Mofebutazone
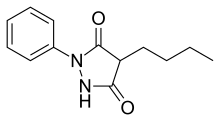
Mofebutazone (or monophenylbutazone) is a drug used for joint and muscular pain.[1][2] It is a 3,5-pyrazolinedione derivative.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.947 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H16N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 232.283 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
The drug binds to plasma albumin and competes with drugs such as coumarin anticoagulants, indomethacin and glucocorticoids.
References
- Kassem MA, Schulte KE (1984-07-01). "Pharmacokinetics of [4-14C] mofebutazone after oral administration in man". European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics. 9 (3): 223–227. doi:10.1007/BF03189645. PMID 6519123. S2CID 10985688.
- Paradies HH (December 1987). "Structure of phenylbutazone and mofebutazone in the crystalline state and in solution". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 76 (12): 920–929. doi:10.1002/jps.2600761217. PMID 3440938.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.