Sasaram
Sasaram (English: // ⓘ) sometimes also spelled as Sahasram, is an ancient historical city and a municipal corporation region in the Rohtas district of the Bihar state in eastern India, with a history that goes to thousands of years. During the prehistoric age, Buddha walked through this way and lived for some days and then travelled to Gaya to be enlightened with verity and wisdom under the Mahabodhi tree, the city is also known as gateway of "Vihar" to visit rest "Bihar" including Gaya, Rajgriha, and Nalanda.
Sasaram | |
|---|---|
City | |
Sher Shah Suri's Tomb, Sasaram | |
 Location in Sasaram block | |
 Sasaram Location in Bihar, India  Sasaram Sasaram (India) | |
| Coordinates: 24.95°N 84.03°E | |
| Country | |
| State | Bihar |
| Division | Patna |
| District | Rohtas |
| Government | |
| • Type | Municipal Corporation (Updated) |
| • Body | Sasaram Municipal Corporation |
| • Member of Parliament | Chhedi Paswan (Bharatiya Janata Party) |
| • Mayor | Kajal Kumari |
| • Vice-Mayor | Satyavati Devi |
| • District Magistrate | Naveen Kumar, Indian Administrative Service |
| • Superintendent of Police | Vineet Kumar , Indian Police Service |
| Elevation | 110 m (360 ft) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 358,283 |
| • Rank | 288th |
| Demonym | Sasaramite |
| Language | |
| • Official | Hindi[1] |
| • Additional official | Urdu[1] |
| • Regional | Bhojpuri |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 |
| PIN | 821115 |
| Telephone code | 06184 |
| Vehicle registration | BR-24 |
| Railway Station | Sasaram Junction |
| Website | Official District Website |
It has also served as the capital of the Sur dynasty during Shershah Suri ruled over India in 16th Century, and was residence place sub capital of epic monarch Sahstrabahu (Kartivirya Arjuna). T
Sasaram and the Kaimur range contain waterfalls, lakes, rivers and picturesque locations as described by the Ain-I-Akbari. Over 200 waterfalls emerge during the rainy season. Dharohar - Karamchat Waterfall, Geetaghat Heaven Holy Waterfall, Panari Ghat/Gaurav Waterfalls, Manjharkund, Dhuvan Kund, Sitakund, Kashish, Mahadev Khoh & Tutla Bhavani Waterfalls are among the most famous. Telhar Kund, Karkat Garh, Mundeshwari Waterfall, Bansi Khoh, Netua Kund, and Chandradhari Waterfalls in the nearby Kaimur range are also well known .
Modern Sasaram city covers the largest sub-metropolitan area of Bihar. It has many famous religious and historical spots to visit such as Shershah tomb, Rohtasgarh fort, Indrapuri Dam, Karamchat Dam Shergarh fort, Kandhar fort, Sacred Tarachandi Shaktipith, Bhaluni dham, Mahadev Khoh, Chaurasan temple, Gupta Dham, Tutla Bhawani temple, Pilot Baba Dham, Godaila Pahad Temple, Anicat Dam, and the Eco park.
Sasaram city is located in the middle of its other sub-towns like Nokha & Kudra which has a large number of agriculture based industries, and the city is also emerging as an educational hub. It is situated in the middle of other industrial twin towns like Dehri-on-sone, Dalmianagar, Sonnagar, Amjhor, Nokha and Banjari.
The main posh places of the sub-metropolitan area are Raj Colony, Gauraxni, New Area, Takiya bazar, Tomb Area and Fazalganj commercial zones, Sahu Cinemax - Mall & Railway cricket stadium area. Several malls have been opened along with the best 3-4 star hotels with good medical facilities in the city and is a medical hub of old Shahabad District too.
Sasaram city Region is the administrative headquarters of Rohtas District, Bihar India. It became a district carved out from Shahabad District in 1972. This district headquarter is best known for having the highest literacy rate and highest agricultural & forest cover area of Bihar. Sasaram is also the headquarters of a community development block of the same name, with a total population of 358,283 as of 2011, making it the most populous block in Rohtas district.[2]
It is known for the production of cement, fertilizers, stone chips, and for the quarrying industry and also Sasaram district is popularly known as the "bowl of rice".
Major languages spoken in this region are Bhojpuri, Hindi, English and Urdu; religions include Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism, Christianity, Sikhism, and Jainism.
History
During the Vedic age, Sasaram was a part of the ancient Kashi kingdom. Sasaram name is originated from the Sahastrarama, meaning a thousand groves. Sasaram was once also named Shah Serai (meaning "Place of King") as it is the birthplace of the Afghan king Sher Shah Suri, who ruled over Delhi, much of northern India, what is now Pakistan, and eastern Afghanistan for five years, after defeating the Mughal Emperor Humayun. Many of Sher Shah Suri's governmental practices were adopted by the Mughals and the British Raj including taxation, administration, and the building of a paved road from Kabul to Bengal, also called the Grand Trunk Road.
Sher Shah Suri's 122 feet (37 m) red sandstone tomb, built in the Indo-Afghan style stands in the middle of an artificial lake in Sasaram. It borrows heavily from the Lodhi style, and was once covered in blue and yellow glazed tiles indicating an Iranian influence. The massive free standing dome also has an aesthetic aspect of the Buddhist stupa style of the Mauryan period. The tomb of Sher Shah's father Hasan Khan Suri is also at Sasaram, and stands in the middle of a green field at Sherganj, which is known as Sukha Rauza. About a kilometer to the north west of Sher Shah's tomb lies the incomplete and dilapidated tomb of his son and successor, Islam Shah Suri.[3] Sasaram also has a Baulia, a pool used by the emperor's consorts for bathing.
The fort of Sher Shah Suri at Rohtasgarh is in Sasaram. This fort has a history dating back to the 7th century AD. It was built by Raja Harishchandra, known for his truthfulness in the name of his son Rohitashwa. It houses the Churasan temple, Ganesh temple, diwan-e khas, diwan-e-aam, and various other structures dating back to different centuries. The fort also served as the headquarters of Raja Man Singh during his reign as the governor of Bihar and Bengal under the regime of Akbar. The Rohtaas fort in Bihar should not be confused with another fort of the same name, near Jhelum, Punjab, in what is now Pakistan. The Rohtaas fort in Sasaram was also built by Sher Shah Suri, during the period when Humayun was exiled from Hindustan.
There is a temple of Goddess Tarachandi, two miles to the south, and an inscription of Pratap Dhawal on the rock close to the temple of Chandi Devi. Hindus in large number assemble to worship the goddess. Dhuwan Kund, located about 36 km (22 mi).
There are several monuments near Sasaram, the headquarter of Rohtas district, including Akbarpur, Deomarkandey, Rohtas Garh, Shergarh, TaraChandi, Dhuwan Kund, Gupta Dham, Bhaluni Dham, Historical Gurudwara and Tombs of Chandan Shaheed, Hasan Khan Sur, Sher Shah, Salim Sah and Alawal Khan.
Rohtas, south of Sasaram, is known to have been the residence of one Satyawadi Raja Harischandra, named for his son, Rohitashwa.
Minor Rock Edict of Ashoka
Sasaram is also famous for an inscription by Ashoka (one of the thirteen Minor Rock Edicts), situated in a small cave of Kaimur hill, near Chandan Shaheed.
The edict is located near the top of the terminal spur of the Kimur Range near Sasaram.[4] There is the Minor rock edict #1 only[5] Ashoka famously mentions pre-existing stone pillars in the Edict: "...And where there are stone pillars here in my dominion, there also cause it to be engraved.". 24.94138°N 84.03833°E
The Sasaram Edict (Minor Rock Edict No.1 only).
- Devanampriya [speaks] thus.
- .................. years since I am a lay-worshipper (upasaka).
- But (I had) not been very zealous.
- A year and somewhat more (has passed) since ............
- And men in Jambudvipa, being during that time unmingled with the gods, have (now) been made (by me) mingled with the gods.
- [For] this is the fruit [of zeal].
- ...........cannot be reached by (persons of) high rank alone, (but) even a lowly (person) is able to attain even the great heaven if he is zealous.
- Now, for the following purpose (has) this proclamation (been issued), (that) both the lowly and the exalted may be zealous, and (that) even (my) borderers may know (it), and (that this) zeal may be of long duration,
- And this matter will (be made by me to) progress, and will (be made to) progress even considerably; it will (be made to) progress to one and a half, to at least one and a half.
- And this proclamation (was issued by me) on tour.
- Two hundred and fifty-six nights (had then been) spent on tour, — (in figures) 256.
- And cause ye this matter to be engraved on rocks.
- And where there are stone pillars here (in my dominions), there also cause (it) to be engraved.
— Sasaram Edict (Translated in Inscriptions of Asoka. New Edition by E. Hultzsch)[6]
 The Edict is located on top of the terminal spur of the Kimur range.
The Edict is located on top of the terminal spur of the Kimur range.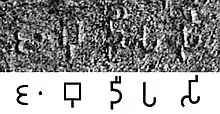 The name Jambudīpasi for "India" (Brahmi script) in the Sahasram Minor Rock Edict of Ashoka, circa 250 BCE.[7][8]
The name Jambudīpasi for "India" (Brahmi script) in the Sahasram Minor Rock Edict of Ashoka, circa 250 BCE.[7][8] Transcription of the Edict.
Transcription of the Edict.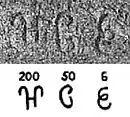 The number "256" towards the end of the Edict.
The number "256" towards the end of the Edict.
Tomb of Sher Shah Suri
Coordinates: 24°56′N 84°01′E


This site is included in UNESCO World Heritage Centre – Tentative list.[9]
Tomb of Sher Shah, built in the middle of the town, is one of the noblest specimens of Pathan architecture in India, is an imposing structure of stone, standing in the middle of a fine tank, and was built towards the middle of sixteenth century. Its height from the floor to the apex of the dome is 101 feet (31 m) and its total height above the water is over 150 feet (46 m) feet. The octagon forming the tomb has an interior diameter of 75 feet (23 m) feet and an exterior diameter of 104 feet (32 m) feet. The tomb is the second highest in India which attracts tourists. The tomb of Shershah Suri at Sasaram is an imposing structure of stone standing in the middle of a fine tank and rising from a large stone terrace. This terrace rests obliquely on a platform with a flight of steps leading to the water's edge. The upper terrace is enclosed by a battlemented parapet wall with octagonal domed chambers at four corners, two small projecting pillared balconies on each of its four sides and pierced with a doorway in the east forms the only approach to the tomb. In the middle of the upper terrace stands the building of the mausoleum on a low octagonal plinth. The building consists of a very large octagonal chamber surrounded by a wide verandah on al the four sides. Internally, the verandah is covered by a series of 24 small domes, each supported on four arches but as the roof is a pillared cupola adorned by panels of white glazed tiles now much discoloured. The tomb chamber has three lofty arches on each of the eight sides. They rise 22 feet (6.7 m) higher than the verandah roof and support the magnificent and lofty dome which is one of the largest domes in India. Surrounding the main dome are eight pillared cupolas on the corners of the octagon of the chamber walls. The interior of the tomb is sufficiently well ventilated and lighted through large windows on the top portion of the walls fitted with stone jalis in varying patterns. The jambs and spandrils of the arch of the mihrab on the western wall were once profusely adorned with verses from the Quran and inscriptions, with glazed tiles of various colours arranged in geometrical patterns and with floral carvings in stone enclosed in enamel borders. Much of this decoration has vanished already. Traces of similar decoration in enamel or glazed tile works are also to be scen on the interior of the dome, the walls and the cupolas on the outside. In a small arched recess above the mihrab on the outside wall is an inscription in two lines recording the completion of the tomb by his son and successor Salim or Islam Shah, some three months after the death of Sher Shah who died in A.H. 952 (A.D.1545). It is second largest dome of India.
The tomb of Hasan Khan Sur, father of Sher Shah is also located in the town. This tomb is also known as Sukha Roza. The incomplete tomb os Sher Shah's son, Islam Shah Suri is also located at Sasaram.
Geography
Sasaram is located at 24.95°N 84.03°E and its area is 15 km^2.[10] It has an average elevation of 200 metres (660 ft).
Climate
As Sasaram is surrounded by hills from two sides, its climate is seasonable. The climate is characterized by relatively high temperatures and evenly distributed precipitation throughout the year. The Köppen Climate Classification sub-type for this climate is "Cfa" (Humid Subtropical Climate).[11]
| Climate data for Sasaram, India | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 23.8 (74.8) |
26.7 (80.1) |
32.7 (90.9) |
38.0 (100.4) |
40.9 (105.6) |
38.5 (101.3) |
33.2 (91.8) |
32.0 (89.6) |
32.4 (90.3) |
31.8 (89.2) |
28.1 (82.6) |
24.1 (75.4) |
31.9 (89.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 16.2 (61.2) |
18.9 (66.0) |
24.2 (75.6) |
29.6 (85.3) |
33.2 (91.8) |
32.8 (91.0) |
29.2 (84.6) |
28.4 (83.1) |
28.2 (82.8) |
25.9 (78.6) |
20.7 (69.3) |
16.5 (61.7) |
25.3 (77.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 8.8 (47.8) |
11.1 (52.0) |
15.8 (60.4) |
21.2 (70.2) |
25.5 (77.9) |
27.0 (80.6) |
25.3 (77.5) |
24.8 (76.6) |
23.9 (75.0) |
20.0 (68.0) |
13.3 (55.9) |
8.9 (48.0) |
18.8 (65.8) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 19.2 (0.76) |
21.2 (0.83) |
14.3 (0.56) |
7.6 (0.30) |
12.2 (0.48) |
120.9 (4.76) |
297.5 (11.71) |
326.2 (12.84) |
181.5 (7.15) |
50.9 (2.00) |
10.2 (0.40) |
3.6 (0.14) |
1,065.3 (41.93) |
| Average rainy days | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 5.9 | 14.3 | 14.3 | 8.9 | 2.8 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 54.7 |
| Source: Weatherbase[12] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
As of 2020 India census, Sasaram had a population of 351,408 but in urban agglomeration. Males constitute 52% of the population and females 48%. Sasaram has an average literacy rate of 80.26%, higher than the national average of 74%; male literacy is 85%, and female literacy is 75%. In Sasaram, 13% of the population is under 6 years of age.[13]
Sasaram is the 10th most populous city in bihar.
Governance

SAHAJ Vasudha Kendra, the first "Common Service Centre", or "eKiosk", in Rohtas District was inaugurated in Jamuhar village on 15 August 2008. The centre is currently planning to start a block information Centre, e-district plan, and Sawan Sasaram.
Lok Sabha constituency
Sasaram (Lok Sabha constituency) is one of the 40 Lok Sabha (parliamentary) constituencies in Bihar state in eastern India.
Vidhan Sabha constituency
Sasaram (Vidhan Sabha constituency) is one of 243 legislative assembly of Bihar. It is comes under Sasaram lok sabha constituency.[14]
Economy
The closure of the industries of the Dalmia Group at Dalmianagar resulted in widespread unemployment. Sasaram's economy is mainly driven by agriculture and related industries like rice polishing. The canal irrigation system is also very prominent in this area. Because of the fertile land around the town it is a local trading center for food grains, agricultural products, and agricultural equipment. The region is known as Dhan Ka Katora, meaning "a bowl of food grains". The rice grown near Sasaram is sold in the markets of Kolkata and New Delhi. The only significant industry is rock quarrying.
Transportation
Railway
Sasaram has a big size railway junction. The station belongs to A class category with 8 platforms. The station has to be developed as the world-class which is located at the centre of the city on the Grand Trunk Road. Sasaram's other stations are Shivsagar, kumahu, Nokha, Karwandiya, Pahleja and Dehri on Sone.
Sasaram station is 101 Kilometers away from Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhaya station (less than 1.5 hours) and about 120 km (75 mi), or two hours journey from Varanasi, and 101 km (63 mi) from Gaya station. Gaya station is 20 km (12 mi) away Bodh Gaya, the most sacred place in Buddhism. Trains run from Sasaram to Kolkata, Ara, Ranchi, Patna, New Delhi, and Bikramganj, Bombay.
The trains which stop in Sasaram include Ajmer seldah, Kalka Mail, Purushottam Express, Mahabodhi Express, Ranchi Garib Rath, Kolkata Mail, Jodhpur Howrah Express, Chambal Express, Shipra Express, Chennai Egmore Express, Nandan Kanan Express, Neelanchal Express and Poorva Express, Jallianwalabagh Express, Durigana Express, Garbha Express, Dikshabhoomi Express and New Delhi- Bhagalpur Express, etc.
A direct weekly AC train had been started from Sasaram to Anand Vihar Terminal in July 2011 (22409/22410 - Sasaram - Anand Vihar Garib Rath Express). However, now this AC train runs between Gaya and Anand Vihar Terminal, still stopping at Sasaram Junction.
Education
Sasaram is the sixth most literate city in Bihar, with Rohtas being the most literate district in Bihar.[17][18]
There are four government colleges, although many students prefer to go to more developed cities for quality education, such as Bangalore, New Delhi, Pune, Patna, Varanasi and Puducherry, for higher education. A new engineering college has been set up in the region.
This Place is also known for preparation of competitive exams at Sasaram Railway junction.[19] According to earlier natives of this city, there was not proper electrification of city around 2007 - 2008 which hampered the studies of students seeking for competitive exams. Indian Railways had 24 hours power supply at Sasaram junction. This led a small group of students to study there at night under electric lights.
Medical colleges
- Narayan Medical College and Hospital[22]
- Mahatma Phule Medical College and Hospital, Muradabad, Sasaram[23]
- Sher Shah Suri Medical Hospital & Training college, Sasaram
Government colleges
Other colleges
Major schools
- St.Michael's Academy School, Chandravanshi Nagar, Fazalganj, Sasaram[32]
- M. P. High School, Adda Road, Sasaram
- Rama Rani Jain Girls High School, Choukhandi Road, Sasaram
- Bal Vikas Vidyalaya, Tomb Road, Sasaram[33]
- Bal Bharti Public School, Sasaram[34]
- D.A.V. Public school, Admapur, Sasaram[35]
- St. Paul's School, Sasaram[36]
- St. Xavier's School, Jagdev Nagar, Nooran Ganj, Sasaram[37]
- G.S. Residential School, Malwar Road, Sasaram[38]
- St. Jeelani's Public School, Shahjuma, Sasaram[39]
- Pragya Niketan Public School, Falzalganj, Sasaram[40]
- Buddha Mission School, Nooranganj, Bauliya Road, Sasaram Rohtas Bihar
Villages
Besides the city of Sasaram itself, there are 171 villages in Sasaram block, of which 144 are inhabited and 27 are uninhabited. The total rural population of Sasaram block is 210,875, in 34,336 households.[2]
| Village name | Total land area (hectares) | Population (in 2011) |
|---|---|---|
| Dhanarhi | 75.3 | 745 |
| Fatehpur | 55.1 | 186 |
| Danwarua | 47 | 0 |
| Patanwan | 116.6 | 454 |
| Mosahebpur | 81.4 | 879 |
| Rasulpur | 87.7 | 804 |
| Bhikhanpura | 132 | 0 |
| Samarodiha | 323.3 | 1,995 |
| Chaukhanda Chitauli | 140.4 | 1,408 |
| Shivpur Chitauli | 44.9 | 1,146 |
| Turki | 69.6 | 2,113 |
| Lodhi | 48.6 | 395 |
| Barawan | 60.6 | 820 |
| Uttimpur Haraha | 33 | 0 |
| Belthua | 60.8 | 487 |
| Banrasia | 55.4 | 2,585 |
| Belarhi | 160.3 | 2,886 |
| Singuhi | 108.1 | 1,653 |
| Patanwan | 38 | 0 |
| Kataprath | 27 | 0 |
| Naugain | 82.1 | 548 |
| Khairi | 105.3 | 437 |
| Khaira | 112.6 | 1,421 |
| Niranjanpur | 17 | 400 |
| Bishunpura | 54.7 | 0 |
| Mahranian | 20.6 | 652 |
| Bhadokhara | 186.2 | 2,988 |
| Belahar | 76.4 | 1,199 |
| Sikaria | 1,171.9 | 4,934 |
| Kota | 206.4 | 2,303 |
| Rajokhar | 118.3 | 0 |
| Ashikpur | 37 | 0 |
| Hetimpur | 12 | 653 |
| Karpurwa | 35.7 | 2,709 |
| Bhatarhi | 71.2 | 839 |
| Beda | 69.2 | 1,852 |
| Kanserwa | 72.2 | 0 |
| Lakhrawan | 8.8 | 0 |
| Mohaddi Ganj | 44.1 | 3,240 |
| Dhanpurwa | 20.4 | 1,340 |
| Dilia | 33.8 | 0 |
| Mirzapur | 3 | 0 |
| Udhopur | 43.7 | 136 |
| Madaini | 254.9 | 815 |
| Sumbha | 70.8 | 745 |
| Ahrawan | 128.7 | 705 |
| Misripur | 56.7 | 532 |
| Madauria | 50 | 161 |
| Dhunan | 67.2 | 708 |
| Karam Dihri | 146.9 | 1,371 |
| Tetari | 91.1 | 709 |
| Haripur | 24.7 | 53 |
| Kuraich | 35 | 1,598 |
| Takia | 8.7 | 5 |
| Muradabad Kalan | 144.8 | 4,291 |
| Muradabad Khurd | 154.2 | 2,310 |
| Uchitpur | 174 | 3,794 |
| Nekara | 140.8 | 2,056 |
| Neae | 131.1 | 1,644 |
| Baradih | 121.8 | 3,202 |
| Nimia | 102.4 | 792 |
| Kothara | 156.2 | 929 |
| Bhagwanpur | 93.9 | 626 |
| Semra | 80.1 | 617 |
| Bajila | 104.8 | 1,112 |
| Gamharia | 67.2 | 707 |
| Mokar | 372.7 | 3,409 |
| Agrer | 263.8 | 3,774 |
| Rakasia | 124.2 | 1,867 |
| Jhalkhoria | 50.2 | 779 |
| Akasi | 391.8 | 4,145 |
| Kunrwa | 106.4 | 1,064 |
| Pipri | 137.2 | 945 |
| Katdehri | 199.8 | 1,137 |
| Gotpa | 228.3 | 1,961 |
| Maudiha | 85.4 | 1,010 |
| Kharaunia | 101.6 | 756 |
| Sumbha | 178.4 | 830 |
| Garara | 206.8 | 2,461 |
| Rudana | 106.8 | 1,020 |
| Rajekarma | 49.4 | 0 |
| Babhanpurwa | 46.1 | 465 |
| Gobina | 89 | 1,039 |
| Karup | 117.3 | 1,636 |
| Dilia | 62.3 | 856 |
| Lok Dehri | 62.8 | 686 |
| Inaihia | 57.9 | 546 |
| Bhainsahi | 172.8 | 1,041 |
| Bishunpura | 76.1 | 696 |
| Bhajea | 103 | 0 |
| Jaipur | 139.2 | 1,359 |
| Nirmalpur | 38 | 302 |
| Nirmalpur | 72.8 | 0 |
| Rampur | 287 | 2,895 |
| Semra | 148 | 186 |
| Bahrar | 143 | 1,355 |
| Khanra | 81.4 | 588 |
| Patia | 118 | 1,476 |
| Dumaria | 86 | 1,301 |
| Kaupa Dih | 89 | 624 |
| Bajinathpur | 39 | 0 |
| Gansa Dih | 170 | 2,695 |
| Chhotka Mor | 76.4 | 1,191 |
| Barka Mor | 201 | 1,439 |
| Pasia Dih | 35 | 433 |
| Bara Dih | 121 | 418 |
| Basuhara | 89 | 683 |
| Nahauna | 288 | 3,208 |
| Bhorman | 64 | 429 |
| Koiria Dih | 36 | 0 |
| Paisara | 107 | 890 |
| Tiwari Dih | 36 | 314 |
| Bhurekunria | 18 | 341 |
| Belwa | 101 | 675 |
| Khurhunu | 178 | 1,684 |
| Jigina | 178 | 754 |
| Tendua | 101 | 1,150 |
| Bararhi | 134 | 1,507 |
| Shahpur | 90 | 1,099 |
| Bishunpur | 62 | 858 |
| Chaubea | 57 | 584 |
| Bisrampur | 138 | 1,907 |
| Karwania | 131 | 3,446 |
| Basa | 101.1 | 2,683 |
| Jagdaun Dih | 48.6 | 400 |
| Durgapur | 87.9 | 1,057 |
| Amra, Sasaram | 205.6 | 4,944 |
| Amri, Sasaram | 197.4 | 5,527 |
| Dawanpur | 238.4 | 2,544 |
| Karma | 136 | 538 |
| Nima | 68.4 | 580 |
| Ghatmapur | 75.6 | 821 |
| Basantpur | 164.8 | 1,084 |
| Admapur | 213.7 | 1,746 |
| Gaeghat | 209 | 1,481 |
| Fazilpur | 123 | 334 |
| Gajdwahi | 327.8 | 2,678 |
| Kanchanpur | 480 | 2,865 |
| Kurdaun | 322 | 711 |
| Dhankarha | 113.3 | 2,696 |
| Lerua | 100.8 | 2,984 |
| Mednipur | 146.9 | 2,084 |
| Dhaudanr | 1,125.4 | 5,816 |
| Mahua Dihra | 2,713 | 0 |
| Jawarh | 662.1 | 0 |
| Palangarh | 580.3 | 0 |
| Kauria | 85 | 0 |
| Tendua | 202.7 | 702 |
| Murhi | 120.1 | 2,071 |
| Karserua | 269.1 | 2,309 |
| Gharbair | 269.9 | 1,344 |
| Barui | 265 | 1,238 |
| Songawan | 288.6 | 2,188 |
| Mundi Sarae | 121 | 0 |
| Molawan | 273.1 | 2,638 |
| Sakas | 156.6 | 1,014 |
| Dhanpurwa | 45.4 | 298 |
| Kusri | 127.1 | 1,417 |
| Dubaulia | 25.9 | 0 |
| Khairi | 35.2 | 72 |
| Babura | 45 | 707 |
| Khaira | 115 | 831 |
| Bichhia | 25 | 0 |
| Darigawan | 362 | 5,964 |
| Agni | 133 | 626 |
| Jamahath | 135 | 680 |
| Karaunia | 316 | 0 |
| Tikra | 195 | 0 |
| Ramgaraha | 1,168 | 0 |
| Goria | 4,072 | 316 |
| shiwan | 312 | 3023 |
Notable people
- Sher Shah Suri: Emperor of India, conquered Mughal Empire defeating 2nd Mughal emperor Humayun.
- Chhedi Paswan, Member Of Indian Parliament, Ex- MLA
- Babu Jagjivan Ram: former Deputy Prime Minister of India[41]
- Meira Kumar: former Speaker of the Lok Sabha of India[42]
- Vijay Kumar: Renowned biologist
- Rameshwar Singh Kashyap, Bhojpuri playwright and author.
- Akash Deep, Indian cricketer, a squad member of Royal Challengers Bangalore in Indian Premier League.
- Ritesh Pandey, Bhojpuri actor and singer
- Kavi Kumar Azad: famous for his role in TV serial Taarak Mehta Ka Ooltah Chashmah as Dr. Hansraj Hathi
- Jyoti Prakash Nirala: recipient of Ashok Chakra posthumously in 2018
See also
References
- "52nd Report of the Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities in India" (PDF). nclm.nic.in. Ministry of Minority Affairs. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 9 August 2020.
- "Census of India 2011: Bihar District Census Handbook - Rohtas, Part A (Village and Town Directory)". Census 2011 India. pp. 33, 41–70, 988–1059, 1191–1192. Retrieved 29 June 2020.
- Sanatani, Rohit Priyadarshi. "The Tomb of Salim Shah Suri (Islam Shah): The glory that never was". The Speaking Arch. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 27 March 2015.
- BLO
- India: An Archaeological History: Palaeolithic Beginnings to Early Historic ... by Dilip K. Chakrabarty p.395
- Inscriptions of Asoka. New Edition by E. Hultzsch (in Sanskrit). 1925. p. 171.
- Inscriptions of Asoka. New Edition by E. Hultzsch (in Sanskrit). 1925. pp. 169–171.
- Lahiri, Nayanjot (2015). Ashoka in Ancient India. Harvard University Press. p. 37. ISBN 9780674057777.
- "Sites along the Uttarapath, Badshahi Sadak, Sadak-e-Azam, Grand Trunk Road". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Archived from the original on 17 January 2018. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- Falling Rain Genomics, Inc - Sasaram Archived 2008-03-11 at the Wayback Machine
- Climate Summary for Sasaram, India Archived 2018-01-17 at the Wayback Machine
- "Sasaram, India — Monthly Weather Averages Summary". weatherbase. Archived from the original on 17 January 2018. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- Sasaram City Census 2020 data Archived 2016-04-05 at the Wayback Machine
- "Sasaram (Bihar) Lok Sabha Election Results 2019, 2014, 2009 -Sasaram Parliamentary Constituency, Winning MP and Party Name". Archived from the original on 31 December 2017. Retrieved 31 December 2017.
- "सासाराम में बनेगा AIRPORT, विमान सेवा के लिए पर्यटन मंत्रालय ने बिहार सरकार से मांगा प्रस्ताव - Live Bihar".
- "सासाराम में एयरपोर्ट बनने की जगी उम्मीद, विमान सेवा के लिए पर्यटन मंत्रालय ने बिहार सरकार से मांगा प्रस्ताव". 21 May 2018.
- SAWAN SASARAM
- Census, India (16 August 2022). "literacy rate in Bihar (2022), including the literacy rate of all districts in Bihar". IndiaCensus.net. Retrieved 16 August 2022.
- "Station students get a platform".
- http://www.gnsu.org/
- Gopal Narayan Singh University
- "Welcome to Narayan Medical College & Hospital!". Archived from the original on 26 July 2011.
- "जनमानस की सेवा में निरंतर लगा हुआ है महात्मा फुले मेडिकल कॉलेज एवं हॉस्पिटल". 11 April 2019.
- https://www.spjainsasaram.co.in Archived 2018-05-17 at the Wayback Machine
- "Veer Kunwar Singh University – वीर कुँवर सिंह विश्वविद्यालय, आरा बिहार – 802301". 31 March 2018. Archived from the original on 18 May 2018. Retrieved 17 May 2018.
- "Varsity branch boon for pupils". Archived from the original on 5 June 2018. Retrieved 23 May 2018.
- http://sscollegesasaram.org Archived 2018-03-25 at the Wayback Machine
- "Sher Shah College, Sasaram – [ A constituent unit of Veer Kunwar Singh University, Ara, Bihar ]".
- http://www.rmcsasaram.org/index.action
- http://www.hnsite.org Archived 2018-03-25 at the Wayback Machine
- Veer Kunwar Singh University (VKSU) Archived 2018-06-05 at the Wayback Machine
- "St.Michael's Academy Sasaram".
- "Bal Vikas Vidyalaya".
- "Bal Bharti Public School - Sasaram, Rohtas - Reviews, Fee Structure, Admission Form, Address, Contact, Rating - Directory".
- "Dav Public School".
- "St Paul's School Sasaram".
- "ST XAVIer's SCHOOL - Ward No-34, District Rohtas (Bihar)".
- "G.S Residential School".
- "SAINT JEELANI S SCHOOL - Ward No-16, District Rohtas (Bihar)".
- "Pragya Niketan Public School Sasaram". Archived from the original on 26 January 2020. Retrieved 26 September 2020.
- Jagjivan Ram
- Meira Kumar



