Portal:Kenya

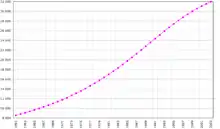
Introduction.svg.png.webp) Location of Kenya  The flag of Kenya Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya (Swahili: Jamhuri ya Kenya), is a country in East Africa. A member of the Commonwealth with a population of more than 47.6 million in the 2019 census, Kenya is the 28th most populous country in the world and 7th most populous in Africa. Kenya's capital and largest city is Nairobi, while its oldest and second largest city, which until 1907 was also Kenya's first capital city, is the coastal city of Mombasa which includes Mombasa Island in the Indian Ocean and the surrounding mainland. Kisumu is the third-largest city and also an inland port in the Winam Gulf which, along with its numerous bays and human settlements, is one of the important maritime transport, fishing, farming, commercial, history and tourism hubs on Lake Victoria. As of 2020, Kenya is the third-largest economy in sub-Saharan Africa after Nigeria and South Africa and hosts the United Nations, UNEP and UN-HABITAT headquarters in Africa. Kenya is bordered by South Sudan to the northwest, Ethiopia to the north, Somalia to the east, Uganda to the west, Tanzania to the south, and the Indian Ocean to the southeast. Kenya, in World War II, sent soldiers to fight in the British Army when the British Empire declared war on Nazi Germany in 1939 and remained an important asset for the Allies until the end of the war in 1945. Kenya got its independence in 1963 and signed an agreement with Britain in 1964 which established BATUK - a permanent British Army Training Unit in Nanyuki which has two support units in Nairobi. Kenya's geography, climate and population vary widely, ranging from cold snow-capped mountaintops (Batian, Nelion and Point Lenana on Mount Kenya) with vast surrounding forests, wildlife and fertile agricultural regions to temperate climates in western and rift valley counties and further on to dry less fertile arid and semi-arid areas and absolute deserts (Chalbi Desert and Nyiri Desert). Kenya's earliest inhabitants were hunter-gatherers, like the present-day Hadza people. According to archaeological dating of associated artifacts and skeletal material, Cushitic speakers first settled in Kenya's lowlands between 3,200 and 1,300 BC, a phase known as the Lowland Savanna Pastoral Neolithic. Nilotic-speaking pastoralists (ancestral to Kenya's Nilotic speakers) began migrating from present-day South Sudan into Kenya around 500 BC. Bantu people settled at the coast and the interior between 250 BC and 500 AD. European contact began in 1500 AD with the Portuguese Empire, and effective colonisation of Kenya began in the 19th century during the European exploration of the interior. Modern-day Kenya emerged from a protectorate established by the British Empire in 1895 and the subsequent Kenya Colony, which began in 1920. Numerous disputes between the UK and the colony led to the Mau Mau revolution, which began in 1952, and the declaration of independence in 1963. After independence, Kenya remained a member of the Commonwealth of Nations. The current constitution was adopted in 2010 and replaced the 1963 independence constitution. Kenya is a presidential representative democratic republic, in which elected officials represent the people and the president is the head of state and government. Kenya is a member of the United Nations, Commonwealth of Nations, World Bank, International Monetary Fund, COMESA, International Criminal Court, as well as other international organisations. With a GNI of 1,840, Kenya is a lower-middle-income economy. Kenya's economy is the largest in eastern and central Africa, with Nairobi serving as a major regional commercial hub. Agriculture is the largest sector: tea and coffee are traditional cash crops, while fresh flowers are a fast-growing export. The service industry is also a major economic driver, particularly tourism. Kenya is a member of the East African Community trade bloc, though some international trade organisations categorise it as part of the Greater Horn of Africa. Africa is Kenya's largest export market, followed by the European Union. (Full article...) Selected article - Lake Turkana (/tɜːrˈkɑːnə, -ˈkæn-/) formerly known as Lake Rudolf, is a lake in the Kenyan Rift Valley, in northern Kenya, with its far northern end crossing into Ethiopia. It is the world's largest permanent desert lake and the world's largest alkaline lake. By volume it is the world's fourth-largest salt lake after the Caspian Sea, Issyk-Kul, and Lake Van (passing the shrinking South Aral Sea), and among all lakes it ranks 24th. Lake Turkana is now threatened by the construction of Gilgel Gibe III Dam in Ethiopia due to the damming of the Omo river which supplies most of the lake's water. (Full article...)Selected picture - Beach in Robinson Island Kenya Beach close to Robinson Island Kenya a couple of kilometres north of Malindi town, Kilifi County.
Selected location - Muranga County showing the landscape Muranga County is one of the counties of Kenya's former Central Province. Its largest town is Makuyu but its capital is Murang'a, called Fort Hall in colonial times (before 1963). It is inhabited mainly by and is considered the home of the Kikuyu, the largest community in Kenya. The county has a population of 942,581 (2009 census). (Read more...)
|


.jpg.webp)



.jpg.webp)







.svg.png.webp)