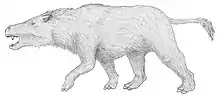
Notostylops
Notostylops ("south pillar face") is a genus of extinct South American ungulates from Eocene Argentina. Fossils of the genus have been found in the Sarmiento, Casamayor, Andesitas Huancache and Koluel Kaike Formations.[1]
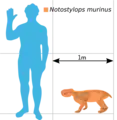 Size comparison of Notostylops murinus with a human.
Size comparison of Notostylops murinus with a human. Life reconstruction.
Life reconstruction.
| Notostylops | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Notostylops | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | †Notoungulata |
| Family: | †Notostylopidae |
| Genus: | †Notostylops Ameghino 1897 |
| Species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
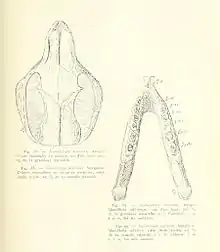
Description
Notostylops was a very generalized animal, very similar to first eutherians and ungulates. It would have superficially resembled a marmot or a wombat and is suspected to have browsed on low-growing plants. It was probably adapted to a fairly wide range of ecological niches, but its robustness indicates it had some digging adaptations.[2][3] Its tall skull housed rodent-like incisor teeth. Notostylops was about 75 centimetres (30 in) long.[4]
References
- Notostylops at Fossilworks.org
- Croft, Darin. Horned Armadillos and Rafting Monkeys. Indiana University Press.
- Lorente, Malena; Gelfo, Javier; Lopez, Guillermo (2018). "First skeleton of the notoungulate mammal Notostylops murinus and palaeobiology of Eocene Notostylopidae". Lethaia. doi:10.1111/let.12310.
- Palmer, D., ed. (1999). The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. London: Marshall Editions. p. 250. ISBN 978-1-84028-152-1.
 Media related to Notostylops at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Notostylops at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.




.jpg.webp)