Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County
Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County
Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg vármegye | |
|---|---|
   | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
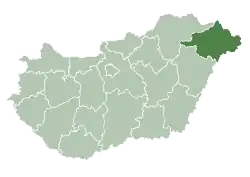 Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County within Hungary | |
| Country | |
| Region | Northern Great Plain |
| County seat | Nyíregyháza |
| Districts | |
| Government | |
| • President of the General Assembly | István Román (Fidesz-KDNP) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 5,935.83 km2 (2,291.84 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 6th in Hungary |
| Population (2018) | |
| • Total | 558,361[1] |
| • Rank | 3rd in Hungary |
| Postal code | 423x, 4244–4246, 4267, 43xx–49xx |
| Area code(s) | (+36) 42, 44, 45 |
| ISO 3166 code | HU-SZ |
| Website | www |
Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg (Hungarian: Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg vármegye, pronounced [ˈsɒbolt͡ʃ ˈsɒtmaːr ˈbɛrɛɡ]) is an administrative county (Hungarian: vármegye) in north-eastern Hungary, bordering Slovakia (Košice Region), Ukraine (Zakarpattia Oblast), and Romania (Bihor and Satu Mare counties). It shares borders with the Hungarian counties Hajdú-Bihar and Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén. The capital of Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg county is Nyíregyháza.
Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County was organised after World War II from the previous counties Szatmár-Ugocsa-Bereg and Szabolcs. Before 1991, it was called Szabolcs-Szatmár County.
Geography
Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg is located in the north-eastern tip of Hungary. It borders Ukraine (Zakarpattia Oblast), Slovakia (Košice Region), and Romania (Bihor and Satu Mare counties), and has good connections both by road and rail. Within Hungary, the county is bordered by Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén County and the Tisza River to the north-west and Hajdú-Bihar County to the south-west.
The early Hungarians transformed this region significantly by clearing large areas of forest to make way for pastures and farmland. Approximately 5 to 6 square kilometres of forest were cleared for the construction of the Szabolcs earthwork in the ninth and tenth centuries, and its ruins are still present. The area was the gateway for the Mongol invasion of Hungary in the 1240s, and suffered considerable destruction and population decrease during the raids. With the subsequent development of the country, the region became even more marginalized in the 15th century. Ongoing civil war, rebellion, and war exacted a heavy price and further hindered the region's development.
The county's borders have been altered frequently over the years, its current territory being established in 1950 with the amalgamation of the counties of Szabolcs-Ung and Szatmár-Bereg-Ugocsa.
There are many forests, fields, pastures, meadows, and moorland forests in the county. The bog moss moors at Csaroda, the Nyíres lake, and the Bábtava lake are especially valuable, as they contain many rare species of fauna and flora.
Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg is Hungary's sixth biggest county with a total land area of 5,936 square kilometres (2,292 square miles). From a geographical aspect, it is possible to divide the county into two main regions: The Upper Tisza Valley and the Nyírség. Tisza is one of the most important rivers of the county, entering Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg — and Hungary — at Tiszabecs, and leaving at Tiszadob. Its segment in Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg county is 235 kilometres long, out of which 208 kilometres (129 miles) belongs to the Upper Tisza Valley, reaching the area of Tokaj and Rakamaz. The larger area named the Nyírség is derived from the word nyír meaning birch, as the region is dominated by birch woodlands. The northern part of Nyírség is covered with sandy forest soils, the southern areas have loose wind-blown sand. Alluvial and meadow soils are found in the Upper Tisza region.
The county has a continental climate; it is cooler than the Great Plain because it is further north. Summers are cooler than in other parts of the Plains. Annual precipitation is 550–600 millimetres. The higher than average number of days of sunshine make ideal conditions for the growing of tomatoes, sunflower, tobacco, apples, and other fruits such as plums—for which the county is famous, being eaten fresh, dried into prunes (some made into lekvar) and fermented into well-known brandies.
The county has 229 settlements, of which 20 are towns. The county capital and largest city is Nyíregyháza with a population of 116,900 in 2003. The other cities have relatively small populations, only those of Kisvárda and Mátészalka having around 18,000 inhabitants. The eastern part of the county is lightly populated and is dotted with small villages which often have very poor economic conditions.
The Tisza River
The Upper Tisza region has many streams and rivers, but the Nyírség region has little surface water. The most important of Tisza's tributaries is the river Szamos, which is also characterised by great variations in water volume. There are irrigation systems, a water barrage, and a hydroelectric power station on the Tisza at Tiszalök.
Lakes of various sizes have evolved in sandy areas such as the basin of the Sóstó (Salty lake) of Nyíregyháza, whose alkaline, hydrogen-carbonated waters have medicinal qualities. Many water reservoirs have been built according to local demand. Thermal waters of 55–65 °C can be brought to the surface from wells as shallow as 1,000 metres. The most important thermal water reserves are in Nyíregyháza, Kisvárda, Mátészalka, and Tiszavasvári. The county's geothermal energy still awaits exploitation.
The county has relatively few mineral reserves. Almost all of the large energy source transport systems cross the county.
Demographics
Religion in Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County (2011 census)
In 2015, it had a population of 562,357 and the population density was 92/km².
| Year | County population[2] | Change |
|---|---|---|
| 1949 | 558,098 | n/a |
| 1960 | 5.08% | |
| 1970 | -3.56% | |
| 1980 | 5.00% | |
| 1990 | -3.63% | |
| 2001 | 1.74% | |
| 2011 | -3.95% | |
| 2015 | 0.55% | |
| 2018 | -0.71% |
Ethnicity
Besides the Hungarian majority, the main minority populations in the county are Romani (about 44,000), German (about 2,000), and Ukrainian (about 1,000).
Total population (2011 census): 559,272
Ethnic groups (2011 census):[3]
- Hungarians: 476,256 (90.55%)
- Romani: 44,133 (8.40%)
- Others and indefinable: 5,569 (1.06%)
About 66,000 people in Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County did not declare their ethnicity during the 2011 census.
Religion
Religious adherence in the county according to 2011 census:[4]
- Reformed – 193,697;
- Catholic – 182,097 (Roman Catholic – 108,666; Greek Catholic – 73,419);
- Evangelical – 11,030;
- Orthodox – 389;
- other religions – 10,367;
- Non-religious – 44,173;
- Atheism – 2,468;
- Undeclared – 115,051.
Regional structure
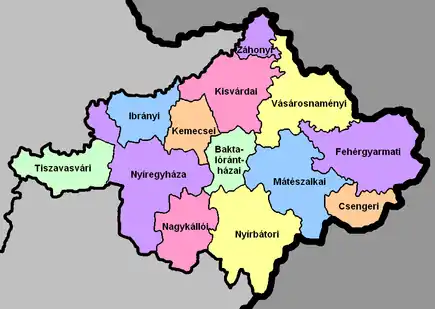
| № | English and Hungarian names |
Area (km²) |
Population (2011) |
Density (pop./km²) |
Seat | № of municipalities |
| 1 | Baktalórántháza District Baktalórántházai járás |
254.47 | 19,123 | 75 | Baktalórántháza | 12 |
| 2 | Csenger District Csengeri járás |
246.51 | 13,485 | 55 | Csenger | 11 |
| 3 | Fehérgyarmat District Fehérgyarmati járás |
707.37 | 37,259 | 53 | Fehérgyarmat | 50 |
| 4 | Ibrány District Ibrányi járás |
304.91 | 23,679 | 78 | Ibrány | 8 |
| 5 | Kemecse District Kemecsei járás |
246.41 | 22,066 | 90 | Kemecse | 11 |
| 6 | Kisvárda District Kisvárdai járás |
523.09 | 56,114 | 107 | Kisvárda | 23 |
| 7 | Mátészalka District Mátészalkai járás |
624.70 | 64,015 | 102 | Mátészalka | 26 |
| 8 | Nagykálló District Nagykállói járás |
377.36 | 30,403 | 81 | Nagykálló | 8 |
| 9 | Nyírbátor District Nyírbátori járás |
695.94 | 43,040 | 62 | Nyírbátor | 20 |
| 10 | Nyíregyháza District Nyíregyházi járás |
809.61 | 168,118 | 208 | Nyíregyháza | 15 |
| 11 | Tiszavasvári District Tiszavasvári járás |
381.61 | 27,684 | 73 | Tiszavasvári | 6 |
| 12 | Vásárosnamény District Vásárosnaményi járás |
617.94 | 35,323 | 57 | Vásárosnamény | 28 |
| 13 | Záhony District Záhonyi járás |
145.95 | 18,963 | 130 | Záhony | 11 |
| Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County | 5,935.83 | 559,272 | 94 | Nyíregyháza | 229 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Economy
The county borders three countries, and it is the only Hungarian county bordering Ukraine. The railway border crossing towards Ukraine is well developed; its high capacity is able to meet the requirements of transit and bilateral trade. Following the reconstruction of the road border crossing, the county is also able to cope with increased road transportation.
Several regions in the county have tourism potential, mostly unexploited. Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg has several agricultural products of excellent quality, with capacity for higher production. There is an abundance of low-cost, semiskilled labour.
The county's biggest problem is the economic crisis. There is a shortage of local capital and inward investment, which restrains the creation of new jobs, thus the unemployment rate remains the second highest in Hungary. Manufacturing lags the rest of the country, most notably lacking high quality, high value-added products. The marginal soil quality limits the scope of agricultural production to a few products which suffer from shrinking export markets to the east.
It is home to the Szakoly Power Plant.
Politics
The Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County Council, elected at the 2019 local government elections, is made up of 25 counselors,[5] with the following party composition:

| Party | Seats | Current County Assembly | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fidesz-KDNP | 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jobbik-Momentum Movement | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hungarian Socialist Party | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Democratic Coalition | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Association for Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Presidents of the General Assembly
| List of presidents since 1990[6] | |
|---|---|
| Oszkár Seszták (Fidesz-KDNP) | 2014– |
Municipalities
Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County has 1 urban county, 27 towns, 15 large villages and 186 villages.
- City with county rights
(ordered by population, as of 2011 census)
- Nyíregyháza (118,125) – county seat
- Towns
- Mátészalka (17,195)
- Kisvárda (16,986)
- Újfehértó (12,931)
- Tiszavasvári (12,848)
- Nyírbátor (12,719)
- Nagykálló (9,702)
- Vásárosnamény (8,471)
- Fehérgyarmat (7,893)
- Ibrány (6,801)
- Nyírtelek (6,654)
- Balkány (6,387)
- Nagyecsed (6,374)
- Tiszalök (6,157)
- Nagyhalász (5,632)
- Csenger (4,853)
- Kemecse (4,755)
- Nyírmada (4,713)
- Rakamaz (4,555)
- Demecser (4,246)
- Mándok (4,191)
- Záhony (4,062)
- Dombrád (3,954)
- Baktalórántháza (3,916)
- Ajak (3,625)
- Vaja (3,608)
- Nyírlugos (2,789)
- Máriapócs (2,186)
- Villages
- Anarcs
- Apagy
- Aranyosapáti
- Balsa
- Barabás
- Bátorliget
- Benk
- Beregdaróc
- Beregsurány
- Berkesz
- Besenyőd
- Beszterec
- Biri
- Botpalád
- Bököny
- Buj
- Cégénydányád
- Csaholc
- Csaroda
- Császló
- Csegöld
- Csengersima
- Csengerújfalu
- Darnó
- Döge
- Encsencs
- Eperjeske
- Érpatak
- Fábiánháza
- Fényeslitke
- Fülesd
- Fülpösdaróc
- Gacsály
- Garbolc
- Gávavencsellő

- Gelénes
- Gemzse
- Geszteréd
- Géberjén
- Gégény
- Győröcske
- Győrtelek
- Gyulaháza
- Gulács
- Gyügye
- Gyüre
- Hermánszeg
- Hetefejércse
- Hodász

- Ilk
- Jánd
- Jánkmajtis
- Jármi
- Jéke
- Kállósemjén

- Kálmánháza
- Kántorjánosi
- Kék
- Kékcse
- Kérsemjén
- Kisar
- Kishódos
- Kisléta
- Kisnamény
- Kispalád
- Kisszekeres
- Kisvarsány
- Kocsord
- Komlódtótfalu
- Komoró
- Kótaj
- Kölcse

- Kömörő
- Laskod
- Levelek

- Lónya
- Lövőpetri
- Magosliget
- Magy
- Mánd
- Márokpapi
- Mátyus
- Mezőladány
- Méhtelek
- Mérk

- Milota
- Nagyar
- Nagycserkesz
- Nagydobos
- Nagyhódos
- Nagyszekeres
- Nagyvarsány
- Napkor
- Nábrád
- Nemesborzova
- Nyírbéltek

- Nyírbogát

- Nyírbogdány
- Nyírcsaholy
- Nyírcsászári
- Nyírderzs
- Nyírgelse
- Nyírgyulaj
- Nyíribrony
- Nyírjákó
- Nyírkarász
- Nyírkáta
- Nyírkércs
- Nyírlövő
- Nyírmeggyes
- Nyírmihálydi
- Nyírparasznya
- Nyírpazony
- Nyírpilis
- Nyírtass
- Nyírtét
- Nyírtura
- Nyírvasvári
- Olcsva
- Olcsvaapáti
- Ófehértó
- Ópályi
- Ököritófülpös

- Ömböly
- Őr
- Panyola
- Pap
- Papos
- Paszab
- Pátroha
- Pátyod
- Penészlek
- Penyige
- Petneháza
- Piricse
- Porcsalma

- Pócspetri
- Pusztadobos
- Ramocsaháza
- Rápolt
- Rétközberencs
- Rohod
- Rozsály
- Sényő
- Sonkád
- Szabolcs
- Szabolcsbáka
- Szabolcsveresmart
- Szakoly
- Szamosangyalos
- Szamosbecs
- Szamoskér
- Szamossályi
- Szamosszeg
- Szamostatárfalva
- Szamosújlak
- Szatmárcseke
- Székely
- Szorgalmatos
- Tarpa

- Tákos
- Terem
- Tiborszállás
- Timár
- Tiszaadony
- Tiszabecs

- Tiszabercel
- Tiszabezdéd
- Tiszacsécse
- Tiszadada
- Tiszadob

- Tiszaeszlár
- Tiszakanyár
- Tiszakerecseny
- Tiszakóród
- Tiszamogyorós
- Tiszanagyfalu
- Tiszarád
- Tiszaszalka
- Tiszaszentmárton
- Tiszatelek
- Tiszavid
- Tisztaberek
- Tivadar
- Tornyospálca
- Tunyogmatolcs
- Túristvándi
- Túrricse
- Tuzsér

- Tyukod

- Ura
- Uszka
- Újdombrád
- Újkenéz
- Vasmegyer
- Vállaj
- Vámosatya
- Vámosoroszi
- Zajta
- Zsarolyán
- Zsurk
![]() municipalities are large villages.
municipalities are large villages.
Gallery
.JPG.webp) Latin Catholic church in Nyíregyháza, the capital of the county
Latin Catholic church in Nyíregyháza, the capital of the county_4.jpg.webp) Greek Catholic church in Máriapócs
Greek Catholic church in Máriapócs Vay Castle in Vaja
Vay Castle in Vaja Andrássy Mansion, Tiszadob
Andrássy Mansion, Tiszadob Reformed Church in Fehérgyarmat
Reformed Church in Fehérgyarmat Báthory Castle in Nyírbátor
Báthory Castle in Nyírbátor
 Rétköz Museum (former Orthodox Synagogue) in Kisvárda
Rétköz Museum (former Orthodox Synagogue) in Kisvárda
Notable people from Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg
- Krúdy Gyula – Nyíregyháza
- Kállay Miklós – Nyíregyháza
- Váci Mihály – Mandabokor II-
- Friderikusz Sándor – Nyíregyháza
- Victor Varconi né Várkonyi Mihály – Kisvárda
International relations
Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County has a partnership relationship with:[7]
|
|
References
- nepesseg.com, population data of Hungarian settlement
- népesség.com, "Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg megye népessége 1870–2015"
- 1.1.6. A népesség anyanyelv, nemzetiség és nemek szerint – Frissítve: 2013.04.17.; Hungarian Central Statistical Office (in Hungarian)
- 2011. ÉVI NÉPSZÁMLÁLÁS, 3. Területi adatok, 3.16 Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg megye, (in Hungarian)
- "Megyei közgyűlés tagjai 2019–2024 (Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg megye)". valasztas.hu. Retrieved 28 October 2019.
- Önkormányzati választások eredményei (in Hungarian)
- "Magyar Hírlap • Testvérmegyei szándéknyilatkozatot írtak alá Szatmárnémetiben". Archived from the original on 2 August 2015.