Vila Franca de Xira
Vila Franca de Xira (Portuguese pronunciation: [ˈvilɐ ˈfɾɐ̃kɐ ðɨ ˈʃiɾɐ] ⓘ) is a city and municipality in the Lisbon District in Portugal. The population in 2021 was 137,659,[1] in an area of 318.19 km2.[2]
Vila Franca de Xira | |
|---|---|
_(cropped).jpg.webp) .jpg.webp) .jpg.webp) .jpg.webp) .JPG.webp) .jpg.webp) | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 38°57′N 8°59′W | |
| Country | |
| Region | Lisbon |
| Metropolitan area | Lisbon |
| District | Lisbon |
| Parishes | 6 |
| Government | |
| • President | Alberto Mesquita (PS) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 318.19 km2 (122.85 sq mi) |
| Population (2021) | |
| • Total | 137,659 |
| • Density | 430/km2 (1,100/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC±00:00 (WET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+01:00 (WEST) |
| Local holiday | Ascension Day date varies |
| Website | www |
Situated on both banks of the Tagus River, 32 km north-east of the Portuguese capital Lisbon, settlement in the area dates back to neolithic times, as evidenced by findings in the Cave of Pedra Furada. Vila Franca de Xira is said to have been founded by French followers of Portugal's first king, Afonso Henriques, around 1200.
The town is mostly famous for its bull-running festivals in July and October. Bulls are raised in the salty marshlands of the Ribatejo, which is also a notable breeding ground for the Lusitano horse, esteemed for its quick reflexes and maneuverability. A number of brightly coloured Portuguese bullfighting costumes are on display in the ethnographic museum in the town's bullring, the Praça de Toiros (or Touros) Palha Blanco.
Notably, the town was the stage for the eponymous Vilafrancada in May of 1823. The Vilafrancada was an insurrection led by prince Miguel I of Portugal, son of King John VI of Portugal, which sought to reestablish an absolutist monarchy in Portugal. This came in response to the Portuguese Constitution of 1822 - the Kingdom's first constitution - which turned Portugal from an absolutist monarchy to a parlamentarian monarchy. The Vilafrancada can be seen as a prelude to the Portuguese Civil War of 1828-34.
In 1951, the town benefited from the completion of the Marechal Carmona Bridge. Located almost equidistantly between Lisbon and Santarém, The town provided an ideal place for a road bridge. The bridge was the first to cross the Tagus in the Lisbon region,[3] and remained its only crossing until the inauguration of the 25 de Abril Bridge fifteen years later. As a result, Vilafranca experienced greater traffic and commercial opportunities during this period.
Nearby, the town's Misericórdia church features striking 18th-century azulejos (glazed tiles). The town also has a Museum of Neo-Realism.[4]
Three km south of Vila Franca de Xira lies the Lezíria Grande Equestrian Centre, where visitors can watch stylish displays of the impressive Lusitano horses. The centre also stages typical bullfighting spectacles in its outdoor bullring. Visitors can ride Lusitano horses and take dressage lessons at the Quinta de São Sebastião, a sprawling estate at Arruda dos Vinhos, 11 km west of Vila Franca de Xira.
The municipality contains several forts built during the Peninsular War and forming part of the Lines of Torres Vedras. These include the Fort of Subserra on the first line of defence and the Forts of Serra da Aguieira and the Fort of Casa on the second line.
Another place of interest, on the left bank, is the Hermitage of Nossa Senhora de Alcamé, which was built so that farmers on the Tagus floodplain would both have somewhere to pray and also somewhere of safety during floods. An annual pilgrimage is held to the hermitage with participants going by boat from the town of Vila Franca de Xira on the right bank.
The current Mayor is Fernando Paulo Ferreira, elected in 2021 as a member of the Socialist Party.[5]
Climate
Vila Franca de Xira has a Mediterranean climate with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
| Climate data for Alverca do Ribatejo (air base), Vila Franca de Xira, 1961-1990, altitude: 2 m (6 ft 7 in) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 20.5 (68.9) |
22.5 (72.5) |
27.0 (80.6) |
29.4 (84.9) |
36.2 (97.2) |
43.5 (110.3) |
40.0 (104.0) |
39.0 (102.2) |
38.8 (101.8) |
33.0 (91.4) |
26.3 (79.3) |
22.2 (72.0) |
43.5 (110.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 14.6 (58.3) |
15.6 (60.1) |
17.8 (64.0) |
19.3 (66.7) |
22.0 (71.6) |
25.9 (78.6) |
28.8 (83.8) |
29.0 (84.2) |
27.9 (82.2) |
22.9 (73.2) |
18.1 (64.6) |
15.4 (59.7) |
21.4 (70.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 10.6 (51.1) |
11.7 (53.1) |
13.2 (55.8) |
14.8 (58.6) |
17.1 (62.8) |
20.4 (68.7) |
22.9 (73.2) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.1 (71.8) |
18.3 (64.9) |
14.1 (57.4) |
11.8 (53.2) |
16.7 (62.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 6.6 (43.9) |
7.8 (46.0) |
8.6 (47.5) |
10.3 (50.5) |
12.2 (54.0) |
14.9 (58.8) |
17.0 (62.6) |
17.2 (63.0) |
16.3 (61.3) |
13.7 (56.7) |
10.1 (50.2) |
8.2 (46.8) |
11.9 (53.4) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 93.0 (3.66) |
104.5 (4.11) |
43.6 (1.72) |
57.1 (2.25) |
41.9 (1.65) |
20.5 (0.81) |
5.2 (0.20) |
8.0 (0.31) |
18.4 (0.72) |
70.4 (2.77) |
73.8 (2.91) |
109.4 (4.31) |
645.8 (25.42) |
| Source: Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera[6] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Vila Franca de Xira Municipality (1801–2011) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1801 | 1849 | 1900 | 1930 | 1960 | 1981 | 1991 | 2001 | 2011 | 2021 |
| 3 839 | 5 202 | 15 766 | 24 053 | 40 594 | 88 193 | 103 571 | 122 908 | 136 886 | 137 659 |
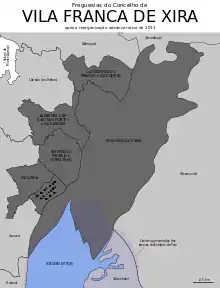
Parishes
Administratively, the municipality is divided into 6 civil parishes (freguesias):[7]
Notable people
.jpg.webp)
- Fernão Álvares da Maia (c.1390-1449) Portuguese nobleman, Lord of Pena, Aguiar, and Trofa
- Afonso de Albuquerque, 1st Duke of Goa (c.1453–1515) a Portuguese general, admiral and statesman; Governor of Portuguese India from 1509 to 1515.[8]
- José da Costa e Silva (1747–1819) a Portuguese neoclassical architect
- Dr José Tomás de Sousa Martins (1843 in Alhandra – 1897) a doctor, worked for the poor
- Reynaldo dos Santos (1880 in Rua das Varinas – 1970) a physician, writer, and art historian.
- Alves Redol (1911–1969) a Portuguese neorealist writer.[9]
- Octávio Pato (1925–1999) PCP activist and candidate in the 1976 presidential election
- Ivone Dias Lourenço (1937-2008) an opponent of Estado Novo Govt. & political prisoner
- Lili Caneças (born 1944) a Portuguese socialite.[10]
- Ana Cristina Silva (born 1964) a Portuguese psychologist, academic and prize-winning novelist.
- Paulo Brissos (born 1970) a Portuguese rock, blues, pop and adult contemporary singer.
- Núria Madruga (born 1980) a Portuguese actress and model.[11]
- Leonor Teles (born 1992) a Portuguese filmmaker.[12]
- Wet Bed Gang (formed 2011 in Vialonga) a Portuguese rap and hip hop tuga group
Sport
.jpg.webp)
- José Carlos (born 1941) a former footballer with 299 club caps and 36 for Portugal
- Bruno Patacas (born 1977) a Portuguese retired footballer with 343 club caps
- Nélson Veríssimo (born 1977) a Portuguese former footballer with 426 club caps and manager
- Pedro Torrão (born 1977) a Portuguese retired footballer with 312 club caps
- Helena Costa (born 1978 in Alhandra) a Portuguese football manager.
- Diogo Santos (born 1984) a Portuguese footballer with over 400 club caps
- Vera Barbosa (born 1989) a track and field athlete, competed at the 2012 Summer Olympics
- Tiago Gomes (born 1985) a Portuguese footballer with over 350 club caps
- Ana Catarina (born 1992) a Portuguese futsal goalkeeper
- Rafa Silva (born 1993) a Portuguese footballer with over 240 club caps and 23 for Portugal
References
- "Resultados Preliminares Censos 2021 INE". INE. Retrieved 7 October 2021.
- "Áreas das freguesias, concelhos, distritos e país". Archived from the original on 5 November 2018. Retrieved 5 November 2018.
- "Ponte de Vila Franca de Xira celebra hoje 55 anos". publico.pt (in Portuguese). 30 December 2006. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- Museu do Neo-Realismo Archived 2 April 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- O Mirante (local weekly paper)
- "Plano Municipal de Defesa da Floresta Contra Incêndios" (PDF). Vila Franca de Xira Municipality. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- Diário da República. "Law nr. 11-A/2013, page 552 131" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Retrieved 4 August 2014.
- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 01 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 516.
- Alves Redol, IMDb Database retrieved 05 July 2021.
- Lili Caneças, IMDb Database retrieved 05 July 2021.
- Nuria Madruga, IMDb Database retrieved 05 July 2021.
- Leonor Teles, IMDb Database retrieved 05 July 2021.
External links
- Official website (in Portuguese)
- Photos from Vila Franca de Xira