Strahan, Tasmania
Strahan (/ˈstrɔːn/ STRAWN), is a small town and former port on the west coast of Tasmania. It is now a significant locality for tourism in the region.
| Strahan Tasmania | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
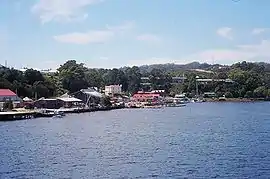 A view of Strahan, taken from a boat in Macquarie Harbour | |||||||||
 Strahan | |||||||||
| Coordinates | 42°09′S 145°19′E | ||||||||
| Population | 658 (2016 census)[1] | ||||||||
| Postcode(s) | 7468 | ||||||||
| Elevation | 20 m (66 ft)[2] | ||||||||
| Location |
| ||||||||
| LGA(s) | West Coast Council | ||||||||
| State electorate(s) | Braddon | ||||||||
| Federal division(s) | Braddon | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Strahan Harbour and Risby Cove form part of the north-east end of Long Bay on the northern end of Macquarie Harbour. At the 2016 census, Strahan had a population of 658.[1]
Port
Originally developed as a port of access for the mining settlements in the area, the town was known as Long Bay or Regatta Point until 1877, when it was formally named after the colony’s Governor, Sir George Cumine Strahan.
Strahan was a vital location for the timber industry that existed around Macquarie Harbour.[4][5][6]
For a substantial part of the nineteenth century and early twentieth century it also was port for regular shipping of passengers and cargo. The Strahan Marine Board was an important authority dealing with the issues of the port and Macquarie Harbour up until the end of the twentieth century when it was absorbed into the Hobart Marine Board.
Post offices
Macquarie Harbour Post Office opened on 16 May 1878, was renamed Strahan in 1881 and closed in 1891. East Strahan Post Office opened in 1891 and was renamed Strahan in 1893.[7]
Fishing and tourism

Historically Strahan has been a port to a small fishing fleet that braves the west coast conditions and Hell's Gates. It is the nearest inhabited locality to Cape Sorell and is literally the 'gateway' to the south-west wilderness - as boats, planes and helicopters utilise Strahan as their base when travelling into the region.
The Huon Pine industry utilised stands around the harbour and up the tributary rivers - including King River, the Franklin River and the Gordon River.
Strahan is the location of the only all weather commercial airport in Western Tasmania, Strahan Airport. Also located at the airport is the Automatic Weather Station, an important western Tasmania weather observation point.
Strahan is the base for boat trips to Sarah Island, the notorious penal settlement that garnered the reputation as the harshest penal settlement in the Australian colonies, and the lower Gordon River.
Strahan is an access point to the Franklin-Gordon Wild Rivers National Park, which was declared part of the Tasmanian Wilderness World Heritage Area in 1982. For several years Strahan became the focus of a conservation campaign opposed to the proposed Franklin-below-Gordon Dam.
It is the home of the Round Earth Theatre Company, which conducts explanatory tours of Sarah Island and also has produced a daily enactment/play about Sarah Island, The Ship That Never Was, which has exceeded 5000 performances and is Australia's longest running play.[8]
Railway stopping place
Strahan was a stopping place on the former Strahan to Zeehan railway. It was also known as Strahan Wharf.[9] The railway was government owned, and ran past the wharf at Strahan, and continued southwards around the harbour before running north on its way to Zeehan. Strahan was connected with the former Mount Lyell railway line at a terminus at Regatta Point which is also the terminus of the currently operating, West Coast Wilderness Railway.
Cultural references
An extinct species of Banksia, fossils of which were found in sediment at nearby Regatta Point, was named Banksia strahanensis after the town.
Climate
Strahan has an oceanic climate (Cfb) with mild damp summers and cool, very rainy winters. Lying on Tasmania's West Coast, Strahan is frequently buffeted by low pressure systems from the Southern Ocean, causing heavy rain and gusty winds. Strahan receives 15.7 days, on average, of clear weather annually.
Temperatures vary little between summer and winter, with minimums below 3 °C (37 °F) having been recorded in every month. Hot weather is rare, with an average of only one day reaching 35 °C (95 °F) or above every three years. The highest recorded temperature is 38.6 °C (101.5 °F) on 14 February 1982, with the lowest recorded being −3.0 °C (26.6 °F) on 30 June 1983. Snow down to sea level is rare but falls frequently in the mountains just a few kilometers inland of Strahan.
| Climate data for Strahan Aerodrome | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 38.0 (100.4) |
38.6 (101.5) |
36.1 (97.0) |
27.8 (82.0) |
22.5 (72.5) |
19.9 (67.8) |
18.3 (64.9) |
22.1 (71.8) |
27.0 (80.6) |
31.9 (89.4) |
32.9 (91.2) |
36.7 (98.1) |
38.6 (101.5) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 20.8 (69.4) |
21.3 (70.3) |
19.5 (67.1) |
16.8 (62.2) |
14.3 (57.7) |
12.6 (54.7) |
12.2 (54.0) |
13.1 (55.6) |
14.4 (57.9) |
16.1 (61.0) |
17.9 (64.2) |
19.8 (67.6) |
16.6 (61.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 10.7 (51.3) |
10.8 (51.4) |
9.8 (49.6) |
8.4 (47.1) |
7.4 (45.3) |
5.5 (41.9) |
5.2 (41.4) |
5.7 (42.3) |
6.3 (43.3) |
7.3 (45.1) |
8.3 (46.9) |
9.7 (49.5) |
7.9 (46.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 0.6 (33.1) |
2.6 (36.7) |
0.8 (33.4) |
−0.2 (31.6) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
0.9 (33.6) |
1.1 (34.0) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 82.5 (3.25) |
68.8 (2.71) |
105.7 (4.16) |
114.0 (4.49) |
158.5 (6.24) |
155.3 (6.11) |
181.6 (7.15) |
181.1 (7.13) |
151.5 (5.96) |
119.3 (4.70) |
94.0 (3.70) |
94.6 (3.72) |
1,552.2 (61.11) |
| Average precipitation days | 15.9 | 12.9 | 18.1 | 19.4 | 23.2 | 21.7 | 23.5 | 25.0 | 23.1 | 21.9 | 18.5 | 18.2 | 241.4 |
| Average afternoon relative humidity (%) | 62 | 60 | 64 | 69 | 75 | 76 | 75 | 71 | 69 | 64 | 61 | 63 | 67 |
| Source: Bureau of Meteorology[3] | |||||||||||||
See also
 Strahan travel guide from Wikivoyage
Strahan travel guide from Wikivoyage- Convicts on the West Coast of Tasmania
- Macquarie Harbour
- Railways on the West Coast of Tasmania
- West Coast Piners
References
- Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 June 2017). "Strahan (L) (Urban Centre/Locality)". 2016 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 10 December 2017.
- Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved on 14 November 2007
- "Climate Data: Strahan Aerodrome". Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 24 September 2019.
- Kerr, Garry J; McDermott, Harry (1999), The Huon pine story : the history of harvest and use of a unique timber, Mainsail Books, ISBN 978-0-9577917-0-1 - page 42, photograph of Strahan wharf with timber awaiting export 1925
- Kok, Arjan; Hind, Greg (1999), A pictorial history of Strahan : a chronicle of the people and events that led to the settlement of Strahan, and the changes to the little port that was once the busiest in Tasmania, Hindsight, retrieved 19 March 2016 chapter 'The Huon Piners', p.45-48
- Pink, Kerry; West Coast Pioneers' Memorial Museum (Zeehan, Tas) (issuing body) (1984), The west coast story : a history of Western Tasmania and its mining fields (Revised ed.), Zeehan, Tasmania West Coast Pioneers' Memorial Museum, ISBN 978-0-9598295-2-5 page 89/90 Strahan, Tasmania's Eldorado and Gateway to the West with two photographs of the Strahan wharf in the 1890s
- Premier Postal History. "Post Office List". Premier Postal Auctions. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- Davey, Richard; Fitzpatrick, Phil (2003), The ship that never was : the last great escape from Sarah Island, Macquarie Harbour : liberty or death!, Round Earth Co, retrieved 21 January 2021
- Atkinson, H. K (1991), Railway tickets of Tasmania, H.K. Atkinson, ISBN 978-0-9598718-7-6 page 105 tickets were issues between 1892 and 1953, and 4 June 1960 was the closure date of the Strahan - Zeehand line
Further reading
- Blainey, Geoffrey (2000). The Peaks of Lyell (6th ed.). Hobart: St. David's Park Publishing. ISBN 0-7246-2265-9.
- Rae, Lou (2001). The Abt Railway and Railways of the Lyell region. Sandy Bay: Lou Rae. ISBN 0-9592098-7-5.
- Whitham, Charles (2003). Western Tasmania - A land of riches and beauty (Reprint 2003 ed.). Queenstown: Municipality of Queenstown.