User journey
A user journey is the experiences a person has when interacting with something, typically software. This idea is generally used by those involved with user experience design, web design, user-centered design, or anyone else focusing on how users interact with software experiences. It is often used as a shorthand for the overall user experience and set of actions that one can take in software or other virtual experiences.
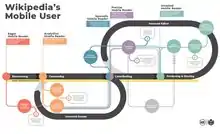
User journeys describe at a high level of detail exactly what steps different users take to complete a specific task within a system, application, or website. This technique shows the current (as-is) user workflow, and reveals areas of improvement for the to-be workflow. When documented, this is often referred to as a User Journey Map.[1]
User journeys are focused on the user and what they see and what they do, in comparison to the related web design term click path which is just a plain list of the text URLs that are hit when a user follows a particular Journey.[2][3]
Phases
The customer journey is divided into four phases which refer to the AIDA model.[4]
- Awareness Awareness for the product is awakened (inspiration)
- Interest The interest in the product is increased (favoritism)
- Desire The customer is considering buying the product (wish)
- Action The product is bought (implementation)
The customer journey can be used in marketing and communication, especially in digital channels, to minimize wastage and make communication more efficient (in technical jargon: conversion rate optimization).
The term "Customer Journey" is also increasingly being used in classic sales channels. In a retail store, for example, there are opportunities to present the product range to the customer so that he can touch it, to advise him personally, to enable a fast, relatively secure and, in the case of cash, anonymous payment process, to hand over the goods immediately after the sale and to offer him a friendly farewell. The stationary trade is striving to use these unique selling propositions in comparison to the mail order business in order to maintain market shares and is investigating how the customer journey can be improved even further to this end. Part of these considerations are also questions of how the possibilities of the Internet can be used for stationary trade. "Click and Collect", i.e. picking up goods ordered via the Internet in the store, or vice versa shipping selected items home from the store, and other mixed forms of the distribution channels "online" and "offline", which are summarized under the generic term "Omni Channel", play an important role in this context.
Benefits
The Customer Journey is particularly interesting in online marketing or digital channels, as here the behavior of the consumers can be precisely mapped with the help of tracking technologies. The technology of customer journey analysis provides the concrete benefit of uncovering all contact points created by advertising. With the insights gained from this, it is possible to uncover causal relationships between channels and contact points and to derive optimization potential. Related effects can occur in the form of both synergy and cannibalization effects.
With the findings of a customer journey analysis, it should also be clarified whether the last contact point alone was decisive for the purchase of a product or whether this was the result of an interaction or a certain sequence of several contacts and channels. This is possible because the Customer Journey not only records the last contact point, but the analysis covers all contact points in the medium Internet. Furthermore, it is also important what effect the channels have on each other or whether they are dependent on each other. Research on the customer journey provides new insights into the behavior and preferences of the target group with regard to their use of and reactions to advertising on the Internet. The new knowledge helps advertising companies and agencies to better allocate media budgets to the individual channels and to improve the efficiency of all activities of a company in online marketing.
Proactive communication is a strategy for the entire life cycle of customer relations to increase customer loyalty. This includes opt-in notifications and chats, easy accessibility in social media and contact possibilities via multiple communication channels. The strategy is applied in all phases of the customer lifecycle. The goal of proactive customer communication is to anticipate and optimize each interaction in order to make it efficient and personalize it for each individual customer.
In addition, processes that depict digital channels (e.g. advertising on the Internet) and the entire spectrum of so-called offline contact points (e.g. TV advertising, sponsoring, word of mouth, etc.) in equal measure - from the customer's perspective - are gaining in importance. The challenge is to capture all channels and touchpoints in one measurement system and in one and the same unit of measurement. This is where integrated approaches come into play, which do not focus exclusively on the online area, but create a comparable "currency" across all contact points with a brand.[5][6]
Function
Customer journey analysis requires exact data storage on consumer behavior in order to generate a valid survey. At present, tracking is usually carried out using cookies. Here it is important to distinguish between "session cookies" and "persistent cookies" as well as "first-party cookies" and "third-party cookies". The information about contact points is stored centrally in a database.
The recognition of customers in the "offline" world is attempted via customer cards and bonus programs such as Payback, but also via iBeacons, which identify visitors' mobile devices. The behavior of the buyer outside the Internet completes the presentation of his customer journey. This approach is hindered by the desire of many consumers to reveal as little about themselves as possible, or at least to expect something in return.[7][8]
Conceptual delimitation
The term Customer Journey is also associated with other subject areas, which do not concretely reflect the same benefits, but nevertheless show a connection.
- Online customer experience primarily refers to the online interface in the technical sense, which aims to optimize the navigation behavior of a website visitor and all interactions.[9]
- Customer Care is the management of existing customers with the essential part of the customer-oriented service offering and the goal of establishing the longest and most satisfying customer relationship possible.
- Touchpoint analysis describes all contact points of a buyer with a brand, a product and a service, no matter if the contact is made before, during or after the purchase.[10]
- Purchase-Funnel is used to optimize the conversion (conversion rate) on the website. So-called conversion paths map the movements of visitors along defined routes (click sequences).
- Multichannel Marketing refers to the parallel use of several marketing channels to provide services and to build and maintain customer relationships.
Problems
The difficulties in measuring a customer journey result from the technical specification of the measuring system. This refers to the tracking system currently used in the market via cookies. Developments in the Internet sector show that this system alone will not be able to hold its own in the long term in order to carry out valid data measurements. Additional measurement systems are needed to supplement missing data information.
The current challenges in marketing, communication and sales show that a measurement of the customer journey based purely on tracking data is not sufficient. It is a matter of answering cross-channel questions: e.g. how efficient is a company's print campaign compared to its appearance in social media, what role does personal recommendation play in the purchase decision process, etc.?
Here, as described above, integrated approaches that cover all activities of a company - whether online or offline - can help. Although a focus on online contact points often has an inviting effect, as these can be easily measured using tracking systems. But a pure "digital journey" only gives a partial picture of the overall process, since many interactions with a brand take place offline.[11][12]
References
- "Home". journeymap.com.
- "What is a User Journey? - thinkTribe | Web Performance". thinkTribe. Retrieved 2020-07-14.
- "Customer-Journey einfach erklärt: Definition, Modelle & FAQ". Aufgesang (in German). Retrieved 2020-07-14.
- "AIDA Model - Understand the Steps in the AIDA Model Hierarchy". Corporate Finance Institute. Retrieved 2020-07-14.
- "Top 5 Benefits Of Customer Journey Mapping". Knexus. 2017-03-21. Retrieved 2020-07-14.
- "Customer Journey Definition". en.ryte.com. Retrieved 2020-07-14.
- "Customer Journey Definition". en.ryte.com. Retrieved 2020-07-14.
- "Customer-Journey einfach erklärt: Definition, Modelle & FAQ". Aufgesang (in German). Retrieved 2020-07-14.
- "Online Customer Experience im E-Commerce". www.estrategy-magazin.de (in German). Retrieved 2020-07-14.
- "Touchpoint Analysis: How to Improve Customer Contact". www.zenloop.com. Retrieved 2020-07-14.
- "Was ist eine Customer Journey? - Ryte Wiki". de.ryte.com. Retrieved 2020-07-14.
- Davey, Neil (2014-10-30). "Seven reasons why customer journey mapping goes wrong". MyCustomer. Retrieved 2020-07-14.