Tartarocyon
Tartarocyon is an extinct genus of Amphicyonidae, who lived during the late Middle Miocene. It was described after fossilized remains found in Sallespisse, France. Despite the scarceness of its fossil remains, being only known from the holotype mandible, its body mass has been estimated to be close to 200 kilograms, far from its closest relative, Cynelos, and making it one of the largest terrestrial predators of Miocene Europe.[1] T. cazanavei is the only species included in the genus.[2] The genus was named after a southwestern French Pyrenees legend of a man eating giant ; the species name honors the owner of the terrain in which the holotype has been discovered.[1][3]
| Tartarocyon | |
|---|---|
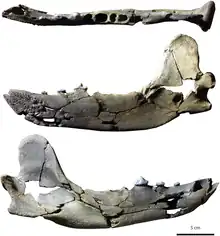 | |
| Tartarocyon cazanavei holotype | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | †Amphicyonidae |
| Genus: | †Tartarocyon Solé, Lesport, Heitz & Mennecart, 2022 |
| Species: | †T. cazanavei |
| Binomial name | |
| †Tartarocyon cazanavei Solé, Lesport, Heitz & Mennecart, 2022 | |

Life reconstruction of a pair of Tartarocyon cazanavei in their natural environment
References
- Solé, F.; Lesport, J.-F.; Heitz, A.; Mennecart, B. (2022). "A new gigantic carnivore (Carnivora, Amphicyonidae) from the late middle Miocene of France". PeerJ. 10: e13457. doi:10.7717/peerj.13457. PMC 9206431. PMID 35726261.
- "Gigantic Bear-Dogs Lived in France 12 Million Years Ago | Sci-News.com". Breaking Science News | Sci-News.com. 16 June 2022. Retrieved 2022-06-22.
- Pskhun (2022-06-18). "Species New to Science: [PaleoMammalogy • 2022] Tartarocyon cazanavei • A New Gigantic Carnivore (Carnivora, Amphicyonidae) from the late middle Miocene of France". Species New to Science. Retrieved 2022-06-22.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
