Pleurogona
Pleurogona is an order of tunicates which is no longer in use as it contains the same families as Stolidobranchia.[1]
| Pleurogona | |
|---|---|
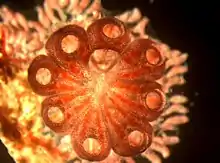 | |
| Botryllus schlosseri | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Subphylum: | Tunicata |
| Class: | Ascidiacea |
| Order: | Pleurogona |
| Families | |
| |
One of the more invasive species of this order is the "stalked (or leathery or solitary) sea squirt" Styela clava .[2][3][4] Other invasive genera include the "chain sea squirts" or "chain tunicates" of the genus Botrylloides [5][6] and the "golden star tunicate" Botryllus schlosseri .[7]
References
- Gittenberger, A.; Sanamyan, K. (2015). Pleurogona. In: Shenkar, N.; Gittenberger, A.; Lambert, G.; Rius, M.; Moreira Da Rocha, R.; Swalla, B.J.; Turon, X. (2015) Ascidiacea World Database. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species on 2015-12-23
- "Leathery sea squirt Styela clava Herdman, 1881". CSIRO. 2006-12-07. Archived from the original on 2007-04-11. Retrieved 2007-02-16.
- "Asian stalked sea squirt, Pacific rough sea squirt (Styela clava)". University of Rhode Island. Archived from the original on 2007-01-26. Retrieved 2007-02-16.
- "Invasive sea squirt (Styela clava) fact sheet". NIWA Science. Archived from the original on 2007-09-27. Retrieved 2007-02-16.
- M.J. de Kluijver & S.S. Ingalsuo. "Macrobenthos of the North Sea: Botrylloides leachi". University of Amsterdam. Archived from the original on 2011-07-17.
- Andrew N. Cohen (2005-06-07). "Guide to the Exotic Species of San Francisco Bay: Botrylloides violaceus Oka, 1927". San Francisco Estuary Institute.
- M.J. de Kluijver & S.S. Ingalsuo. "Macrobenthos of the North Sea: Botrylloides schlosseri". University of Amsterdam. Archived from the original on 2010-09-01.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.