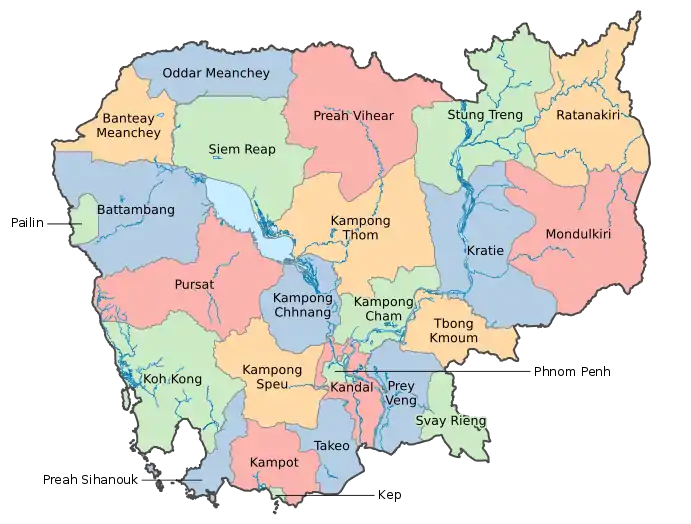
Provinces of Cambodia
Cambodia is divided into 25 provinces (Khmer: ខេត្ត, khétt [kʰaet]). The capital Phnom Penh is not a province but an "autonomous municipality" (Khmer: រាជធានី, réachôthéani [riəceaʔtʰiəniː]; lit. 'Capital'), equivalent to a province governmentally and administered at the same level as the other 24 provinces.
| Province ខេត្ត | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | First-level administrative subdivision of a unitary state |
| Location | |
| Number | 25 |
| Populations | 42,665 (Kep) – 2,281,951 (Phnom Penh)[1] |
| Areas | 336 km2 (130 sq mi) (Kep) – 14,288 km2 (5,517 sq mi) (Mondulkiri) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions | |
| Administrative divisions of Cambodia |
|---|
| First-level |
| Second-level |
| Third-level |
| Fourth-level |
|
| Fifth-level |
|
Phnom Penh has both the highest population and the highest population density of all provinces, but is the second smallest in land area. The largest province by area is Mondulkiri and the smallest is Kep which is also the least populated province. Mondulkiri has the lowest population density.
Each province is administered by a governor, who is nominated by the Ministry of Interior, subject to approval by the Prime Minister.
Provinces are divided into districts (ស្រុក srok). The districts in Phnom Penh are called khan (ខណ្ឌ) normally written as for addresses in English followed by the districts' names (Ex: Khan Chamkar Mon; lit. 'Chamkar Mon District'). The number of districts in each province varies, from two in the smallest provinces to 14 in Battambang, Prey Veng, and Siem Reap. Further subdivision levels are communes (ឃុំ khum), and further subdivided into villages (ភូមិ, phum). In Phnom Penh, sangkat (សង្កាត់) is used in the place of khum and, similar to khan, normally preferred for writing addresses in English (Ex: Sangkat Mittapheap; lit. 'Mittapheap Commune').
List of provinces
| Name | Khmer | Capital (seat) | Population (2019)[1] | Area (km2)[1] | Density | ISO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Banteay Meanchey | បន្ទាយមានជ័យ | Serei Saophoan Municipality | 861,883 | 6,679 | 129 | KH-1 |
| Battambang | បាត់ដំបង | Battambang Municipality | 997,169 | 11,702 | 84 | KH-2 |
| Kampong Cham | កំពង់ចាម | Kampong Cham Municipality | 899,791 | 4,549 | 197 | KH-3 |
| Kampong Chhnang | កំពង់ឆ្នាំង | Kampong Chhnang Municipality | 527,027 | 5,521 | 95 | KH-4 |
| Kampong Speu | កំពង់ស្ពឺ | Chbar Mon Municipality | 877,523 | 7,017 | 124 | KH-5 |
| Kampong Thom | កំពង់ធំ | Steung Saen Municipality | 681,549 | 13,814 | 49 | KH-6 |
| Kampot | កំពត | Kampot Municipality | 593,829 | 4,873 | 122 | KH-7 |
| Kandal | កណ្តាល | Ta Khmau Municipality | 1,201,581 | 3,179 | 376 | KH-8 |
| Koh Kong | កោះកុង | Khemarak Phoumin Municipality | 125,902 | 10,090 | 12 | KH-9 |
| Kratié | ក្រចេះ | Kratié Municipality | 374,755 | 11,094 | 34 | KH-10 |
| Mondulkiri | មណ្ឌលគិរី | Senmonorom Municipality | 92,213 | 14,288 | 6 | KH-11 |
| Phnom Penh | ភ្នំពេញ | Doun Penh Section | 2,281,951 | 679 | 3,136 | KH-12 |
| Preah Vihear | ព្រះវិហារ | Tbaeng Meanchey Municipality | 254,827 | 13,788 | 18 | KH-13 |
| Prey Veng | ព្រៃវែង | Prey Veng Municipality | 1,057,720 | 4,883 | 217 | KH-14 |
| Pursat | ពោធិ៍សាត់ | Pursat Municipality | 419,752 | 12,692 | 32 | KH-15 |
| Ratanakiri | រតនគិរី | Banlung Municipality | 217,453 | 10,782 | 19 | KH-16 |
| Siem Reap | សៀមរាប | Siem Reap Municipality | 1,014,234 | 10,299 | 98 | KH-17 |
| Preah Sihanouk | ព្រះសីហនុ | Sihanoukville Municipality | 310,072 | 1,938 | 156 | KH-18 |
| Stung Treng | ស្ទឹងត្រែង | Stung Treng Municipality | 165,713 | 11,092 | 14 | KH-19 |
| Svay Rieng | ស្វាយរៀង | Svay Rieng Municipality | 525,497 | 2,966 | 177 | KH-20 |
| Takéo | តាកែវ | Doun Kaev Municipality | 900,914 | 3,563 | 252 | KH-21 |
| Oddar Meanchey | ឧត្តរមានជ័យ | Samraong Municipality | 276,038 | 6,158 | 42 | KH-22 |
| Kep | កែប | Kep Municipality | 42,665 | 336 | 124 | KH-23 |
| Pailin | ប៉ៃលិន | Pailin Municipality | 75,112 | 803 | 89 | KH-24 |
| Tboung Khmum | ត្បូងឃ្មុំ | Suong Municipality | 776,841 | 5,250 | 148 | KH-25 |
History
- 1974: The Khmer Rouge government did away with the former Cambodian traditional administrative divisions. Instead of provinces, Democratic Kampuchea was divided into seven geographic zones (Khmer: តំបន់, tâmbán): the Northwest, the North, the Northeast, the East, the Southwest, the West, and the Centre. These zones were derived from divisions established by the Khmer Rouge when they fought against the Khmer Republic during the Cambodian Civil War.[2]
- 2008: On 22 December 2008, King Norodom Sihamoni signed a decree that changed the municipalities of Kep, Pailin and Sihanoukville into provincial municipalities, as well as adjusting several provincial borders.[3]
- 2013: On 31 December 2013, King Norodom Sihamoni signed a decree that split Kampong Cham into two provinces: Kampong Cham (west of the Mekong River) and Tboung Khmum (east of the Mekong River).[4]
- 2018: In September 2018, Interior Minister Sar Kheng proposed establishing two more provinces, with areas taken from Kandal, Mondulkiri, and Ratanakiri.[5] Prime Minister Hun Sen rejected the plan.
See also
References
- "General Population Census of the Kingdom of Cambodia 2019 – Final Results" (PDF). National Institute of Statistics. Ministry of Planning. 26 January 2021. Retrieved 9 February 2021.
- Tyner, James A (2008). The Killing of Cambodia: Geography, Genocide and the Unmaking of Space. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. ISBN 978-0-7546-7096-4. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- Vong, Sokheng (31 December 2008). "Decree creates three new provinces". Phnom Penh Post.
- Mom, Kunthear; Ponniah, Kevin (10 January 2014). "Kampong Cham's great divide". Phnom Penh Post.
- Vicheika, Kann (31 August 2018). "Cambodia to Create Two New Provinces in Bid for 'Efficiency'". Voice of America. Retrieved 5 July 2019.