Methoni Castle
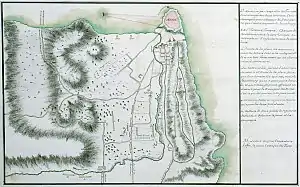
The Castle of Methoni is a medieval fortification in the port town of Methoni, Messenia, in southwestern Greece. The castle of Methoni occupies the whole area of the cape and the southwestern coast to the small islet that has also been fortified with an octagonal tower and is protected by the sea on its three sides. Its north part, the one that looks to land, is covered by a heavily fortified acropolis. A deep moat separates the castle from the land and communication was achieved by a wooden bridge. The Venetians built on the ancient battlements and added on and repaired it during both periods that they occupied the castle.

Description



Its entrance is accessed by a stone bridge of 14 arches, that was built over a moat by the technicians of the Expédition scientifique de Morée, that accompanied general Maison. The entrance gate ends in an arch framed on the right and left by pilasters with Corinthian capitals. It is considered to be the work of Venetians after 1700. On the right and left of the entrance two large battlements can be seen. One battlement is the one built by general Antonio Loredan, during the second period of Venetian occupation.
Right after the central gate, a domed road opens up that leads through a second gate and then a third in the interior of the castle, where the habitable part was and which was separated from the north part with a vertical low wall (approximately 6 meters), fortified with five towers (four square and one octagonal) is dated to the period after 1500, when the Turks tried to reinforce the population and the fortification of the caste. In the interior there are ruins of the houses where the Venetian lords lived during the period of rise, the paved street that led to the sea gate, the ruins of a Turkish bath, the Byzantine church of St. Sophia, close to which a slate with Latin lettering was found (dating back to 1714), parts of Doric pillars, a monolithic granite pillar (1493/4), unlined, with a capital on the top of Byzantine style, which is supposed to have supported either the winged lion of Saint Mark, the symbol of Venice, or the bust of Morosini. That is why it is erroneously called "Morosini's stele".[1] There was an inscription on the capital that has not survived to this day. On the left of the entrance are the ruins of the building which originally Imbrahem used as a residence in 1826 and later general Maison. The French of the liberating corps remained in the area till 1833 and the construction of the church of Santa Sotira, which is still attributed to them. In the interior of the castle there are also a few cisterns and the remains of the British prisoner's cemetery during the World War II.
On the south part of the walls rises the spectacular sea gate which has recently been restored. A stone-paved stretch leads over a small bridge to the small fortified islet of Bourtzi. This is the place where many soldiers and inhabitants of Methoni were slaughtered, when the Turks occupied the fort in 1500.
History
The Bourtzi is dated back to the period after 1500 and has been used in various instances as a prison. It has a two-floor octagonal tower. The tower finishes in a round dome. On the lower floor there was a cistern and the whole works, with small defensive value, and is dated during the first period that the Turks occupied the fortress.
The west part of the walls is not as well constructed as the others. It was here that during the Second World War, after an explosion, parts of well constructed stones from the ancient walls of Methoni were found. In the interior of the walls, ruins of Turkish military establishments are preserved.
The east side of the walls also reached initially to the sea. Nowadays, a long strand of beach lies in front of a large part of it. Parallel to the east wall, up to the Bourtzi, there was a pier and this is where the small fortified harbor was formed (mandrachio), while the big one was to the northeast where ships could be pulled. The long east side has suffered many repairs, performed on the initial venetian battlements of the 13th century, mainly during the second Venetian occupation and the Turkish occupation. In one of the towers parts of the Byzantine fortification are preserved.
On various parts of the fortification there are Venetian emblems with the winged lion of St. Mark and inscriptions. This is the case on the north part of the Loredan battlement, where there is an inscribed plaque from the time when general Loredan was in command in the Peloponnese. On the north wall, on the right of the main entrance, there is also a plaque with the coat of arms of the families of the Foscarini, Foscolo and Bembo, to which the inscription denotes the construction of the Bembo battlement, just before 1500.
References
- "The granite column in Modon" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-01-15. Retrieved 2016-07-30.
Sources
- Bees, Nikos A. (1993). "Modon". The Encyclopedia of Islam, New Edition, Volume VII: Mif–Naz. Leiden and New York: BRILL. pp. 216–218. doi:10.1163/1573-3912_islam_SIM_5250. ISBN 978-90-04-09419-2.
- Bon, Antoine (1969). La Morée franque. Recherches historiques, topographiques et archéologiques sur la principauté d'Achaïe (in French). Paris: De Boccard.
- A. Nanetti, Atlas of Venetian Messenia. Coron, Modon, Pylos and their islands (1207-1500 & 1685-1715), trilingual (English, Italian, Modern Greek), University of Bologna and State Archive of Venice. Imola: Editrice La Mandragora, 2011 (ISBN 978-88-7586-301-2).
- Interactive scholarly edition, with critical English translation and multimodal resources mashup (publications, images, videos) Engineering Historical Memory
