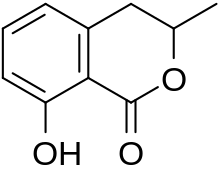
Mellein
Mellein is a dihydroisocoumarin, a phenolic compound produced by the mold species Aspergillus ochraceus.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
8-Hydroxy-3-methyl-3,4-dihydroisochromen-1-one | |
| Other names
(−)-Mellein (R)-(−)-Mellein Ochracin 3,4-Dihydro-8-hydroxy-3-methyl-1H-2-benzopyran-1-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 178.187 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Derivatives
4-Hydroxymellein is also produced by Aspergillus ochraceus.[1]
6-Hydroxymellein, together with S-adenosyl methionine, is a substrate of the enzyme 6-hydroxymellein O-methyltransferase to form 6-methoxymellein and S-adenosylhomocysteine in Apiaceae.[2] 6-Methoxymellein is one of the compounds responsible for bitterness in carrots.
References
- Moore, J. H.; Davis, N. D.; Diener, U. L. (1972). "Mellein and 4-hydroxymellein production by Aspergillus ochraceus Wilhelm". Applied Microbiology. 23 (6): 1067–1072. doi:10.1128/AEM.23.6.1067-1072.1972. PMC 380508. PMID 5064985.
- 6-methoxymellein biosynthesis pathway on www.biocyc.org
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.