Outer enamel epithelium
The outer enamel epithelium, also known as the external enamel epithelium, is a layer of cuboidal cells located on the periphery of the enamel organ in a developing tooth. This layer is first seen during the bell stage.
| Outer enamel epithelium | |
|---|---|
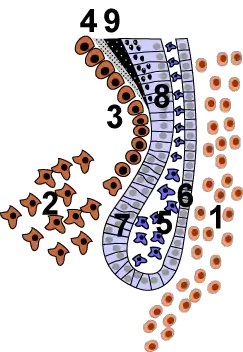 The cervical loop area: (1) dental follicle cells, (2) dental mesenchyme, (3) Odontoblasts, (4) Dentin, (5) stellate reticulum, (6) outer enamel epithelium, (7)inner enamel epithelium, (8) ameloblasts, (9) enamel. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | epithelium enameleum externum |
| TE | enamel epithelium_by_E5.4.1.1.2.3.12 E5.4.1.1.2.3.12 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The rim of the enamel organ where the outer and inner enamel epithelium join is called the cervical loop.
References
- Cate, A.R. Ten. Oral Histology: development, structure, and function. 5th ed. 1998. ISBN 0-8151-2952-1.
- Ross, Michael H., Gordon I. Kaye, and Wojciech Pawlina. Histology: a text and atlas. 4th edition. 2003. ISBN 0-683-30242-6.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.