Zapotlán el Grande
Zapotlán el Grande (also known as Guzmán and Ciudad Guzmán) is a municipality in the Mexican state of Jalisco.
Zapotlán el Grande | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) City Hall of Ciudad Guzmán, Municipality Seat of Zapotlán el Grande | |
 Flag  Seal | |
| Nickname: Athens of Jalisco | |
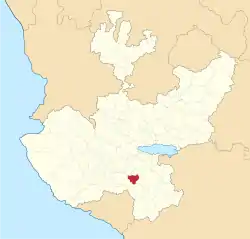 Location of the municipality in Jalisco | |
| Coordinates: 19°42′13″N 103°27′53″W | |
| County | |
| State | Jalisco |
| Government | |
| • Type | Municipality |
| • Municipal President | Lic. Alberto Esqueda Gutiérrez |
| • Presidential Office Coordinator | Lic. Bernardo Rodriguez Muñoz |
| Elevation | 1,507 m (4,944 ft) |
| Population (2015) | |
| • Total | 105,423 |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (CST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (CDT) |
| Website | http://www.zapotlan.gob.mx/ |
Name
There are several meanings given to the root name of the "Zapotlán el Grande". "Zapote" is the name given to all the round fruits from the general region; another well-known fact among the locals, it states The full name Zapotlán means "my round fruits" in the ancient language. Round sweet fruits, not exactly zapotes as most people believe; however, it means guavas, tunas, tejocotes, cherries found in this region and still found in the low, wet valleys. A new theory of the name is Tzapot, which ends with Tzapotlan, and it refers to the goddess of medicine named Tzaputlatena.
Image
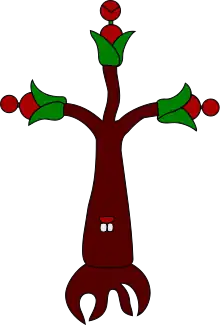
In 1971 the figure shown below became part of the city of Zapotlán el Grande, shown as a tree with three branches, with round fruits at the end of each branch and at the trunk a pair of teeth simulating a human mouth. This oil painting was embraced by the city officials under the administration of Lic. Genaro Álvarez López, who ordered this work of art to be displayed in the city hall. This work of art eventually became a representation of the city, indicating its strong ties with its ancestors of Zapotlán el Grande, also known as Ciudad Guzmán or plainly just Guzmán.
History
Prior to the arrival of the Spanish Conquistadors, this area was the pre-Columbian kingdom of Zapotlán and was at different times under the domain of the nearby kingdoms of Colima and Michoacán. Zapotlán el Grande was conquered in 1526. Many treasures and weapons are said to be buried throughout the town's old colonial homes, buildings, and farms. In the mid-19th century, the name of the town was changed from Zapotlán el Grande to Ciudad Guzman, after the Mexican federalist insurgent Gordiano De Guzmán.
The valley of Zapotlán was discovered by Friar Juan de Padilla who arrived to Tuxpan in 1532 in which he found three small towns. The small towns were Tzapotlán, Tlayolan, Tenamaxcatitlan and Mochitla. Friar Padilla settled down in Tenamaxcatitlan, where he taught the natives the Catholic doctrine. On August 15, 1533, the Spanish crown recognized the Pueblo de Santa Maria de la Asunción de Zapotlán in the place called the Portal de Sandoval.
Demographics

The city is located at 19°42′N 103°28′W, 124 km south of Guadalajara, at a height of 1,507 metres above sea level. Its population totaled 93,609 in the 2005 census, ranking as the sixth-largest city in the state. Other geographical location explanations are as follows the city is located south-central in the state of Jalisco, west-central of Mexico. It is placed between the Sierra de Tapalpa and the Cerro del Tigre. Between Puerto Vallarta and Guadalajara.
Tourism

From the beginning of the last century this important agricultural region became known for its unique geography and climate, that is inherently ideal for the abundant production of corn as well as for the commercial rearing of cattle. The general region has a noticeable French influence coalesced within the architecture of this Spanish colonial era settlement. This influence can be seen throughout the city, in the residences, municipal buildings, and public spaces. The Santa Catarina Hacienda, also a remnant from the Spanish colonial era, is one of the most popular and highly visited sites found in the region located just a few miles from the center of downtown Zapotlán. A site that is very popular among the locals is "El Nevado" National Park and wildlife preserve. Located approximately 33 miles southwest from the city. The period between the beginning of January and the later of February are the most popular and eventful times to enjoy "El Nevado" peak. "El Nevado", now dormant and the seventh highest mountain in Mexico is the higher and elder of the two volcanoes that comprise the Neo-Volcanic Cordela. The Volcano to its south is known as "El Volcan de Colima", or "El Volcan de Fuego" It has been active since June 1998 and thus, hiking on "El Volcan de Fuego" is dangerous and prohibited.
Zapotlán el Grande has been celebrating the customs and religious beliefs of thanksgiving adoring St Joseph for over 258 years. Señor Don José Prieto y Tovar committed himself to propagate the rituals of honoring the St. Joseph known in Spanish as "Señor San José" across America with the blessings of the archbishop Señor Don Geronimo Antonio de Obregón. Señor Obregón gave his superior permission on April 13, 1778 according to Cathedral of Nueva Granada, documentation located in Morelia, Michoacán, Mexico. This religious celebration gave birth to the "Fiestas de Octubre" begin on October 5–23. The "Fiestas de Octubre" offer sports activities, such as professional and amateur soccer, bullfighting till death, bicycle races, mariachi band competitions, the use of fighting cocks in cockfighting until one bird dies or both, animal exhibits, horse racing, girl beauty contests, and carnival rides totaling 19 days of celebration.

Elevation

Zapotlán el Grande is located at an elevation of 1530 meters above the sea level. It borders with six municipalities known as Gomes Farias towards the north, Tamazula de Gordiano towards the east, Zapotiltic is located on the southeast, Tuxpan is located south, Zapotiltic de Vadillo towards the east with San Gabriel. The municipality of Zapotlán el Grande has an area of 295.29 square kilometers.
Attractions
- "Fiestas de Octubre" 19 days of Fiesta time every October
- Museo Regional
- Santa Catarina
- "El Nevado" Mount icy Peak
- "Volcan de Fuego" Active volcano
- Casa de Artesanías Regionales (the official handicrafts shop)
Education (section in progress)
Postsecondary Institutions
Universidad de Guadalajara, Centro Universitario del Sur (Southern University center), commonly known as CUSUR. E stablished in 1994, after the previously existing veterinary school was integrated with the newly established medical school and law school. It belongs to the University of Guadalajara system; which has 10 campuses (9 regional centers) throughout the state. The university offers 2 technical careers in healthcare, 18 Bachelor's degrees (licenciaturas), 6 Master's degrees, and 2 PhD programs.
Instituto Technólogico de Ciudad Guzmán (ITCG) was established in 1972 and offers bachelor's degrees in engineering, including, environmental, electrical, electronical, mechanical, industrial, computer systems, information technology. The institute also offers degrees in architecture, accounting, business administration, as well as graduate studies in computer science and electronic engineering.
See also
- Cornish pasty
- Paste, the Mexican version of a Cornish pasty
References
- Link to tables of population data from Census of 2015 INEGI: Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática
- Official website
External links
Sister cities
 Longmont, Colorado, USA
Longmont, Colorado, USA