Rancho Corral de Tierra
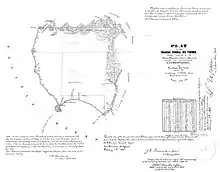
Rancho Corral de Tierra (Guerrero y Palomares) was a 7,766-acre (31.43 km2) Mexican land grant in present-day coastal western San Mateo County, northern California.
The larger northern part of Rancho Corral de Tierra was given in 1839 by Governor Pro-Tem Manuel Jimeno to Francisco Guerrero y Palomares.[1] The name means earthen corral in Spanish. Jimeno granted Tiburcio Vasquez the smaller southern Rancho Corral de Tierra (Vasquez) part.
Guerrero y Palomares's northern portion extended from Martini Creek south along the Pacific coast past Montara to Arroyo de en Medio just south of El Granada, and included the present-day communities of Moss Beach, and Princeton-by-the-Sea.[2][3] Most of its former land grant is now a part of the Golden Gate National Recreation Area.[4]
History
Francisco Guerrero y Palomares (1811–1851) came to California with the Híjar-Padrés Colony in 1834, and settled in San Francisco. He married Josefa de Haro, daughter of Francisco de Haro, and had five sons. He was Alcalde of Yerba Buena in 1836 and in 1839. Guerrero was murdered in San Francisco in 1851.[4]
With the cession of California to the United States following the Mexican-American War, the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo provided that the land grants would be honored. As required by the Land Act of 1851, a claim for Rancho Corral de Tierra was filed with the Public Land Commission in 1852,[5][6] and the grant was patented to Josefa de Haro de Guerrero in 1866.[7]
Guerrero's widow, Josefa de Haro, later married American James Denniston, for whom Denniston Creek (formerly Guerrero Creek) on Rancho Corral de Tierra is named.[4]
In the 1930s Japanese-American families arrived to farm some of the rancho lands that are now within the Golden Gate National Recreation Area section. In the World War II Internment of Japanese Americans, they were removed in 1942 and imprisoned.[4]
National Park
A large portion of the historic rancho, known as "The RCDT," is now within the southern Golden Gate National Recreation Area (GGNRA). The National Park Service purchased 3,858 acres (15.61 km2) from the Peninsula Open Space Trust (POST). POST had previously bought the property from private owners and developers, preventing the planned "ranchettes" and golf course from being built. POST retained ownership of the agricultural areas, which remain in use as privately run operations by the Ocean View Farms, Renegade Ranch, Moss Beach Ranch, and Ember Ridge Stables . The NPS now owns and manages the protected recreation area.[8]
The park contains sensitive habitat for several rare and endangered species, including the San Francisco garter snake and the Montara manzanita.[9] Hiking, biking, and horse trails are present, but are still being developed, and may not be in good condition until repaired.[10]
Landmarks
- Ember Ridge Barn (c.1883-1884) — A large wooden barn built by Henry Cowell for dairy ranch. Part of present-day Ember Ridge Equestrian Center.[4]
- Montara Lighthouse Station — A fog whistle was completed 1873 on Point Montara. In 1880 a coal fueled double horn system was installed, and in 1900 a kerosene lantern was placed on a post near the fog whistle. In 1928, the present Point Montara lighthouse was constructed.[4]
- Montara State Marine Reserve & Pillar Point State Marine Conservation Area
See also
- Rancho Corral de Tierra (Vasquez) — southern section.
- Ranchos of San Mateo County, California
- List of Ranchos of California
References
- Ogden Hoffman, 1862, Reports of Land Cases Determined in the United States District Court for the Northern District of California, Numa Hubert, San Francisco
- Diseño del Rancho Corral de Tierra
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Rancho Corral de Tierra
- 2010 Historic Resource Study for Golden Gate National Recreation Area in San Mateo County: The Rancho Corral de Tierra , by Mitchell P. Postell, President San Mateo County Historical Association.
- United States District Court (California : Northern District) Land Case 49 ND
- Finding Aid to the Documents Pertaining to the Adjudication of Private Land Claims in California, circa 1852-1892
- SIC.ca.gov: Report of the Surveyor General 1844−1886 Archived 2013-03-20 at the Wayback Machine
- NPS.gov: GGNRA, RCDT−Rancho Corral de Tierra property − history, images.
- Openspacetrust.org: Rancho Corral de Tierra historic corral
- ParksConservancy.org: RCDT−Rancho Corral de Tierra
External links
- NPS.gov: Historic Resource Study for GGNRA in San Mateo County: The Rancho Corral de Tierra — with detailed cultural histories, images, vintage maps.
