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds
Parabolic case :
Using MPFR-3.0.0-p8 with GMP-4.3.2 with precision = 100 bits and Escape Radius = 2.000000 n = 1 distance = 5.0000000000e-01 LI = 3 log2(LI) = 2; time = 0 seconds n = 2 distance = 2.5000000000e-01 LI = 5 log2(LI) = 2; time = 0 seconds n = 3 distance = 1.2500000000e-01 LI = 10 log2(LI) = 3; time = 0 seconds n = 4 distance = 6.2500000000e-02 LI = 19 log2(LI) = 4; time = 0 seconds n = 5 distance = 3.1250000000e-02 LI = 35 log2(LI) = 5; time = 0 seconds n = 6 distance = 1.5625000000e-02 LI = 68 log2(LI) = 6; time = 0 seconds n = 7 distance = 7.8125000000e-03 LI = 133 log2(LI) = 7; time = 0 seconds n = 8 distance = 3.9062500000e-03 LI = 261 log2(LI) = 8; time = 0 seconds n = 9 distance = 1.9531250000e-03 LI = 518 log2(LI) = 9; time = 0 seconds n = 10 distance = 9.7656250000e-04 LI = 1031 log2(LI) = 10; time = 0 seconds n = 11 distance = 4.8828125000e-04 LI = 2055 log2(LI) = 11; time = 0 seconds n = 12 distance = 2.4414062500e-04 LI = 4104 log2(LI) = 12; time = 0 seconds n = 13 distance = 1.2207031250e-04 LI = 8201 log2(LI) = 13; time = 0 seconds n = 14 distance = 6.1035156250e-05 LI = 16394 log2(LI) = 14; time = 0 seconds n = 15 distance = 3.0517578125e-05 LI = 32778 log2(LI) = 15; time = 0 seconds n = 16 distance = 1.5258789062e-05 LI = 65547 log2(LI) = 16; time = 0 seconds n = 17 distance = 7.6293945312e-06 LI = 131084 log2(LI) = 17; time = 0 seconds n = 18 distance = 3.8146972656e-06 LI = 262156 log2(LI) = 18; time = 0 seconds n = 19 distance = 1.9073486328e-06 LI = 524301 log2(LI) = 19; time = 0 seconds n = 20 distance = 9.5367431641e-07 LI = 1048590 log2(LI) = 20; time = 1 seconds n = 21 distance = 4.7683715820e-07 LI = 2097166 log2(LI) = 21; time = 0 seconds n = 22 distance = 2.3841857910e-07 LI = 4194319 log2(LI) = 22; time = 2 seconds n = 23 distance = 1.1920928955e-07 LI = 8388624 log2(LI) = 23; time = 2 seconds n = 24 distance = 5.9604644775e-08 LI = 16777232 log2(LI) = 24; time = 6 seconds n = 25 distance = 2.9802322388e-08 LI = 33554449 log2(LI) = 25; time = 11 seconds n = 26 distance = 1.4901161194e-08 LI = 67108882 log2(LI) = 26; time = 21 seconds n = 27 distance = 7.4505805969e-09 LI = 134217747 log2(LI) = 27; time = 42 seconds n = 28 distance = 3.7252902985e-09 LI = 268435475 log2(LI) = 28; time = 87 seconds n = 29 distance = 1.8626451492e-09 LI = 536870932 log2(LI) = 29; time = 175 seconds n = 30 distance = 9.3132257462e-10 LI = 1073741845 log2(LI) = 30; time = 351 seconds n = 31 distance = 4.6566128731e-10 LI = 2147483669 log2(LI) = 31; time = 698 seconds n = 32 distance = 2.3283064365e-10 LI = 4294967318 log2(LI) = 32; time = 1386 seconds n = 33 distance = 1.1641532183e-10 LI = 8589934615 log2(LI) = 33; time = 2714 seconds n = 34 distance = 5.8207660913e-11 LI = 17179869207 log2(LI) = 34; time = 5595 seconds n = 35 distance = 2.9103830457e-11 LI = 34359738392 log2(LI) = 35; time = 11175 seconds n = 36 distance = 1.4551915228e-11 LI = 68719476762 log2(LI) = 36; time = 22081 seconds
Analysis
Maximal n in hyperbolic case is almost the same as the precision of the significand [27]
In parabolic case maximal is
Last Iteration ( escape time = iteration fro which abs(zn) > ER ) is : in hyperbolic case equal to n :
in parabolic case equal to 2^n :
Time of computations is proportional to number of iterations. In hyperbolic case is is short. In parabolic case grows quickly as number of iterations.
Checking one point if escapes in parabolic case :
- for n = 34 take about one hour ( 5 595 seconds )
- for n = 40 take about one day
- for n = 45 take about one month
- for n = 50 take about one year
Q&A
Why programs fails ?
Cancellation of significant digits[28] and loss of significance (LOS).[29][30]
The program fails because of limited precision of used number types. Addition of big (zp) and small number (distance) gives number which has more decimal digits then can be saved ( floating point type has only 7 decimal digits). Some of the most right digits are cancelled and iteration goes into an infinite loop.
For example : when using floating point in parabolic case lets take
float cx = 0.25;
float Zpx = 0.5;
float Zx ;
float distance;
float Zx2;
float n = 13;
so
distance = pow(2.0,-n); // = 1.2207031250e-04 = 0,00012207
It is greater then machine epsilon:[31]
distance > FLT_EPSILON // = pow(2, -24) = 5.96e-08 = 0,00000006
so this addition still works :
Zx = Zpx + distance; // adding big and small number gives 0,50012207
After multiplication it gives :
Zx2 = Zx*Zx; // = 0,250122
next step is addition. Because floating point format saves only 7 decimal digits it is truncated to :
Zx = Zx2 + cx; // = 0,500122 = Zp + (distance/2)
Here relative error is to big and
d2= 0.0000000149 // distance*distance
is smaller then FLT_EPSILON/2.0 = 0.0000000596;
Solution : increase precision !
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h> /* pow() */
#include <float.h> /* FLT_EPSILON */
#include <time.h>
#include <fenv.h> /* fegetround() */
int main()
{
float cx = 0.25;
/* Escape Radius ; it defines target set = { z: abs(z) > ER }
all points z in the target set are escaping to infinity */
float ER = 2.0;
float ER2;
time_t start, end;
float dif;
ER2= ER*ER;
float Zpx = 0.5;
float Zx; /* bad value = 0.5002; good value = 0.5004 */
float Zx2; /* Zx2=Zx*Zx */
float i = 0.0;
float d; /* distance between Zpx=1/2 and zx */
float d2; /* d2=d*d; */
int n = 13;
d = pow (2.0, -n);
Zx = Zpx + d;
d2 = d * d;
time (&start);
Zx2 = Zpx * Zpx + 2.0 * d * Zpx + d2;
printf ("Using c with float and Escape Radius = %f \n", ER);
printf ("Round mode is = %d \n", fegetround ());
printf ("i= %3.0f; Zx = %f; Zx2 = %10.8f ; d = %f ; d2 = %.10f\n", i, Zx, Zx2, d, d2);
if (d2 < (FLT_EPSILON / 2.0) )
{
printf("error : relative error to big and d2= %.10f is smaller then FLT_EPSILON/2.0 = %.10f; increase precision ! \a\n",
d2, FLT_EPSILON / 2.0);
return 1;
}
while (Zx2 < ER2) /* ER2=ER*ER */
{
Zx = Zx2 + cx;
d = Zx - Zpx;
d2 = d * d;
Zx2 = 0.25 + d + d2; /* zx2 = zx * zx = (zp + d) * (zp + d) = zp2 +2 * d * zp + d2 = 2.25 + d + d2 */
i += 1.0;
/* printf("i= %3.0f; Zx = %f; Zx2 = %10.8f ; d = %f ; d2 = %f \n", i,Zx, Zx2, d,d2); */
}
time (&end);
dif = difftime (end, start);
printf ("n = %d; distance = %3f; LI = %10.0f log2(LI) = %3.0f time = %2.0lf seconds\n", n, d, i, log2 (i), dif);
return 0;
}
Explanation in polish[32]
What precision do I need for escape test ?
Why MPFR / GMP is slower than standard library ?
Why parabolic dynamics is so weak ?
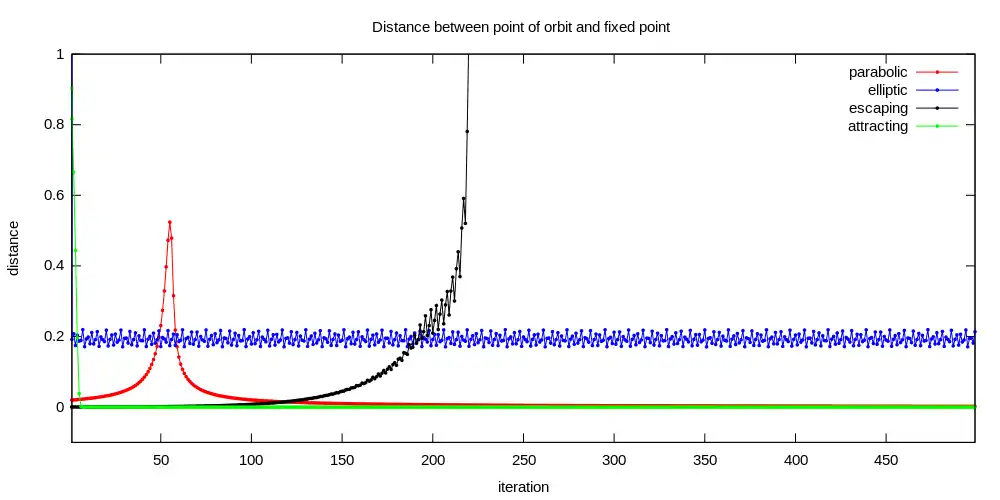 Distance to fixed point for various types of local discrete dynamics near fixed point . See how parabolic dynamics is complicated
Distance to fixed point for various types of local discrete dynamics near fixed point . See how parabolic dynamics is complicated Orbits near fixed point of fat Douady rabbit Julia set. See that to analyze one orbit one have to include period and petal
Orbits near fixed point of fat Douady rabbit Julia set. See that to analyze one orbit one have to include period and petal
Finding roots of equations
 Example image with code showing importance of precision in solving equations
Example image with code showing importance of precision in solving equations
Methods :
- Newton method
- "A useful way to visualize the roots of a complex function is to plot the 0 contours of the real and imaginary parts. That is, compute z = Dm(...) on a reasonably dense grid, and then use matplotlib's contour function to plot the contours where z.real is 0 and where z.imag is zero. The roots of the function are the points where these contours intersect." Warren Weckesser[33]
Papers:
Programs:
- Free Online Polynomials root finder (factoring)
- gsl : Example-programs-for-Multidimensional-Root-finding
- mpsolve
quadratic equation
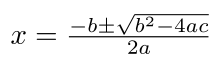
A quadratic equation (from the Latin quadratus for "square") is any equation having the form
where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c represent known numbers such that a is not equal to 0. If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic. The numbers a, b, and c are the coefficients of the equation, and may be distinguished by calling them, respectively, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant or free term.[34]
Although the quadratic formula provides an exact solution, the result is not exact if real numbers are approximated during the computation, as usual in numerical analysis, where real numbers are approximated by floating point numbers (called "reals" in many programming languages). In this context, the quadratic formula is not completely numerical stable.[35]
This occurs when :
- the roots have different order of magnitude, or, equivalently, when b2 and b2 − 4ac are close in magnitude. In this case, the subtraction of two nearly equal numbers will cause loss of significance or catastrophic cancellation in the smaller root. To avoid this, the root that is smaller in magnitude, r, can be computed as where R is the root that is bigger in magnitude.
- a second form of cancellation can occur between the terms b2 and 4ac of the discriminant, that is when the two roots are very close. This can lead to loss of up to half of correct significant figures in the roots.[36][37]
When the term inside the square root (the "Discriminant") goes negative, i.e.
if (b*b - 4*a*c < 0 ):
then doesn't have real roots, but have complex roots. ( see square root of negative number)
square root of Negative or complex number
If S is negative real numnber :
then its principal square root is
If S is a complex number : S = a+bi where a and b are real and b ≠ 0,
then its principal square root ( = the root with the non-negative real part) is :
where :
is the absolute value (modulus) of S.
Distance estimation
Example [40]
Zoom
What precision do I need for zoom ? [41][42][43][44]
- Pixel density [45]
- Pixel spacing is a distance between the centers of each two-dimensional pixel
/*
precision based on pixel spacing
code by Claude Heiland-Allen
http://mathr.co.uk/
*/
static void dorender(struct view *v, struct mandelbrot_image *image) {
mpfr_div_d(v->pixel_spacing, v->radius, G.height / 2.0, GMP_RNDN);
mpfr_t pixel_spacing_log;
mpfr_init2(pixel_spacing_log, 53);
mpfr_log2(pixel_spacing_log, v->pixel_spacing, GMP_RNDN);
int pixel_spacing_bits = -mpfr_get_d(pixel_spacing_log, GMP_RNDN);
mpfr_clear(pixel_spacing_log);
int interior = 1;
int float_type = 1;
if (interior) {
if (pixel_spacing_bits > 50 / 2) {
float_type = 2;
}
if (pixel_spacing_bits > 60 / 2) {
float_type = 3;
}
} else {
if (pixel_spacing_bits > 50) {
float_type = 2;
}
if (pixel_spacing_bits > 60) {
float_type = 3;
}
}
const char *float_type_str = 0;
switch (float_type) {
case 0: float_type_str = "float"; break;
case 1: float_type_str = "double"; break;
case 2: float_type_str = "long double"; break;
case 3: float_type_str = "mpfr"; break;
default: float_type_str = "?"; break;
}
One can check it using such program ( automatic math precision [46]) :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <gmp.h>
#include <mpfr.h>
/*
what precision of floating point numbers do I need
to draw/compute part of complex plane ( 2D rectangle ) ?
http://fraktal.republika.pl/mandel_zoom.html
https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Fractals/Computer_graphic_techniques/2D/plane
https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Fractals/Mathematics/Numerical
uses the code from
https://gitorious.org/~claude
by Claude Heiland-Allen
view = " cre cim radius"
view="-0.75 0 1.5"
view="0.275336142511115 6.75982538465039e-3 0.666e-5"
view="-0.16323108442468427133 1.03436384057374316916 1e-5"
gcc p.c -lmpfr -lgmp -Wall
*/
int main()
{
//declare variables
int height = 720;
int float_type ;
int pixel_spacing_bits;
mpfr_t radius;
mpfr_init2(radius, 53); //
mpfr_set_d(radius, 1.0e-15, GMP_RNDN);
mpfr_t pixel_spacing;
mpfr_init2(pixel_spacing, 53); //
mpfr_t pixel_spacing_log;
mpfr_init2(pixel_spacing_log, 53);
printf ("radius = "); mpfr_out_str (stdout, 10, 0, radius, MPFR_RNDD); putchar ('\n');
// compute
// int mpfr_div_d (mpfr_t rop, mpfr_t op1, double op2, mpfr_rnd_t rnd)
mpfr_div_d(pixel_spacing, radius, height / 2.0, GMP_RNDN);
printf ("pixel_spacing = "); mpfr_out_str (stdout, 10, 0, pixel_spacing, MPFR_RNDD); putchar ('\n');
mpfr_log2(pixel_spacing_log, pixel_spacing, MPFR_RNDN);
printf ("pixel_spacing_log = "); mpfr_out_str (stdout, 10, 0, pixel_spacing_log, MPFR_RNDD); putchar ('\n');
pixel_spacing_bits = -mpfr_get_d(pixel_spacing_log, GMP_RNDN);
printf ("pixel_spacing_bits = %d \n", pixel_spacing_bits);
float_type = 0;
if (pixel_spacing_bits > 40) float_type = 1;
if (pixel_spacing_bits > 50) float_type = 2;
if (pixel_spacing_bits > 60) float_type = 3;
switch (float_type) {
case 0: fprintf(stderr, "render using float \n"); break;
case 1: fprintf(stderr, "render using double \n"); break;
case 2: fprintf(stderr, "render using long double \n"); break;
case 3: fprintf(stderr, "render using MPFR - arbitrary precision \n");
}
return 0;
}
Tent map

Numerical error in computing orbit of the tent map with parameter m = 2. Aftere 50 iterations of double numbers all orbits fall into zero.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
/*
https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/2453939/is-this-characteristic-of-tent-map-usually-observed
gcc t.c -Wall
a@zelman:~/c/varia/tent$ ./a.out
*/
/* ------------ constans ---------------------------- */
double m = 2.0; /* parameter of tent map */
double a = 1.0; /* upper bound for randum number generator */
int iMax = 100;
/* ------------------- functions --------------------------- */
/*
tent map
*/
double f(double x0, double m){
double x1;
if (x0 < 0.5)
x1 = m*x0;
else x1 = m*(1.0 - x0);
return x1;
}
/* random double from 0.0 to a
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/13408990/how-to-generate-random-float-number-in-c
*/
double GiveRandom(double a){
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
return (((double)rand()/(double)(RAND_MAX)) * a);
}
int main(void){
int i = 0;
double x = GiveRandom(a); /* x0 = random */
for (i = 0; i<iMax; i++){
printf("i = %3d \t x = %.16f\n",i, x);
x = f(x,m); /* iteration of the tent map */
}
return 0;
}
Result:
i = 0 x = 0.1720333817284710 i = 1 x = 0.3440667634569419 i = 2 x = 0.6881335269138839 i = 3 x = 0.6237329461722323 i = 4 x = 0.7525341076555354 i = 5 x = 0.4949317846889292 i = 6 x = 0.9898635693778584 i = 7 x = 0.0202728612442833 i = 8 x = 0.0405457224885666 i = 9 x = 0.0810914449771332 i = 10 x = 0.1621828899542663 i = 11 x = 0.3243657799085327 i = 12 x = 0.6487315598170653 i = 13 x = 0.7025368803658694 i = 14 x = 0.5949262392682613 i = 15 x = 0.8101475214634775 i = 16 x = 0.3797049570730451 i = 17 x = 0.7594099141460902 i = 18 x = 0.4811801717078197 i = 19 x = 0.9623603434156394 i = 20 x = 0.0752793131687213 i = 21 x = 0.1505586263374425 i = 22 x = 0.3011172526748851 i = 23 x = 0.6022345053497702 i = 24 x = 0.7955309893004596 i = 25 x = 0.4089380213990808 i = 26 x = 0.8178760427981615 i = 27 x = 0.3642479144036770 i = 28 x = 0.7284958288073540 i = 29 x = 0.5430083423852921 i = 30 x = 0.9139833152294159 i = 31 x = 0.1720333695411682 i = 32 x = 0.3440667390823364 i = 33 x = 0.6881334781646729 i = 34 x = 0.6237330436706543 i = 35 x = 0.7525339126586914 i = 36 x = 0.4949321746826172 i = 37 x = 0.9898643493652344 i = 38 x = 0.0202713012695312 i = 39 x = 0.0405426025390625 i = 40 x = 0.0810852050781250 i = 41 x = 0.1621704101562500 i = 42 x = 0.3243408203125000 i = 43 x = 0.6486816406250000 i = 44 x = 0.7026367187500000 i = 45 x = 0.5947265625000000 i = 46 x = 0.8105468750000000 i = 47 x = 0.3789062500000000 i = 48 x = 0.7578125000000000 i = 49 x = 0.4843750000000000 i = 50 x = 0.9687500000000000 i = 51 x = 0.0625000000000000 i = 52 x = 0.1250000000000000 i = 53 x = 0.2500000000000000 i = 54 x = 0.5000000000000000 i = 55 x = 1.0000000000000000 i = 56 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 57 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 58 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 59 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 60 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 61 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 62 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 63 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 64 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 65 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 66 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 67 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 68 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 69 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 70 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 71 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 72 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 73 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 74 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 75 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 76 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 77 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 78 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 79 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 80 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 81 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 82 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 83 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 84 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 85 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 86 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 87 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 88 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 89 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 90 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 91 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 92 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 93 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 94 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 95 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 96 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 97 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 98 x = 0.0000000000000000 i = 99 x = 0.0000000000000000
See also
References
- ↑ mathoverflow question : /rounding-errors-in-images-of-julia-sets
- ↑ limit of series at gmane.org discussion
- ↑ math.stackexchange questions : levins-u-transformation
- ↑ math.stackexchange questions : accelerating-convergence-of-a-sequence
- ↑ gsl-1.0 : Series Acceleration
- ↑ gsl manual : Series-Acceleration
- ↑ Fractal Forum : series-acceleration
- ↑ wolframalpha series calculator
- ↑ stackoverflow : Dealing with lack of floating point precision in OpenCL particle system
- ↑ Heavy computing with GLSL – Part 5: Emulated quadruple precision by Henry Thasler
- ↑ Arb by Fredrik Johansson
- ↑ Computing π with Chudnovsky and GMP by Beej Jorgensen
- ↑ [:w:Extended precision: Extended precision in wikipedia]
- ↑ [:w:GNU MPFR|GNU MPFR in wikipedia]
- ↑ Significant Digits and Rounding Copyright © 2003–2014 by Stan Brown
- ↑ mathforum : Rules for Significant Figures and Decimal Places
- ↑ Roundoff Error Robert P. Munafo, 1996 Dec 3.
- ↑ wikipedia : Shadowing_lemma
- ↑ Wolf Jung's test for precision of drawing parameter rays
- ↑ One can find it using program Mandel by Wolf Jung using Ray to point menu position ( or Y key)
- ↑ Dynamics in one complex variable: introductory lectures version of 9-5-91 Appendix G by John W. Milnor
- ↑ Parabolic Julia Sets are Polynomial Time Computable Mark Braverman
- ↑ Roundoff Error by Robert P. Munafo, 1996 Dec 3.
- ↑ math.stackexchange questions : what-is-the-shape-of-parabolic-critical-orbit
- ↑ Parabolic Julia Sets are Polynomial Time Computable by Mark Braverman
- ↑ fractalforums : numerical-problem-with-bailout-test
- ↑ wikipedia :Floating point , EEE_754
- ↑ wikipedia : Significant figures
- ↑ wikipedia : Loss of significance
- ↑ IEEE Arithmetic from Numerical Computation Guide by Oracle
- ↑ Machine epsilon
- ↑ Dyskusja po polsku na pl.comp.os.linux.programowanie
- ↑ stackoverflow question : storing-roots-of-a-complex-function-in-an-array-in-scipy
- ↑ Protters & Morrey: " Calculus and Analytic Geometry. First Course"
- ↑ HOW DO YOU SOLVE A QUADRATIC EQUATION? BY GEORGE E._ FORSYTHE
- ↑ Kahan, Willian (November 20, 2004), On the Cost of Floating-Point Computation Without Extra-Precise Arithmetic
- ↑ Higham, Nicholas (2002), Accuracy and Stability of Numerical Algorithms (2nd ed.), SIAM, p. 10, ISBN 978-0-89871-521-7
- ↑ Abramowitz, Miltonn; Stegun, Irene A. (1964). Handbook of mathematical functions with formulas, graphs, and mathematical tables. Courier Dover Publications. p. 17. ISBN 0-486-61272-4. http://books.google.com/books?id=MtU8uP7XMvoC., Section 3.7.26, p. 17
- ↑ Cooke, Roger (2008). Classical algebra: its nature, origins, and uses. John Wiley and Sons. p. 59. ISBN 0-470-25952-3. http://books.google.com/books?id=lUcTsYopfhkC., Extract: page 59
- ↑ Precision and mandel zoom using DEM/M
- ↑ reenigne blog : arbitrary precision mandelbrot sets
- ↑ hpdz : Bignum by Michael Condron
- ↑ fractint : Arbitrary Precision and Deep Zooming
- ↑ chaospro documentation : parmparm
- ↑ Pixel density
- ↑ Automatic Math-Precision Robert P. Munafo, 1993 Apr 15.