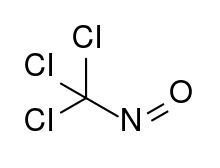
Trichloronitrosomethane
Trichloronitrosomethane is a chlorinated nitrosoalkane. It is a deep blue liquid with powerful lachrymatory effects.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
TL-358 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CCl3NO | |
| Molar mass | 148.37 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Deep blue liquid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Synthesis
Trichloronitrosomethane can be produced with following methods:[1][2]
- Oxidation of trichloromethylsulfinic acid with nitric acid.
- Reaction of sodium trichloromethylsulfinate with sodium nitrite and sodium nitrate or potassium nitrate in sulfuric acid.
- Pyrolysis of trichloroacethydroxamic acid.
Chemistry
Trichloronitrosomethane is an unstable substance. It slowly decomposes into nitrosyl chloride, nitrogen oxides, and chloropicrin over time.[1]
Trichloronitrosomethane can be reduced to phosgene oxime by hydrogen sulfide.[1]
References
- Sartori, Mario (1939). The War Gases (PDF).
- Sutcliffe, H. (September 1965). "The Synthesis of Trichloronitrosomethane". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 30 (9): 3221–3222. doi:10.1021/jo01020a516.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.