Rapallo
Rapallo (US: /rəˈpɑːloʊ/ rə-PAH-loh,[3] Italian: [raˈpallo], Ligurian: [ɾaˈpalːu]) is a municipality in the Metropolitan City of Genoa, located in the Liguria region of northern Italy.
Rapallo | |
|---|---|
| Comune di Rapallo | |
 The sea front and harbour of Rapallo. | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Rapallo | |
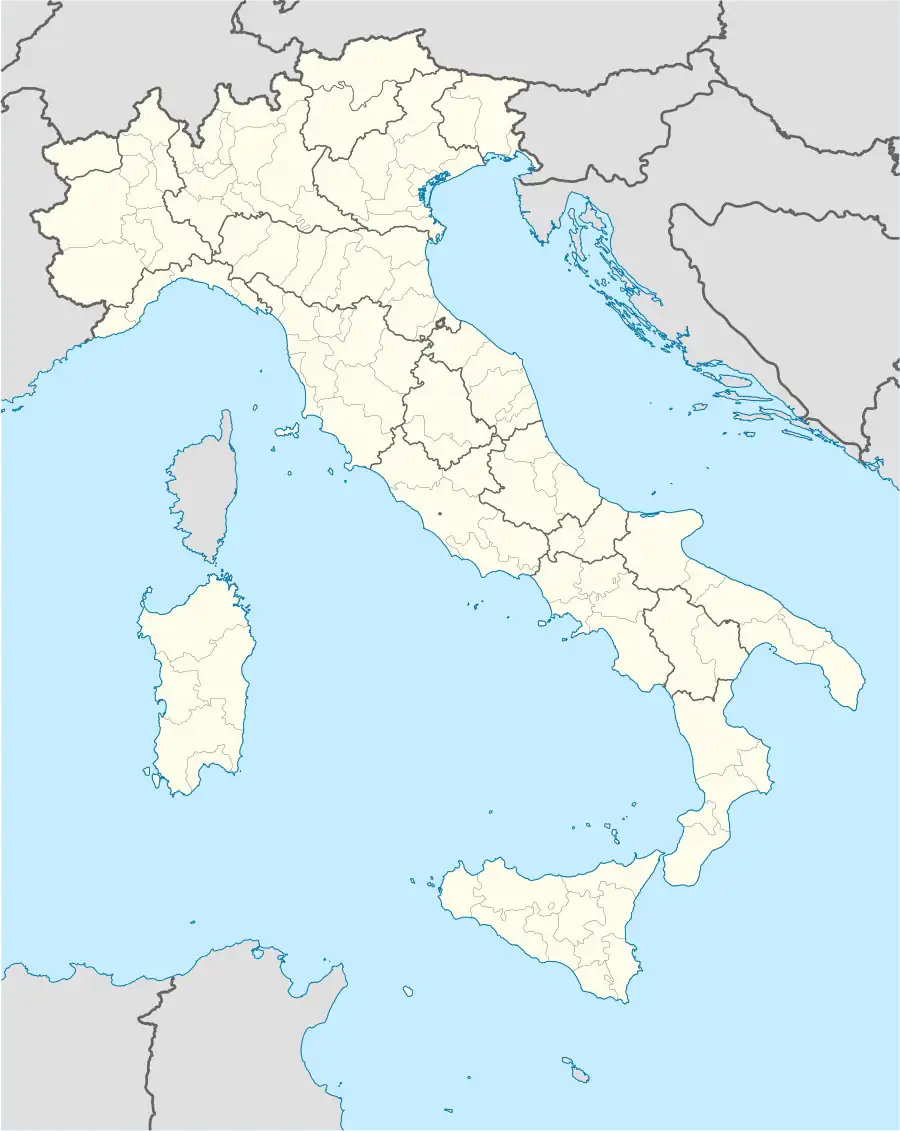 Rapallo Location of Rapallo in Italy  Rapallo Rapallo (Liguria) | |
| Coordinates: 44°21′N 09°14′E | |
| Country | Italy |
| Region | Liguria |
| Metropolitan city | Genoa (GE) |
| Frazioni | Montepegli, San Martino di Noceto, San Massimo, San Maurizio di Monti, San Michele di Pagana, San Pietro di Novella, San Quirico d'Assereto, Santa Maria del Campo, Sant'Andrea di Foggia, Santuario di Montallegro |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Carlo Bagnasco |
| Area | |
| • Total | 33.70 km2 (13.01 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 3 m (10 ft) |
| Population (31 May 2022)[2] | |
| • Total | 29,030 |
| • Density | 860/km2 (2,200/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Rapallesi |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 16035 |
| Dialing code | 0185 |
| Patron saint | Our Lady of Montallegro |
| Saint day | July 2 |
| Website | Official website |




As of 2017 it had 29,778 inhabitants.[2] It lies on the Ligurian Sea coast, on the Tigullio Gulf, between Portofino and Chiavari, 25 kilometers east-south east of Genoa itself.
The climate is moderate. Many of the villas are built in the hills that rise immediately behind the city, protecting them from strong northern winds.
The Parco Naturale Regionale di Portofino, encompassing the territory of six Ligurian communes, includes the Rapallo area.
History
The first settlement dates probably from the 8th century BC, although the findings have not clarified if it was Etruscan or Greek.
The name of the city appears for the first time in a document from 964. In 1203 the Podestà of Rapallo was created, and the town became a Genoese dominion in 1229, remaining under that aegis until the Napoleonic Wars. Galleys from Rapallo took part to the Battle of Meloria of 1284. On 5 September 1494, it was captured by the Aragonese, but three days later 2,500 Swiss troops ousted them.
During the 16th century it was attacked and sacked by the Ottomans and Barbary pirates. To help defend the village against such attacks a castle was built on the seafront. In 1608 Rapallo was made into a Capitaneato (captainship) of its own, as part of the Republic of Genoa.
In the late 18th century it was captured by the French who, after several clashes against Austro-Russian troops, in 1805 annexed it to the Apennins region. In 1814 the English freed it, and the following year the city was given to the Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont as part of the Duchy of Genoa.
In late 1917 the Anglo-Franco-Italian Rapallo Conference met following the disastrous Italian defeat at Caporetto. It was decided to create a supreme war council at Versailles and to shift some French and British troops to the Italian front. On 12 November 1920, Italy and the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes (later renamed Yugoslavia) signed the Treaty of Rapallo, 1920, which resolved the frontier issues between them without reference to the other Allies. Italy acquired the strategically important crest of the Julian Alps as its boundary in the northeast. Also concluded at Rapallo was the Russian-German Treaty of Rapallo of April 1922, in which both countries renounced claims to war reparations and renewed diplomatic relations. This agreement marked the emergence of Russia and Germany from the diplomatic isolation caused by World War I (1914–18).
During World War II numerous partisans from Rapallo were shot by German occupation troops.
Rapallo has been known for its climate that made it over the years the winter residence of preference for most of the affluent Italians living in the North West of Italy. Its proximity to the coast makes for mild winters where people can enjoy easy strolls on the sunny promenade and the golfers can enjoy one of the oldest courses in Italy, opened in 1930.
Main sights
- The Castello sul Mare (Castle-on-the-Sea), erected in 1551 to counter the frequent pirate attacks. It includes a small chapel dedicated to St. Cajetan, built in 1688.
- The Castello di Punta Pagana is a seat of the Sovereign Military Order of Malta. It was finished on 28 July 1631.
- The historical Tower of the Fieschi and the Torre Civica (1473).
- The Porta delle Saline, the only remaining gate from the ancient walls.
- Basilica of Sts. Gervasius and Protasius, consecrated in 1118 and restored in the early 17th century. In 1679 a new apse was added, deleting the former Romanesque character of the edifice. It has a leaning bell tower.
- The church of St. Francis of Assisi (begun in 1519).
- The Sanctuary of Nostra Signora di Montallegro ("Our Lady of Montallegro", 1558–1640).
- The ruined Monastery of Valle Christi (13th century), abandoned in 1568 after pirate ravages.
- Interesting ancient Hannibal's Bridge dating back to 218 BC
People
- The polymath Fortunio Liceti was born in Rapallo in 1577.
- Cornelia Wicker Armsby, an American golfer and socialite, died at Rapallo in 1969.
- Max Beerbohm, the caricaturist and essayist, lived in Rapallo from 1910 until his death in 1956, with the exception of the two World Wars.
- Domingo Ghirardelli, founder of the Ghirardelli Chocolate Company was born in Rapallo in 1817 and also died there while visiting in 1894.
- Sir Edmund Grimani Hornby, former Chief Judge of the British Supreme Consular Court at Constantinople and British Supreme Court for China and Japan died in Rapallo in 1896 and was buried there.[4]
- The poet Ezra Pound lived in Rapallo between the years 1924 and 1945 and wrote much of his Cantos there. His father, Homer Pound, is buried in the non-Catholic section of Cimitero Urbano on Via Cerisola.
- Sir Charles Hercules Read, British archaeologist and curator, died in Rapallo in 1929 and is buried in the non-Catholic section of Cimitero Urbano.
- The Finnish composer Jean Sibelius stayed with his family in Rapallo in 1901, where he conceived ideas for his Symphony No. 2.
- Alexandra Zazzi, Swedish-Italian chef and television personality, was born in 1966 and grew up in Rapallo.
Honorary citizens
Among the recipients of the honorary citizenship of Rapallo are:
| Date | Name | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1992 | Andrew Bertie | 78th Grand Master of the Knights Hospitaller 1988-2008[5] |
| 18 September 2008 | Matthew Festing | 79th Grand Master of the Knights Hospitaller 2008-2017[6] |
Transportation
Rapallo railway station, opened in 1868, forms part of the Pisa–La Spezia–Genoa railway.
Twin towns
 Iquique, Chile
Iquique, Chile
Literature

Rapallo was the first goal for the Finland Swedish author Göran Schildt's travels on the Mediterranean Sea with the ketch Daphne in 1948.
Later Nobel laureate Eugenio Montale has a poem entitled "Caffe a Rapallo" in his early collection Ossi di Seppia (Cuttlefish Bones).
Friedrich Nietzsche wrote that the ideas for Zarathustra first came to him while walking on two roads surrounding Rapallo, according to Elisabeth Förster-Nietzsche in the introduction of Thomas Common's translation of Thus Spoke Zarathustra.
The writer Ezra Pound spent much of the late 1920s and 1930s living in the town.
The author, caricaturist and parodist Max Beerbohm lived in Rapallo from 1910 until his death in 1956, returning to Britain during World War I and World War II.
The American war poet John Allan Wyeth lived in Rapallo during the 1920s and early '30s and is believed to have written his only published poetry collection, This Man's Army: A War in Fifty-Odd Sonnets, while residing there.
The influential theatre designer and artist Gordon Craig lived in Villa Raggio, next door to Beerbohm, from 1917 to 1928. Rapallo is the setting for most of Elmore Leonard's crime novel Pronto.
References
- "Superficie di Comuni Province e Regioni italiane al 9 ottobre 2011". Italian National Institute of Statistics. Retrieved 16 March 2019.
- ISTAT
- "Rapallo". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Retrieved 30 July 2019.
- Hornby, An Autobiography, Introduction by Constance Drummond (nee Hornby)
- "The Order of Malta Federal Association, USA is a lay religious order of the Catholic Church".
- "THE GRAND MASTER HONORARY CITIZEN OF RAPALLO » Sovereign Order of Malta - Official site". Archived from the original on 2015-12-08. Retrieved 2015-11-27.