Portal:Guatemala
The Guatemala portal
Republic of Guatemala | |
|---|---|
Motto:
| |
| Anthem: Himno Nacional de Guatemala (English: "National Anthem of Guatemala") | |
| ISO 3166 code | GT |
Guatemala (/ˌɡwɑːtəˈmɑːlə/ ⓘ GWAH-tə-MAH-lə; Spanish: [ɡwateˈmala] ⓘ), officially the Republic of Guatemala (Spanish: República de Guatemala), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is touched to the south by the Pacific Ocean and to the northeast by the Gulf of Honduras. With an estimated population of around 17.6 million,0 Guatemala is the most populous country in Central America and the 11th most populous country in the Americas. It is a representative democracy with its capital and largest city being Nueva Guatemala de la Asunción, also known as Guatemala City, the most populous city in Central America.
The territory of modern Guatemala hosted the core of the Maya civilization, which extended across Mesoamerica. In the 16th century, most of this area was conquered by the Spanish and claimed as part of the viceroyalty of New Spain. Guatemala attained independence in 1821 from Spain and Mexico. In 1823, it became part of the Federal Republic of Central America, which dissolved by 1841.
From the mid- to late 19th century, Guatemala suffered chronic instability and civil strife. Beginning in the early 20th century, it was ruled by a series of dictators backed by the United Fruit Company and the United States government. In 1944, authoritarian leader Jorge Ubico was overthrown by a pro-democratic military coup, initiating a decade-long revolution that led to sweeping social and economic reforms. A U.S.-backed military coup in 1954 ended the revolution and installed a dictatorship.
From 1960 to 1996, Guatemala endured a bloody civil war fought between the U.S.-backed government and leftist rebels, including genocidal massacres of the Maya population perpetrated by the military. A peace accord negotiated by the United Nations has resulted in continued economic growth and successful democratic elections, although poverty, crime, drug trafficking, and civil instability remain major issues. (Full article...)
Selected article -
La Blanca is a Maya pre-Columbian Mesoamerican archaeological site in the municipality of Melchor de Mencos in the northern Petén Department of Guatemala. It has an occupation dating predominantly from the Middle Preclassic (900–600 BC) period of Mesoamerican chronology. This site belongs to the later period of the Mokaya culture. The site is located in the lower reaches of the Mopan River valley and features a large acropolis complex. Activity at the site has been dated as far back as the Early Classic (AD 250–600), with principal occupation of the site occurring in the Late Classic period (AD 600–900), although some level of occupation continued into the Early Postclassic (AD 900–1200).
La Blanca occupied a frontier zone between the northeastern and southeastern Petén regions and the site is dominated by the acropolis, an especially well built palace complex. The city appears to have been an administrative centre with comparatively little emphasis upon religious or ceremonial activity. It is likely that La Blanca was a subsidiary of a major Maya city such as Yaxha or Naranjo, given the complete absence of hieroglyphic texts and sculpted monuments, and archaeologists presume that La Blanca served as a frontier post or trading centre. (Full article...)Did you know (auto-generated)
- ... that the Adelaide L. T. Douglas House, built for a New York City socialite, housed the United States Olympic Committee before being sold to Guatemala?
- ... that the Central American government voted for annexation to the First Mexican Empire after a request from Regent Agustín de Iturbide?
Subcategories
WikiProjects
WikiProject Central America
 Good article -
Good article -
Haʼ Kʼin Xook (Mayan pronunciation: [haʔ kʼin ʃoːk]), also known as Ruler 6, was an ajaw of Piedras Negras, an ancient Maya settlement in Guatemala. He ruled during the Late Classic Period, from 767–780 AD. Haʼ Kʼin Xook was a son of Itzam Kʼan Ahk II, and he ascended the throne following the death of his brother, Yoʼnal Ahk III. Haʼ Kʼin Xook's reign ended with either his death or his abdication in favor of his brother Kʼinich Yat Ahk II; archaeologists and Mayanists have not arrived at a clear consensus. Haʼ Kʼin Xook left behind several monuments, including stelae at Piedras Negras and a stone fragment from El Porvenir. In addition, a stone seat known as Throne 1 and erected by Kʼinich Yat Ahk II records either the death or abdication of Haʼ Kʼin Xook. (Full article...)
Selected image -
More did you know -
- Mano Blanca was an anti-communist death squad set up and run by the Guatemalan military with considerable assistance from the United States.
 Featured article -
Featured article -
Pinguicula moranensis /pɪŋˈɡwɪkjʊlə ˌmɒrəˈnɛnsɪs/ is a perennial rosette-forming insectivorous herb in the flowering plant family Lentibulariaceae. It is native to El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras and Mexico. A species of butterwort, it forms summer rosettes of flat, succulent leaves up to 10 centimeters (4 in) long, which are covered in mucilaginous (sticky) glands that attract, trap, and digest arthropod prey. Nutrients derived from the prey are used to supplement the nutrient-poor substrate that the plant grows in. In the winter the plant forms a non-carnivorous rosette of small, fleshy leaves that conserves energy while food and moisture supplies are low. Single pink, purple, or violet flowers appear twice a year on upright stalks up to 25 centimeters long.
The species was first collected by Humboldt and Bonpland on the outskirts of Mina de Morán in the Sierra de Pachuca of the modern-day Mexican state of Hidalgo on their Latin American expedition of 1799–1804. Based on these collections, Carl Sigismund Kunth described this species in Nova Genera et Species Plantarum in 1817. The extremely variable species has been redefined at least twice since, while several new species have been segregated from it based on various geographical or morphological distinctions, although the legitimacy of some of these is still debated. P. moranensis remains the most common and most widely distributed member of the Section Orcheosanthus. It has long been cultivated for its carnivorous nature and attractive flowers, and is one of the most common butterworts in cultivation. (Full article...)List of Featured articles |
|---|
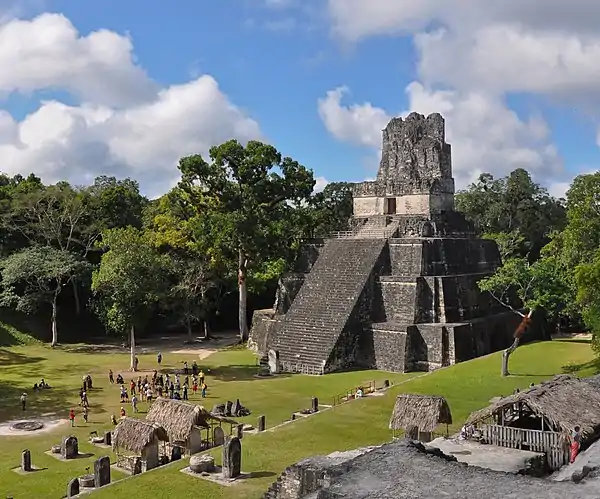
General images -
The following are images from various Guatemala-related articles on Wikipedia.
Topics
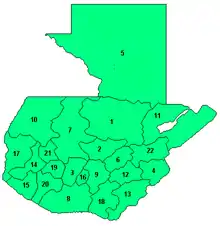
Departments
Guatemala is divided into 22 departments (departamentos) and sub-divided into about 332 municipalities (municipios).
The departments include:
Related portals
Things you can do

Here are some things you can do for WikiProject Guatemala:
- Create requested articles:
- El Viejo Palmar -- Village south of Quetzaltenango, hit by a volcanic eruption
- Expand "stub" and "start" articles:
- Stub-Class Guatemala articles
- Start-Class Guatemala articles
- Assess the importance of articles:
- Unknown-importance Guatemala articles
Recognized content
| This is a list of recognized content, updated weekly by JL-Bot (talk · contribs) (typically on Saturdays). There is no need to edit the list yourself. If an article is missing from the list, make sure it is tagged (e.g. {{WikiProject Guatemala}}) or categorized correctly and wait for the next update. See WP:RECOG for configuration options. |
Featured articles
Good articles
- 5to Piso
- 2010 Guatemala City sinkhole
- Adentro
- Gómez de Alvarado
- El Amor (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Francisco Javier Arana
- Jacobo Árbenz
- Ricardo Arjona
- La Blanca, Peten
- Bartolomé de las Casas
- Central America under Mexican rule
- Como Duele (Ricardo Arjona song)
- El Chal
- Fuiste Tú
- Guatemala at the 2016 Summer Paralympics
- Guatemalan Revolution
- Haʼ Kʼin Xook
- Independiente (Ricardo Arjona album)
- Itzam Kʼan Ahk II
- Iximche
- Kʼinich Yat Ahk II
- Kʼinich Yoʼnal Ahk I
- Manche Chʼol
- Marta (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Mi Novia Se Me Está Poniendo Vieja
- Mixco Viejo
- Motul de San José
- Mundo Perdido, Tikal
- North Acropolis, Tikal
- Poquita Ropa
- Puente (song)
- Quién Dijo Ayer
- Quién (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Quiero (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Battle of Roatán
- Simplemente Lo Mejor
- Spanish conquest of Yucatán
- Spanish conquest of the Maya
- Te Quiero (Ricardo Arjona song)
- Tikal
- Trópico (Ricardo Arjona album)
- Vida (Ricardo Arjona song)
- White-lipped peccary
- Yoʼnal Ahk III
- Zaculeu
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Guatemala news
The current date and time in Guatemala is Thursday, October 26, 2023, 04:13.
News media:
- The Guatemala Times
- La Prensa Libre (in Spanish)
- Wikinews Guatemala portal
Sources
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals












_-_Guatemala-1525.jpg.webp)