Thủ Đức
Thủ Đức is a municipal city (sub-city) under the administration of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.
Thủ Đức
Thành phố Thủ Đức | |
|---|---|
| Thủ Đức City | |
 Thủ Thiêm New Urban Area viewed from District 1 | |
| Nickname: Eastern City | |
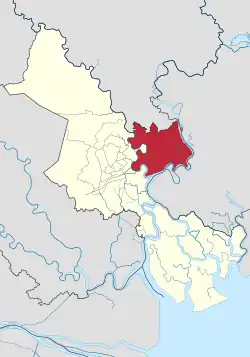 Location of Thu Duc City within Ho Chi Minh City | |
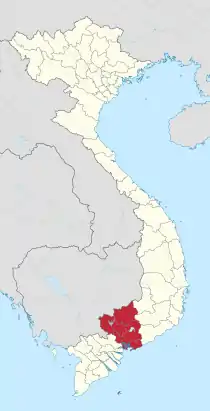
 Thủ Đức | |
| Coordinates: 10°49′35.62″N 106°45′39.23″E | |
| Country | |
| Municipality | Ho Chi Minh City |
| Founded | January 1, 2021 |
| Wards | 34 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Urban Governance |
| • Body | Thu Duc City People's Council |
| • Secretary of CPV | Nguyễn Văn Hiếu[1] |
| • Chairman of People's Council | Nguyễn Phước Hưng[2] |
| • Chairman of People's Committee | Hoàng Tùng[3] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 211.56 km2 (81.68 sq mi) |
| Population (2019) | |
| • Total | 1,013,795 |
| • Density | 4,800/km2 (12,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (Indochina Time) |
| Website | https://tpthuduc.hochiminhcity.gov.vn/ |
The city was founded by the Standing Committee of the National Assembly on December 9, 2020 from the districts of 2, 9, and Thủ Đức District.[4][5] Thu Duc City covers 211.56 km², the population as of 2019 was 1,013,795 inhabitants.[6][7] With the establishment of Thu Duc City, the main city will contribute more to the national economic growth and boost the development in Southern Key Economic Zone (SKEZ).[8]
This new city-within-city model has been used by many places in the world including financial center Canary Wharf in London, Silicon Valley in the United States, Gangnam in Seoul or Pudong in Shanghai, etc. It was suggested that Thu Duc should be given autonomy in decision making and policy incentives to develop innovation capacity to improve competitiveness like what China did to Shenzhen, whose economy now is larger than Hong Kong's.[9][10]
Administration
Thu Duc is a class-1 city of Ho Chi Minh City and the first city to use city-within-city model in Vietnam.[11][12]
Thủ Đức City has 34 wards: An Khánh, An Lợi Đông, An Phú, Bình Chiểu, Bình Thọ, Bình Trưng Đông, Bình Trưng Tây, Cát Lái, Hiệp Bình Chánh, Hiệp Bình Phước, Hiệp Phú, Linh Chiểu, Linh Đông, Linh Tây, Linh Trung, Linh Xuân, Long Bình, Long Phước, Long Thạnh Mỹ, Long Trường, Phú Hữu, Phước Bình, Phước Long A, Phước Long B, Tam Bình, Tam Phú, Tân Phú, Tăng Nhơn Phú A, Tăng Nhơn Phú B, Thạnh Mỹ Lợi, Thảo Điền, Thủ Thiêm, Trường Thạnh, Trường Thọ.[13][14]
After arrangement, Ho Chi Minh City consists of 22 district-level subdivisions including 1 city, 16 urban districts, and 5 rural districts. The further commune-level subdivisions would have 312 in total including 249 wards, 58 communes, 5 commune-level towns.[15]
Innovation Centers
There are eight innovation centers in total of Thu Duc city:[16][17][18][19][20][21]
- Thu Thiem Fintech Hub
- Truong Tho Port Urban Area
- Rach Chiec Sports and Wellness Hub
- National University IT and EduTech Hub
- Saigon Hi-Tech Park and Automated Manufacturing Hub
- Tam Da Ecotech Hub
- Creative Startup Center
- Traffic Hub connecting the Southeastern parts and Cat Lai International Port
Economy
Thu Duc City will contribute one third of Ho Chi Minh City's gross regional domestic product (GRDP) and account for 7 percent of the national gross domestic product (GDP), which is only behind Hanoi's GRDP in scale but higher than that of Binh Duong and Dong Nai.[15][22]
Infrastructure
Highway and Expressway
- Hà Nội Highway
- Ho Chi Minh City–Long Thanh–Dau Giay Expressway
- Ring Road 2
- Ring Road 3
Services
Facilities
During the existence of South Vietnam, it was the location of Thu Duc Military Academy.
- Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City
- Saigon Hi-Tech Park
- Cát Lái - Phú Hữu Port
- Suối Tiên Amusement Park
References
- Tá, Lâm (January 22, 2021). "Nguyen Van Hieu to become a secretary of Thu Duc City Communist Party of Vietnam" (in Vietnamese).
- "Nguyen Phuoc Hung to become a chairman of Thu Duc City People's Council" (in Vietnamese). January 22, 2021.
- Thanh, Tuyền; Lê, Thoa (January 22, 2021). "Hoang Tung to become a chairman of Thu Duc City People's Committee" (in Vietnamese).
- "Standing Committee of the National Assembly approved the establishment of Thu Duc City (in Vietnamese)". December 9, 2020.
- "Thu Duc City was approved by Standing Committee of the National Assembly (in Vietnamese)". December 9, 2020.
- "NA Standing Committee likely to approve proposal to establish Thu Duc City this week". The Saigon Times. 2020-12-09. Archived from the original on 2021-09-20. Retrieved 2020-12-09.
- "The founding of Thu Duc City)" (in Vietnamese). VnExpress. 2020-12-09. Retrieved 2020-12-09.
- Doan Loan, Hoang Thuy (December 9, 2020). "It's official: HCMC to get its Thu Duc City". VnExpress.
- Viet Anh (December 24, 2020). "What can make Thu Duc a successful city within a city?". VnExpress.
- "Seminar talks prospects, challenges of Thu Duc city". VietnamPlus. December 11, 2020.
- Huu, Cong (November 12, 2020). "HCMC set to carve out class-1 city by merging three districts". VnExpress.
- "Good governance essential for proposed new Thu Duc City: experts". VietNamNet Newspaper. December 10, 2020.
- "HCMC to announce establishment of Thu Duc City on Dec 31". VietNamNet Newspaper. December 28, 2020.
- Manh Hoa - Translated by Kim Khanh (December 28, 2020). "Thu Duc City not to charge fees of altering personal documents". Sài Gòn Giải Phóng.
- Đoàn, Loan; Viết, Tuân (December 9, 2020). "The establishment of Thu Duc City". VnExpress (in Vietnamese).
- VietNamNet (June 1, 2020). "City adjusts zoning plan for innovative hub".
- Kieu Phong - Translated by Kim Khanh (September 2, 2020). "Thu Duc City, an aspiration for HCMC's growth". Sài Gòn Giải Phóng.
- Christele, Harrouk (December 10, 2019). "Sasaki to Design Ho Chi Minh City Innovation District in Vietnam". ArchDaily.
- Minh, Hằng (December 9, 2020). "Eight important innovation centers of Thu Duc City (in Vietnamese)".
- Kiều, Phong (September 7, 2020). "Ho Chi Minh City status to grow with Thu Duc City".
- "Ho Chi Minh City Innovation District". Sasaki.
- "Resolution on establishment of Thu Duc City under Ho Chi Minh City announced". Nhân Dân. December 31, 2020.
- "New Eastern Bus Station in HCM City to open next month". VOV. September 24, 2020.
External links
- Resolution No.1111/NQ-UBTVQH14 on establishment of Thu Duc City under Ho Chi Minh City (in Vietnamese) by 14th Standing Committee of the National Assembly.