Río Cuarto (canton)
Río Cuarto is a canton in the Alajuela province of Costa Rica.[2][3] The head city is in Río Cuarto district.
Río Cuarto | |
|---|---|
 Rio Cuarto Central Park | |
 Flag  Seal | |
Río Cuarto canton | |
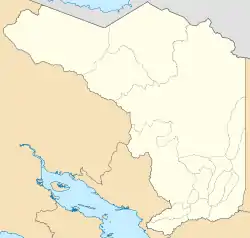 Río Cuarto Río Cuarto canton location in Alajuela Province 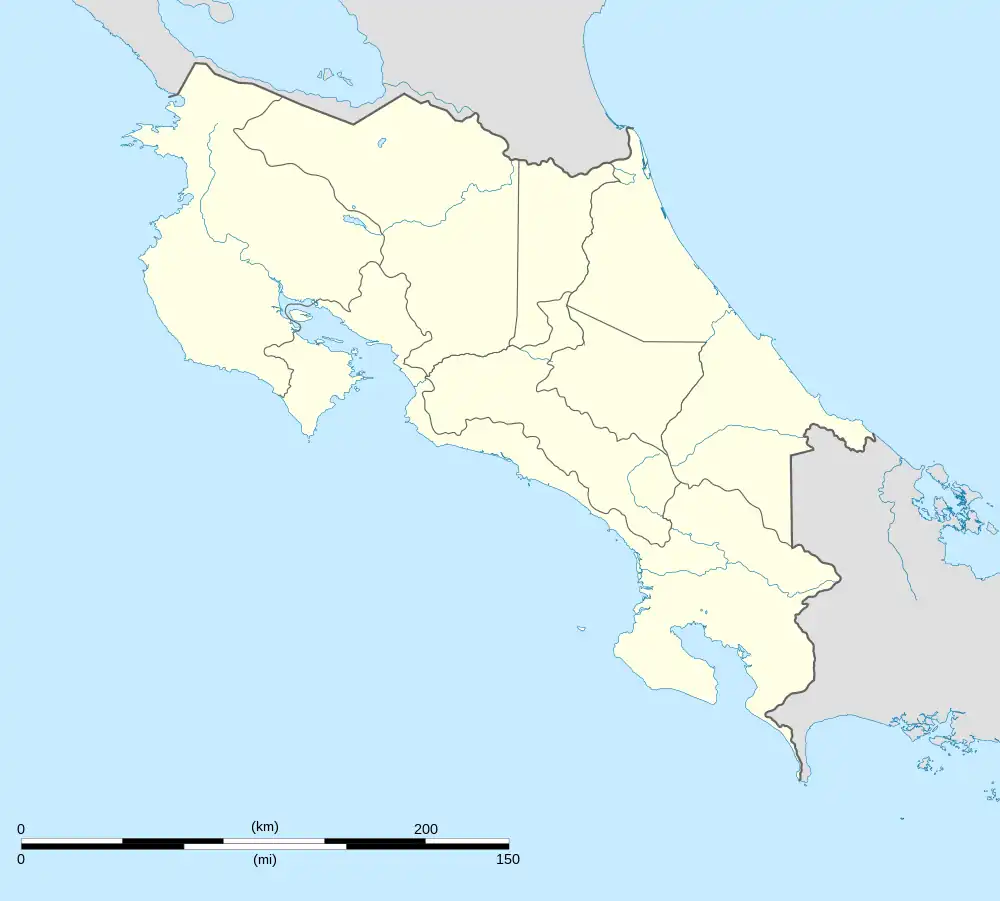 Río Cuarto Río Cuarto canton location in Costa Rica | |
| Coordinates: 10.407618°N 84.2134503°W | |
| Country | |
| Province | Alajuela |
| Creation | 20 April 2018[1] |
| Head city | Río Cuarto |
| Districts | Districts |
| Government | |
| • Type | Municipality |
| • Body | Municipalidad de Río Cuarto |
| Area | |
| • Total | 254.2 km2 (98.1 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 277 m (909 ft) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 11,074 |
| • Density | 44/km2 (110/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC−06:00 |
| Canton code | 216 |
Toponymy
Translates to Fourth River.
History
Río Cuarto was created on 20 April 2018 by decree 9440.[1]
It was originally a district of Grecia, however not on contiguous land as it was separated from Grecia when Sarchí canton, which was also part of Grecia originally, became a canton in 1949. After agreement of the Legislative Assembly of Costa Rica in second debate the Thursday 30 March 2017, Río Cuarto district became a canton, then in 2018 three districts were created in the canton.[4][5]
Geography
Río Cuarto has an area of 254.2 km²[6] and a mean elevation of 277 metres.[2]
It is located to the north of the Poás Volcano. It limits to the north and the west with the canton of San Carlos, to the east and also to the north with the canton of Sarapiquí to the south with the cantons of Alajuela and Zarcero.
Its head city is Río Cuarto, which is located 70.8 km (44.0 mi) north of San José, the nation's capital, of which by road it is around two hours taking Route 126.
The vegetation overflows with green, multicolored flowers, fruits and trees. The fauna is composed of dozens of species, some with animals as striking as the caribbean monkeys, sloths, and birds of all tones.
The type of vegetation is typical of the Humid Tropical Forest, characterized by the presence of trees up to 40 meters in height, ferns, epiphytic plants and mosses. The area also has abundant fruit plantations, ornamental and medicinal plants.
Area
The canton has an area of 254.20 km² and is located between 10°24'44" north latitude and 84°12'56" west longitude.
Dimensions
It has a maximum width of 38 km and is delimited by the rivers Toro and Caño Negro, and the massif of the Congo Volcano.
Its territory has an elongated form that extends from northeast to southwest.
Altitude
The territory has an altitude of between 100 and 1800 meters above sea level.
It presents these great variations of altitude, since in the south zone of the canton are the foothills of the central volcanic mountain range (reaching its maximum point in the already mentioned Congo Volcano), whereas in north direction the land descends until its lowest point in the surroundings of the town of San Rafael.
Climate
Its climate is temperate humid, between 16 °C to 28 °C, depending on the locality.
Geology
It has materials of volcanic origin of the Quaternary period. Also predominant are Pleistocene rocks, as well as lahar is, recent and present volcanic buildings, and Holocene pyroclastics. The presence of this large amount of volcanic material explains the fertility of the soils of the canton.
Geomorphology
The main volcanic massif is the Poás Volcano in the south, to which belong other subunits such as the Congo Volcano, the Hule Caldera (which forms the Lake Congo and Lake Hule) and the maar that forms Lake Río Cuarto.
Hydrography
The water resource in the area is also abundant; proof of this is the presence of high waterfalls, lakes, rivers and frequent falls. And the weather is cool and pleasant, although a bit rainy at this time of year.
The main rivers are the Toro, Río Cuarto, Sardinal, María Aguilar and Caño Negro rivers. The Caño Negro, Pozo Azul and Quebrada Gata rivers are tributaries of the Toro River. All these rivers discharge their waters in the Sarapiquí River, that takes them to the San Juan River.
Districts
The canton of Río Cuarto is subdivided into the following districts:
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1927 | 517 | — | |
| 1950 | 1,216 | 135.2% | |
| 1963 | 2,116 | 74.0% | |
| 1973 | 2,840 | 34.2% | |
| 1984 | 3,341 | 17.6% | |
| 2000 | 7,744 | 131.8% | |
| 2011 | 11,074 | 43.0% | |
|
Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos[7] |
|||
For the 2011 census, Río Cuarto district had a population of 11,074 inhabitants, as the population of the district became that of the canton, the historical population details are equivalent since 1927.[9]
Transportation
Road transportation
The canton is covered by the following road routes:
Economy
Produce, milk, beef, pork, chicken meat, pineapple, cassava, electric power, ornamental plants, among others.
References
- Hernández, Hermógenes (1985). Costa Rica: evolución territorial y principales censos de población 1502 - 1984 (in Spanish) (1 ed.). San José: Editorial Universidad Estatal a Distancia. pp. 164–173. ISBN 9977-64-243-5. Retrieved 5 October 2020.
- "Declara oficial para efectos administrativos, la aprobación de la División Territorial Administrativa de la República N°41548-MGP". Sistema Costarricense de Información Jurídica (in Spanish). 19 March 2019. Retrieved 26 September 2020.
- División Territorial Administrativa de la República de Costa Rica (PDF) (in Spanish). Editorial Digital de la Imprenta Nacional. 8 March 2017. ISBN 978-9977-58-477-5.
- "Río Cuarto will be the 82nd canton of Costa Rica". El País.
- "It's official! Río Cuarto is the canton 82 of Costa Rica". La Prensa Libre.
- "Área en kilómetros cuadrados, según provincia, cantón y distrito administrativo". Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos (in Spanish). Retrieved 26 September 2020.
- "Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos" (in Spanish).
- "Sistema de Consulta de a Bases de Datos Estadísticas". Centro Centroamericano de Población (in Spanish).
- "Censo. 2011. Población total por zona y sexo, según provincia, cantón y distrito". Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos (in Spanish). Retrieved 26 September 2020.